Iina Hellsten
Implicit media frames: Automated analysis of public debate on artificial sweeteners
Jan 25, 2010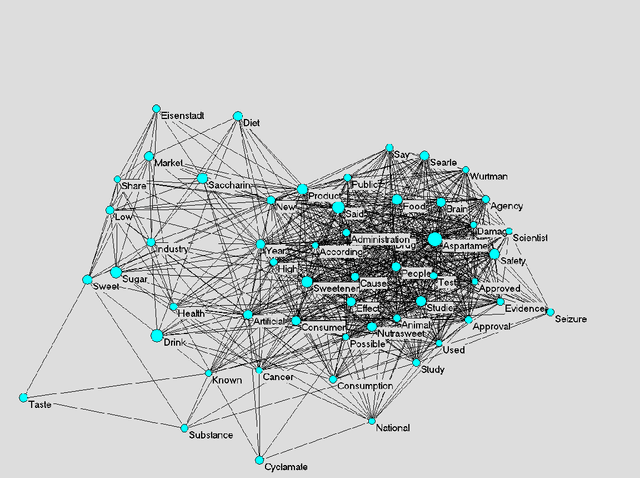
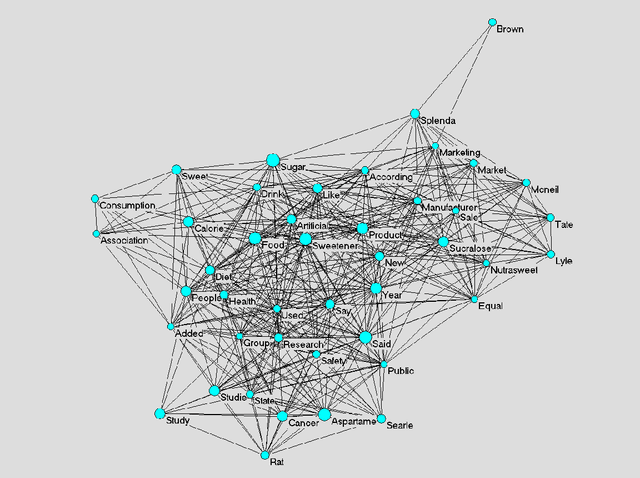
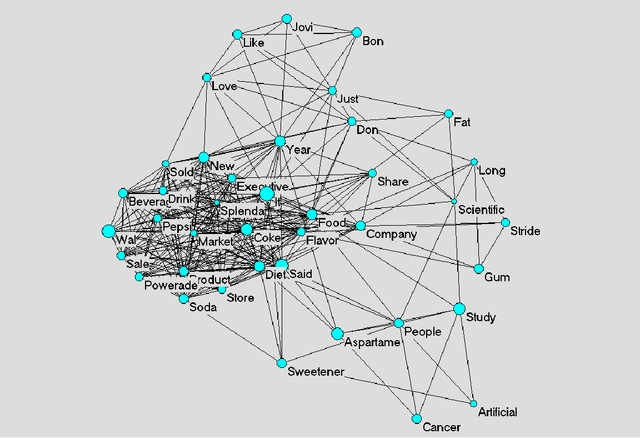
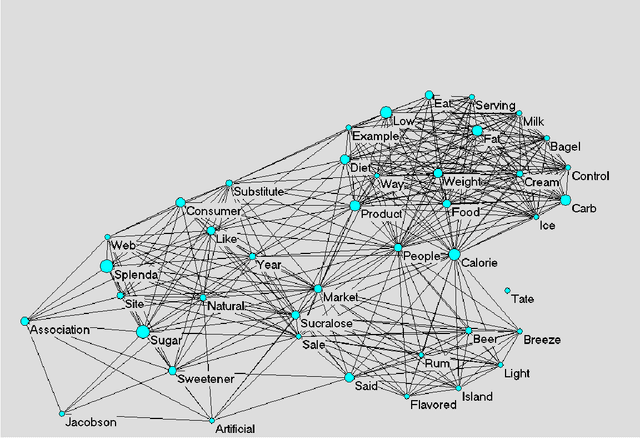
Abstract:The framing of issues in the mass media plays a crucial role in the public understanding of science and technology. This article contributes to research concerned with diachronic analysis of media frames by making an analytical distinction between implicit and explicit media frames, and by introducing an automated method for analysing diachronic changes of implicit frames. In particular, we apply a semantic maps method to a case study on the newspaper debate about artificial sweeteners, published in The New York Times (NYT) between 1980 and 2006. Our results show that the analysis of semantic changes enables us to filter out the dynamics of implicit frames, and to detect emerging metaphors in public debates. Theoretically, we discuss the relation between implicit frames in public debates and codification of information in scientific discourses, and suggest further avenues for research interested in the automated analysis of frame changes and trends in public debates.
Measuring the Meaning of Words in Contexts: An automated analysis of controversies about Monarch butterflies, Frankenfoods, and stem cells
Nov 17, 2009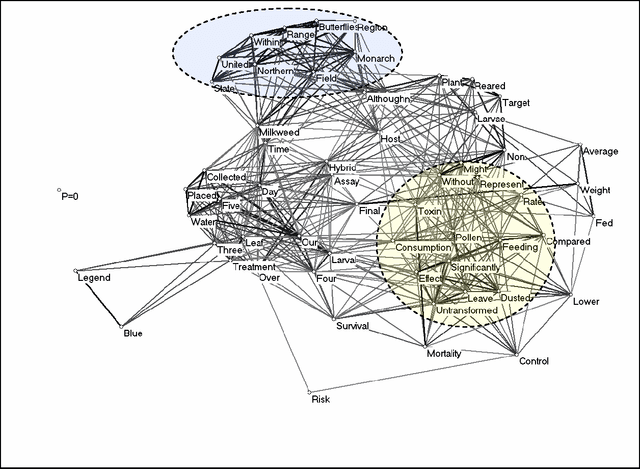
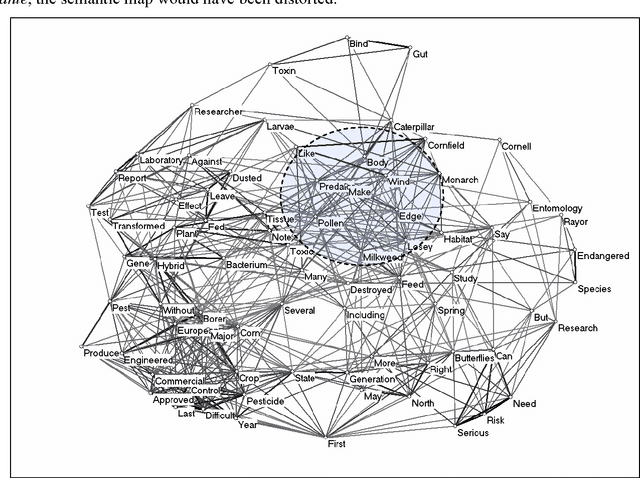
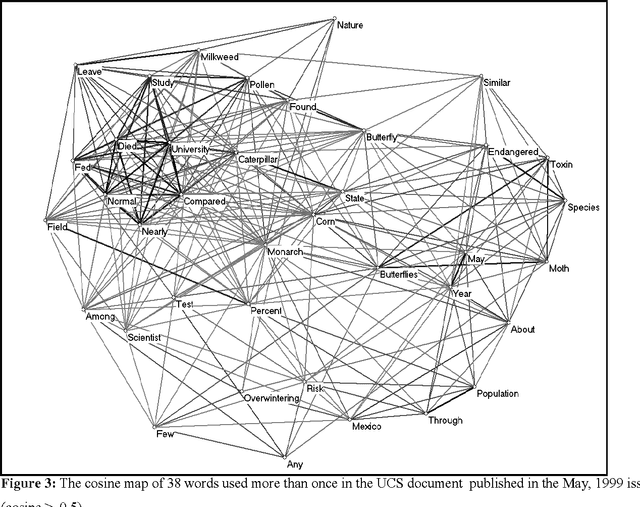
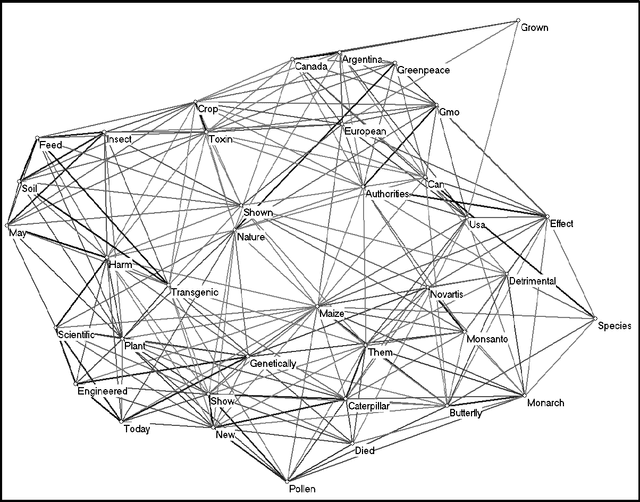
Abstract:Co-words have been considered as carriers of meaning across different domains in studies of science, technology, and society. Words and co-words, however, obtain meaning in sentences, and sentences obtain meaning in their contexts of use. At the science/society interface, words can be expected to have different meanings: the codes of communication that provide meaning to words differ on the varying sides of the interface. Furthermore, meanings and interfaces may change over time. Given this structuring of meaning across interfaces and over time, we distinguish between metaphors and diaphors as reflexive mechanisms that facilitate the translation between contexts. Our empirical focus is on three recent scientific controversies: Monarch butterflies, Frankenfoods, and stem-cell therapies. This study explores new avenues that relate the study of co-word analysis in context with the sociological quest for the analysis and processing of meaning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge