Ilse van der Linden
Global Aggregations of Local Explanations for Black Box models
Jul 05, 2019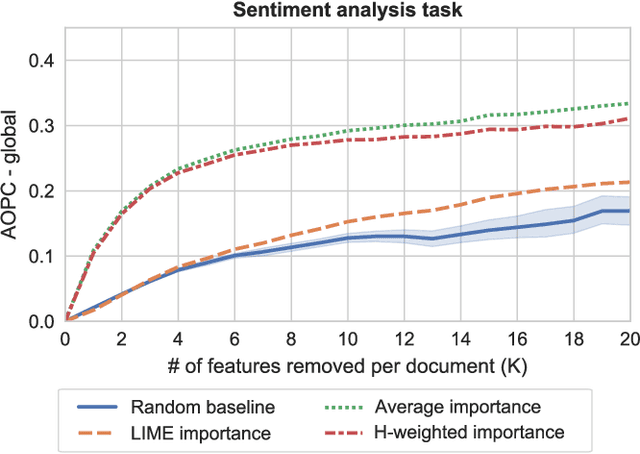
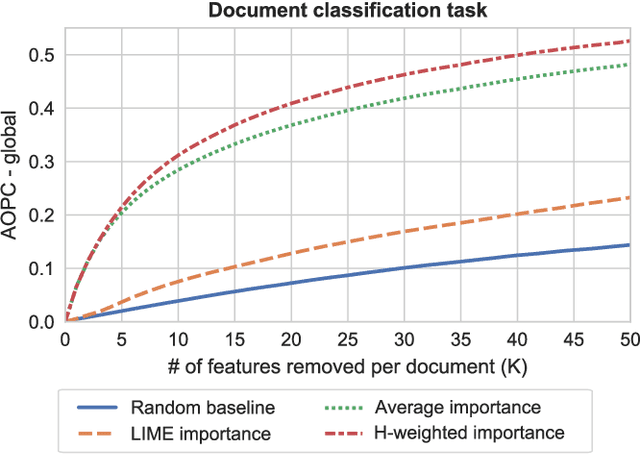
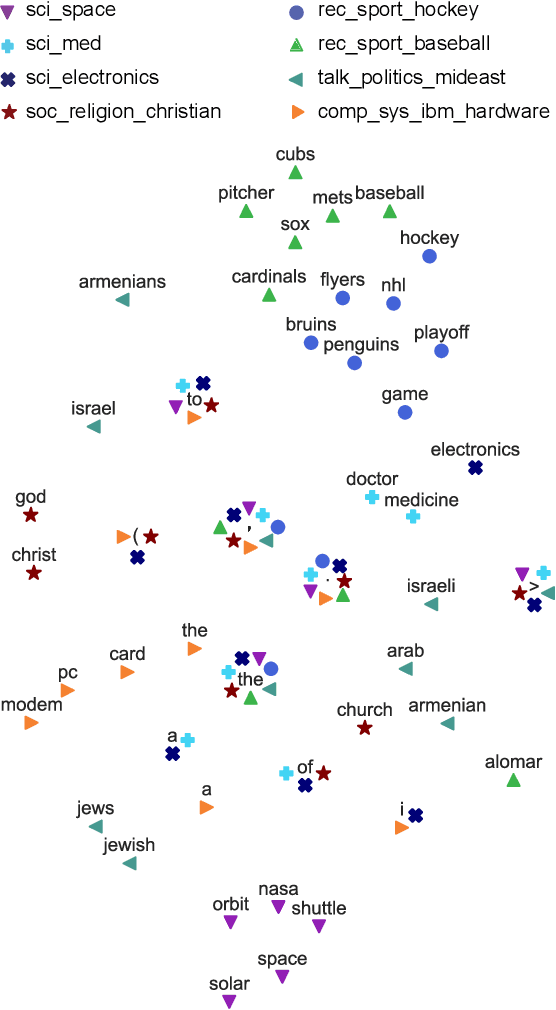
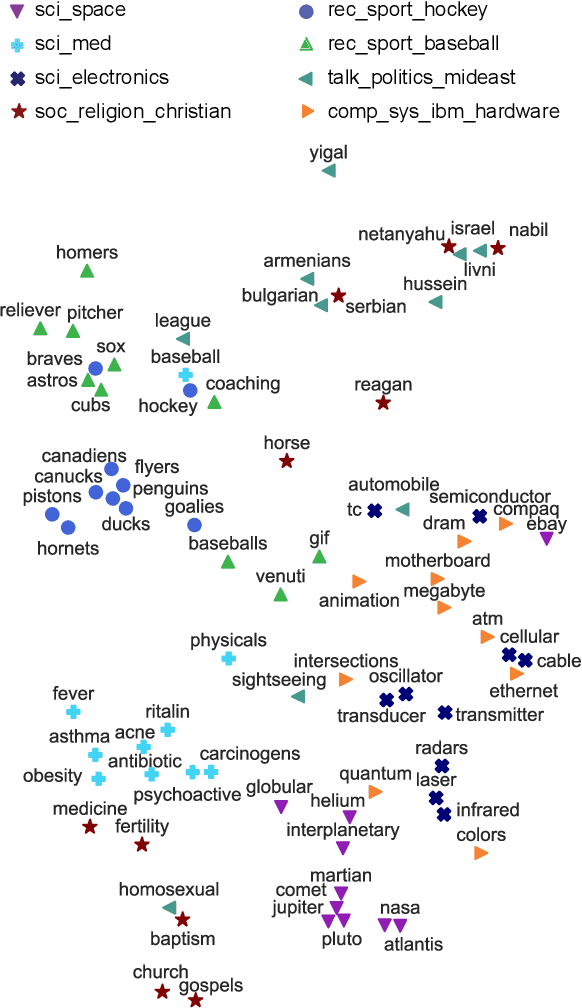
Abstract:The decision-making process of many state-of-the-art machine learning models is inherently inscrutable to the extent that it is impossible for a human to interpret the model directly: they are black box models. This has led to a call for research on explaining black box models, for which there are two main approaches. Global explanations that aim to explain a model's decision making process in general, and local explanations that aim to explain a single prediction. Since it remains challenging to establish fidelity to black box models in globally interpretable approximations, much attention is put on local explanations. However, whether local explanations are able to reliably represent the black box model and provide useful insights remains an open question. We present Global Aggregations of Local Explanations (GALE) with the objective to provide insights in a model's global decision making process. Overall, our results reveal that the choice of aggregation matters. We find that the global importance introduced by Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations (LIME) does not reliably represent the model's global behavior. Our proposed aggregations are better able to represent how features affect the model's predictions, and to provide global insights by identifying distinguishing features.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge