Get our free extension to see links to code for papers anywhere online!Free add-on: code for papers everywhere!Free add-on: See code for papers anywhere!
Ilya Sochenkov
The Limitations of Cross-language Word Embeddings Evaluation
Jun 06, 2018Figures and Tables: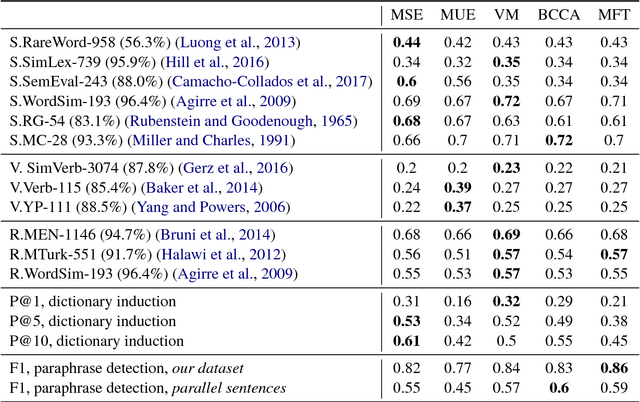
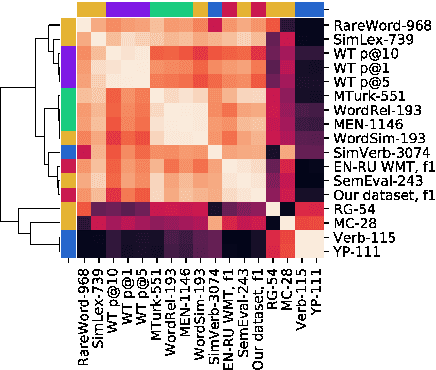


Abstract:The aim of this work is to explore the possible limitations of existing methods of cross-language word embeddings evaluation, addressing the lack of correlation between intrinsic and extrinsic cross-language evaluation methods. To prove this hypothesis, we construct English-Russian datasets for extrinsic and intrinsic evaluation tasks and compare performances of 5 different cross-language models on them. The results say that the scores even on different intrinsic benchmarks do not correlate to each other. We can conclude that the use of human references as ground truth for cross-language word embeddings is not proper unless one does not understand how do native speakers process semantics in their cognition.
* In Proceedings of the 7th Joint Conference on Lexical and
Computational Semantics (*SEM 2018)
Via
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge