Jamie McCusker
LOKE: Linked Open Knowledge Extraction for Automated Knowledge Graph Construction
Nov 15, 2023



Abstract:While the potential of Open Information Extraction (Open IE) for Knowledge Graph Construction (KGC) may seem promising, we find that the alignment of Open IE extraction results with existing knowledge graphs to be inadequate. The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs), especially the commercially available OpenAI models, have reset expectations for what is possible with deep learning models and have created a new field called prompt engineering. We investigate the use of GPT models and prompt engineering for knowledge graph construction with the Wikidata knowledge graph to address a similar problem to Open IE, which we call Open Knowledge Extraction (OKE) using an approach we call the Linked Open Knowledge Extractor (LOKE, pronounced like "Loki"). We consider the entity linking task essential to construction of real world knowledge graphs. We merge the CaRB benchmark scoring approach with data from the TekGen dataset for the LOKE task. We then show that a well engineered prompt, paired with a naive entity linking approach (which we call LOKE-GPT), outperforms AllenAI's OpenIE 4 implementation on the OKE task, although it over-generates triples compared to the reference set due to overall triple scarcity in the TekGen set. Through an analysis of entity linkability in the CaRB dataset, as well as outputs from OpenIE 4 and LOKE-GPT, we see that LOKE-GPT and the "silver" TekGen triples show that the task is significantly different in content from OIE, if not structure. Through this analysis and a qualitative analysis of sentence extractions via all methods, we found that LOKE-GPT extractions are of high utility for the KGC task and suitable for use in semi-automated extraction settings.
Can Machines Read Coding Manuals Yet? -- A Benchmark for Building Better Language Models for Code Understanding
Sep 15, 2021
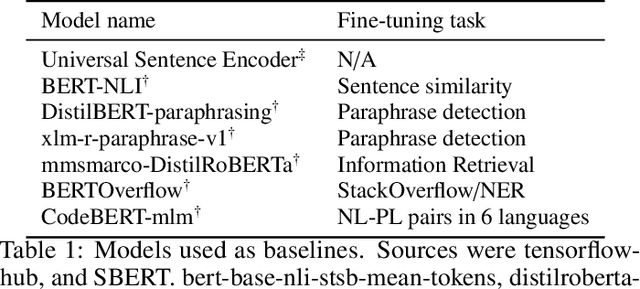
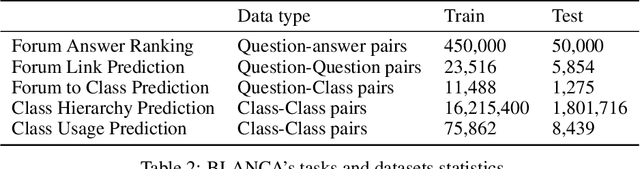
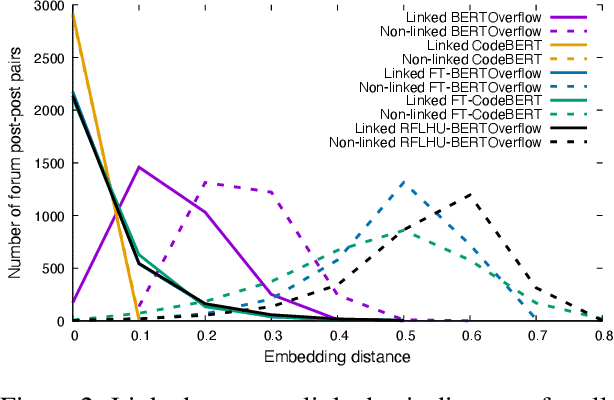
Abstract:Code understanding is an increasingly important application of Artificial Intelligence. A fundamental aspect of understanding code is understanding text about code, e.g., documentation and forum discussions. Pre-trained language models (e.g., BERT) are a popular approach for various NLP tasks, and there are now a variety of benchmarks, such as GLUE, to help improve the development of such models for natural language understanding. However, little is known about how well such models work on textual artifacts about code, and we are unaware of any systematic set of downstream tasks for such an evaluation. In this paper, we derive a set of benchmarks (BLANCA - Benchmarks for LANguage models on Coding Artifacts) that assess code understanding based on tasks such as predicting the best answer to a question in a forum post, finding related forum posts, or predicting classes related in a hierarchy from class documentation. We evaluate the performance of current state-of-the-art language models on these tasks and show that there is a significant improvement on each task from fine tuning. We also show that multi-task training over BLANCA tasks helps build better language models for code understanding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge