Isabella Hall
Trends in Remote Learning-based Google Shopping in the United States due to COVID-19
Apr 27, 2022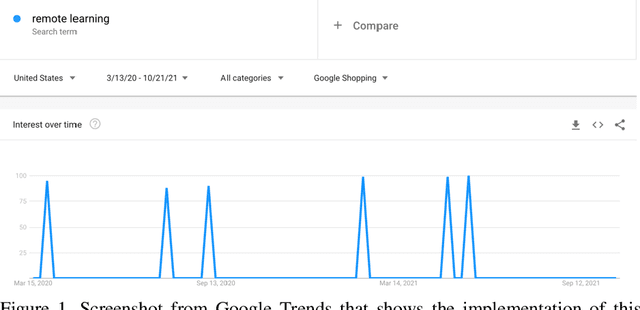
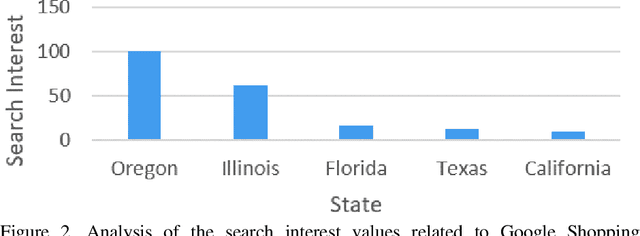
Abstract:The United States of America has been the worst affected country in terms of the number of cases and deaths on account of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) or COVID-19, a highly transmissible and pathogenic coronavirus that started spreading globally in late 2019. On account of the surge of infections, accompanied by hospitalizations and deaths due to COVID-19, and lack of a definitive cure at that point, a national emergency was declared in the United States on March 13, 2020. To prevent the rapid spread of the virus, several states declared stay at home and remote work guidelines shortly after this declaration of an emergency. Such guidelines caused schools, colleges, and universities, both private and public, in all the 50-United States to switch to remote or online forms of teaching for a significant period of time. As a result, Google, the most widely used search engine in the United States, experienced a surge in online shopping of remote learning-based software, systems, applications, and gadgets by both educators and students from all the 50-United States, due to both these groups responding to the associated needs and demands related to switching to remote teaching and learning. This paper aims to investigate, analyze, and interpret these trends of Google Shopping related to remote learning that emerged since March 13, 2020, on account of COVID-19 and the subsequent remote learning adoption in almost all schools, colleges, and universities, from all the 50-United States. The study was performed using Google Trends, which helps to track and study Google Shopping-based online activity emerging from different geolocations. The results and discussions show that the highest interest related to Remote Learning-based Google Shopping was recorded from Oregon, which was followed by Illinois, Florida, Texas, California, and the other states.
Investigating the Emergence of Online Learning in Different Countries using the 5 W's and 1 H Approach
Apr 27, 2022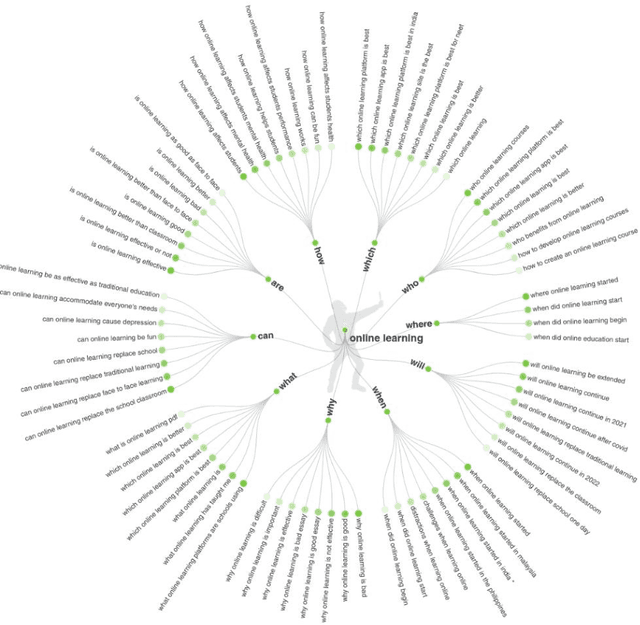
Abstract:The rise of the Internet of Everything lifestyle in the last decade has had a significant impact on the increased emergence and adoption of online learning in almost all countries across the world. E-learning 3.0 is expected to become the norm of learning globally in almost all sectors in the next few years. The pervasiveness of the Semantic Web powered by the Internet of Everything lifestyle is expected to play a huge role towards seamless and faster adoption of the emerging paradigms of E-learning 3.0. Therefore, this paper presents an exploratory study to analyze multimodal components of Semantic Web behavior data to investigate the emergence of online learning in different countries across the world. The work specifically involved investigating relevant web behavior data to interpret the 5 W's and 1 H - Who, What, When Where, Why, and How related to online learning. Based on studying the E-learning Index of 2021, the study was performed for all the countries that are member states of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. The results presented and discussed help to interpret the emergence of online learning in each of these countries in terms of the associated public perceptions, queries, opinions, behaviors, and perspectives. Furthermore, to support research and development in this field, we have published the web behavior-based Big Data related to online learning that was mined for all these 38 countries, in the form of a dataset, which is avail-able at https://dx.doi.org/10.21227/xbvs-0198.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge