J. Kelly
University of Toronto Robotics Institute
Navigating the EU AI Act: A Methodological Approach to Compliance for Safety-critical Products
Mar 26, 2024



Abstract:In December 2023, the European Parliament provisionally agreed on the EU AI Act. This unprecedented regulatory framework for AI systems lays out guidelines to ensure the safety, legality, and trustworthiness of AI products. This paper presents a methodology for interpreting the EU AI Act requirements for high-risk AI systems by leveraging product quality models. We first propose an extended product quality model for AI systems, incorporating attributes relevant to the Act not covered by current quality models. We map the Act requirements to relevant quality attributes with the goal of refining them into measurable characteristics. We then propose a contract-based approach to derive technical requirements at the stakeholder level. This facilitates the development and assessment of AI systems that not only adhere to established quality standards, but also comply with the regulatory requirements outlined in the Act for high-risk (including safety-critical) AI systems. We demonstrate the applicability of this methodology on an exemplary automotive supply chain use case, where several stakeholders interact to achieve EU AI Act compliance.
Making Sense of the Robotized Pandemic Response: A Comparison of Global and Canadian Robot Deployments and Success Factors
Sep 21, 2020


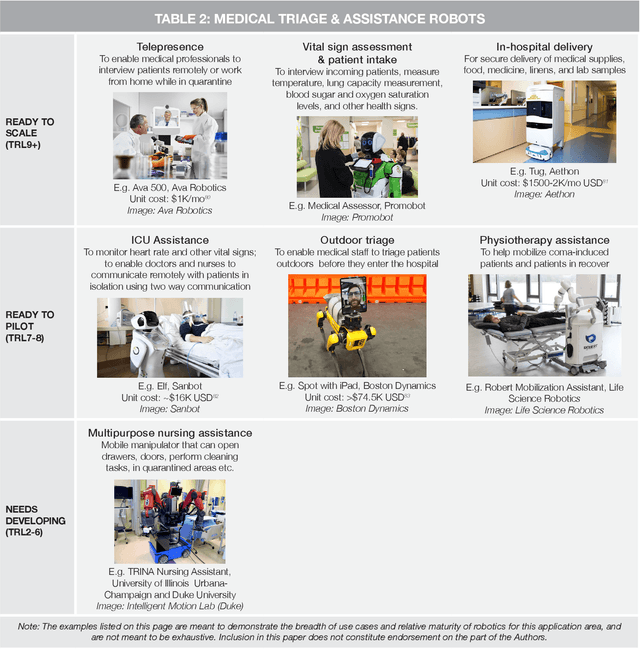
Abstract:From disinfection and remote triage, to logistics and delivery, countries around the world are making use of robots to address the unique challenges presented by the COVID-19 pandemic. Robots are being used to manage the pandemic in Canada too, but relative to other regions, we have been more cautious in our adoption -- this despite the important role that robots of Canadian origin are now playing on the global stage. This white paper discusses why this is the case, and argues that strategic investment and support for the Canadian robotics industry are urgently needed to bring the benefits of robotics home, where we have more control in shaping the future of this game-changing technology. Such investments will not only serve to support Canada's current pandemic response and post pandemic recovery, but will also prepare this country to weather future crises. Without such support, Canada risks falling behind other developed nations that are investing heavily in hardware automation at this time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge