Ilyas Cicekli
Learning Translation Rules From A Bilingual Corpus
Jul 26, 1996Abstract:This paper proposes a mechanism for learning pattern correspondences between two languages from a corpus of translated sentence pairs. The proposed mechanism uses analogical reasoning between two translations. Given a pair of translations, the similar parts of the sentences in the source language must correspond the similar parts of the sentences in the target language. Similarly, the different parts should correspond to the respective parts in the translated sentences. The correspondences between the similarities, and also differences are learned in the form of translation rules. The system is tested on a small training dataset and produced promising results for further investigation.
* 8 pages, Latex, uses nemlap.sty
Tactical Generation in a Free Constituent Order Language
May 05, 1996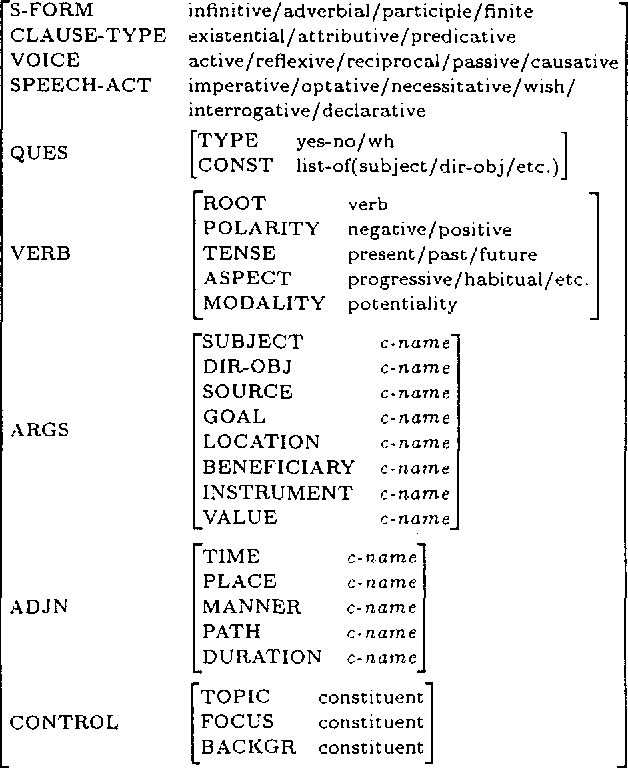
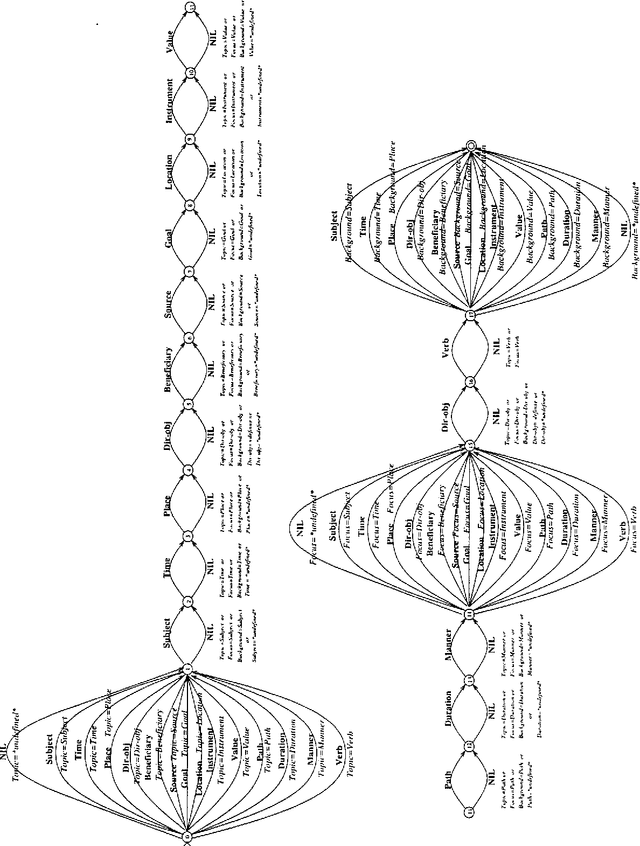
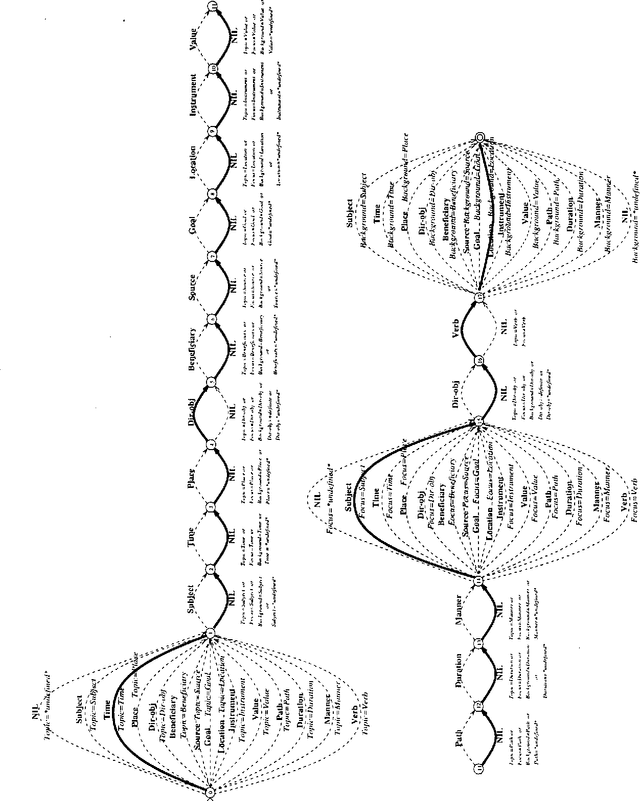
Abstract:This paper describes tactical generation in Turkish, a free constituent order language, in which the order of the constituents may change according to the information structure of the sentences to be generated. In the absence of any information regarding the information structure of a sentence (i.e., topic, focus, background, etc.), the constituents of the sentence obey a default order, but the order is almost freely changeable, depending on the constraints of the text flow or discourse. We have used a recursively structured finite state machine for handling the changes in constituent order, implemented as a right-linear grammar backbone. Our implementation environment is the GenKit system, developed at Carnegie Mellon University--Center for Machine Translation. Morphological realization has been implemented using an external morphological analysis/generation component which performs concrete morpheme selection and handles morphographemic processes.
* gzipped, uuencoded postscript file
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge