James Weng
Image Segmentation using U-Net Architecture for Powder X-ray Diffraction Images
Oct 24, 2023



Abstract:Scientific researchers frequently use the in situ synchrotron high-energy powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) technique to examine the crystallographic structures of materials in functional devices such as rechargeable battery materials. We propose a method for identifying artifacts in experimental XRD images. The proposed method uses deep learning convolutional neural network architectures, such as tunable U-Nets to identify the artifacts. In particular, the predicted artifacts are evaluated against the corresponding ground truth (manually implemented) using the overall true positive rate or recall. The result demonstrates that the U-Nets can consistently produce great recall performance at 92.4% on the test dataset, which is not included in the training, with a 34% reduction in average false positives in comparison to the conventional method. The U-Nets also reduce the time required to identify and separate artifacts by more than 50%. Furthermore, the exclusion of the artifacts shows major changes in the integrated 1D XRD pattern, enhancing further analysis of the post-processing XRD data.
Denoising total scattering data using Compressed Sensing
Oct 19, 2023



Abstract:To obtain the best resolution for any measurement there is an ever-present challenge to achieve maximal differentiation between signal and noise over as fine of sampling dimensions as possible. In diffraction science these issues are particularly pervasive when analyzing small crystals, systems with diffuse scattering, or other systems in which the signal of interest is extremely weak and incident flux and instrument time is limited. We here demonstrate that the tool of compressed sensing, which has successfully been applied to photography, facial recognition, and medical imaging, can be effectively applied to diffraction images to dramatically improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in a data-driven fashion without the need for additional measurements or modification of existing hardware. We outline a technique that leverages compressive sensing to bootstrap a single diffraction measurement into an effectively arbitrary number of virtual measurements, thereby providing a means of super-resolution imaging.
Artifact Identification in X-ray Diffraction Data using Machine Learning Methods
Jul 29, 2022

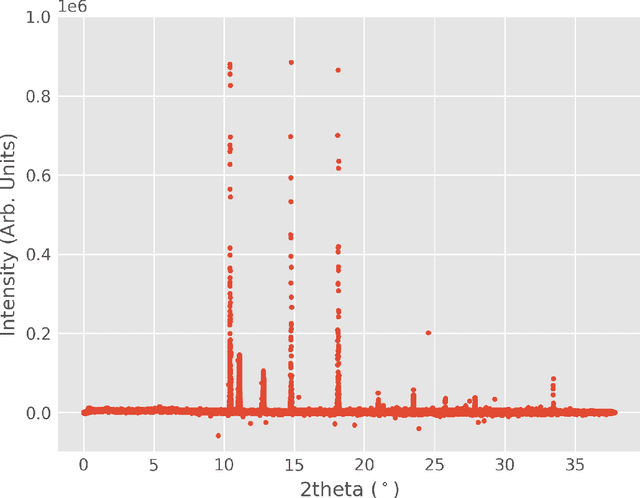
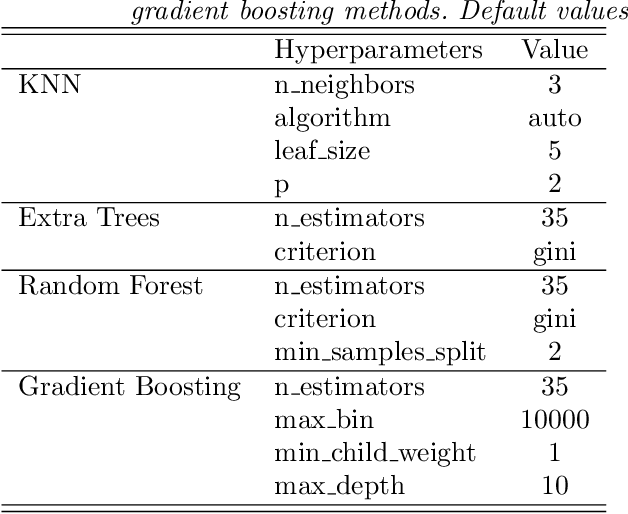
Abstract:The in situ synchrotron high-energy X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) technique is highly utilized by researchers to analyze the crystallographic structures of materials in functional devices (e.g., battery materials) or in complex sample environments (e.g., diamond anvil cells or syntheses reactors). An atomic structure of a material can be identified by its diffraction pattern, along with detailed analysis such as Rietveld refinement which indicates how the measured structure deviates from the ideal structure (e.g., internal stresses or defects). For in situ experiments, a series of XRD images is usually collected on the same sample at different conditions (e.g., adiabatic conditions), yielding different states of matter, or simply collected continuously as a function of time to track the change of a sample over a chemical or physical process. In situ experiments are usually performed with area detectors, collecting 2D images composed of diffraction rings for ideal powders. Depending on the material's form, one may observe different characteristics other than the typical Debye Scherrer rings for a realistic sample and its environments, such as textures or preferred orientations and single crystal diffraction spots in the 2D XRD image. In this work, we present an investigation of machine learning methods for fast and reliable identification and separation of the single crystal diffraction spots in XRD images. The exclusion of artifacts during an XRD image integration process allows a precise analysis of the powder diffraction rings of interest. We observe that the gradient boosting method can consistently produce high accuracy results when it is trained with small subsets of highly diverse datasets. The method dramatically decreases the amount of time spent on identifying and separating single crystal spots in comparison to the conventional method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge