Get our free extension to see links to code for papers anywhere online!Free add-on: code for papers everywhere!Free add-on: See code for papers anywhere!
Jacob Mackay
Autocorrelation, Wigner and Ambiguity Transforms on Polygons for Coherent Radiation Rendering
Feb 06, 2022Figures and Tables:
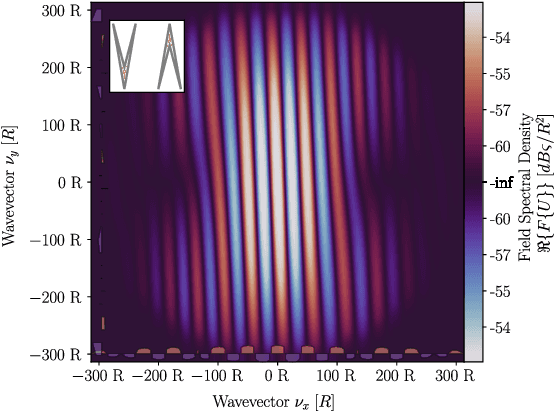

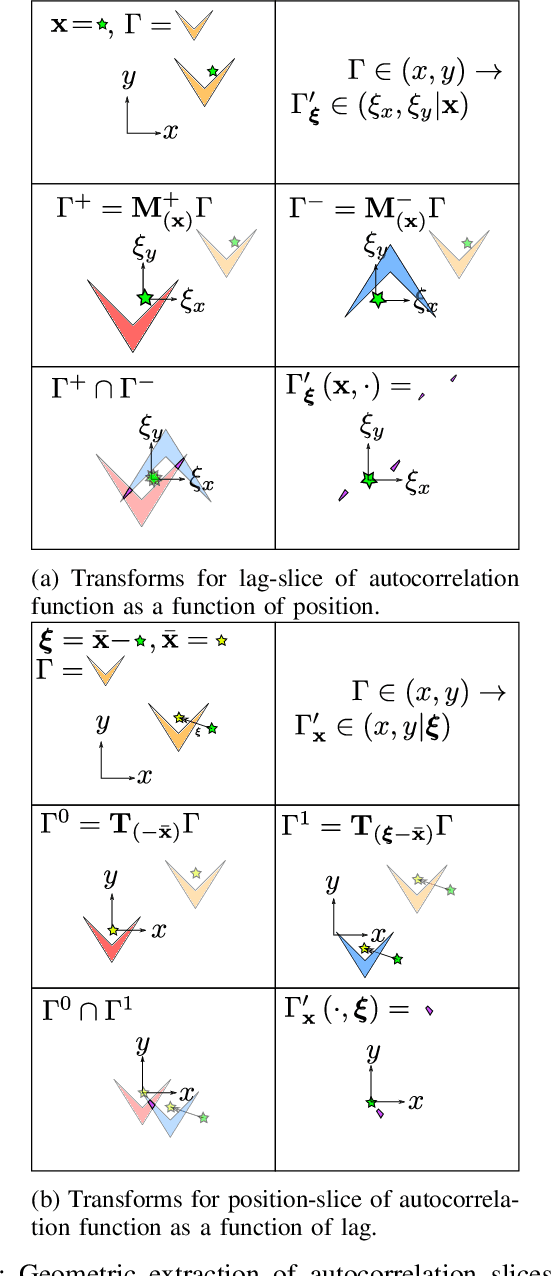




Abstract:Simulating the radar illumination of large scenes generally relies on a geometric model of light transport which largely ignores prominent wave effects. This can be remedied through coherence ray-tracing, but this requires the Wigner transform of the aperture. This diffraction function has been historically difficult to generate, and is relevant in the fields of optics, holography, synchrotron-radiation, quantum systems and radar. In this paper we provide the Wigner transform of arbitrary polygons through geometric transforms and the Stokes Fourier transform; and display its use in Monte-Carlo rendering.
Via
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge