Jakub Harasta
Gender Bias in LLMs: Preliminary Evidence from Shared Parenting Scenario in Czech Family Law
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Access to justice remains limited for many people, leading laypersons to increasingly rely on Large Language Models (LLMs) for legal self-help. Laypeople use these tools intuitively, which may lead them to form expectations based on incomplete, incorrect, or biased outputs. This study examines whether leading LLMs exhibit gender bias in their responses to a realistic family law scenario. We present an expert-designed divorce scenario grounded in Czech family law and evaluate four state-of-the-art LLMs GPT-5 nano, Claude Haiku 4.5, Gemini 2.5 Flash, and Llama 3.3 in a fully zero-shot interaction. We deploy two versions of the scenario, one with gendered names and one with neutral labels, to establish a baseline for comparison. We further introduce nine legally relevant factors that vary the factual circumstances of the case and test whether these variations influence the models' proposed shared-parenting ratios. Our preliminary results highlight differences across models and suggest gender-dependent patterns in the outcomes generated by some systems. The findings underscore both the risks associated with laypeople's reliance on LLMs for legal guidance and the need for more robust evaluation of model behavior in sensitive legal contexts. We present exploratory and descriptive evidence intended to identify systematic asymmetries rather than to establish causal effects.
LLMs & Legal Aid: Understanding Legal Needs Exhibited Through User Queries
Jan 03, 2025



Abstract:The paper presents a preliminary analysis of an experiment conducted by Frank Bold, a Czech expert group, to explore user interactions with GPT-4 for addressing legal queries. Between May 3, 2023, and July 25, 2023, 1,252 users submitted 3,847 queries. Unlike studies that primarily focus on the accuracy, factuality, or hallucination tendencies of large language models (LLMs), our analysis focuses on the user query dimension of the interaction. Using GPT-4o for zero-shot classification, we categorized queries on (1) whether users provided factual information about their issue (29.95%) or not (70.05%), (2) whether they sought legal information (64.93%) or advice on the course of action (35.07\%), and (3) whether they imposed requirements to shape or control the model's answer (28.57%) or not (71.43%). We provide both quantitative and qualitative insight into user needs and contribute to a better understanding of user engagement with LLMs.
It Cannot Be Right If It Was Written by AI: On Lawyers' Preferences of Documents Perceived as Authored by an LLM vs a Human
Jul 09, 2024
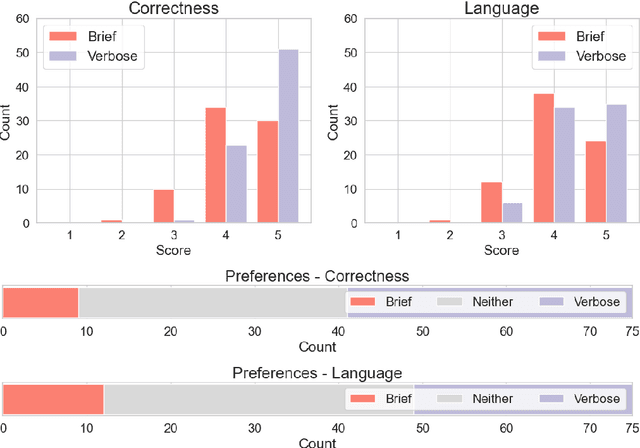
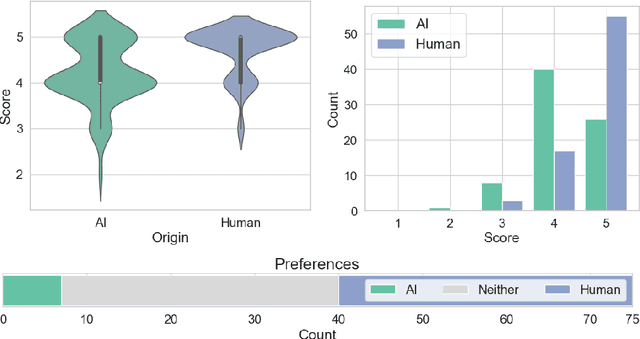
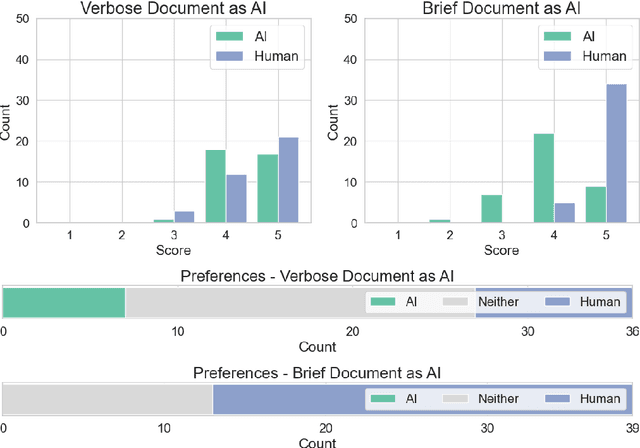
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) enable a future in which certain types of legal documents may be generated automatically. This has a great potential to streamline legal processes, lower the cost of legal services, and dramatically increase access to justice. While many researchers focus their efforts on proposing and evaluating LLM-based applications supporting tasks in the legal domain, there is a notable lack of investigations into how legal professionals perceive content if they believe it has been generated by an LLM. Yet, this is a critical point as over-reliance or unfounded skepticism may influence whether such documents bring about appropriate legal consequences. This study is the necessary analysis in the context of the ongoing transition towards mature generative AI systems. Specifically, we examined whether the perception of legal documents' by lawyers (n=75) varies based on their assumed origin (human-crafted vs AI-generated). The participants evaluated the documents focusing on their correctness and language quality. Our analysis revealed a clear preference for documents perceived as crafted by a human over those believed to be generated by AI. At the same time, most of the participants are expecting the future in which documents will be generated automatically. These findings could be leveraged by legal practitioners, policy makers and legislators to implement and adopt legal document generation technology responsibly, and to fuel the necessary discussions into how legal processes should be updated to reflect the recent technological developments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge