Igor L. R. Azevedo
NewsReX: A More Efficient Approach to News Recommendation with Keras 3 and JAX
Aug 29, 2025Abstract:Reproducing and comparing results in news recommendation research has become increasingly difficult. This is due to a fragmented ecosystem of diverse codebases, varied configurations, and mainly due to resource-intensive models. We introduce NewsReX, an open-source library designed to streamline this process. Our key contribution is a modern implementation built on Keras 3 and JAX, which provides an increase in computational efficiency. Experiments show that NewsReX is faster than current implementations. To support broader research, we provide a straightforward guide and scripts for training models on custom datasets. We validated this functionality using a proprietary Japanese news dataset from Nikkei News, a leading Japanese media corporation renowned for its comprehensive coverage of business, economic, and financial news. NewsReX makes reproducing complex experiments faster and more accessible to a wider range of hardware making sure the speed up it also achieved for less powerful GPUs, like an 8GB RTX 3060 Ti. Beyond the library, this paper offers an analysis of key training parameters often overlooked in the literature, including the effect of different negative sampling strategies, the varying number of epochs, the impact of random batching, and more. This supplementary analysis serves as a valuable reference for future research, aiming to reduce redundant computation when comparing baselines and guide best practices. Code available at https://github.com/igor17400/NewsReX.
From Votes to Volatility Predicting the Stock Market on Election Day
Dec 15, 2024

Abstract:Stock market forecasting has been a topic of extensive research, aiming to provide investors with optimal stock recommendations for higher returns. In recent years, this field has gained even more attention due to the widespread adoption of deep learning models. While these models have achieved impressive accuracy in predicting stock behavior, tailoring them to specific scenarios has become increasingly important. Election Day represents one such critical scenario, characterized by intensified market volatility, as the winning candidate's policies significantly impact various economic sectors and companies. To address this challenge, we propose the Election Day Stock Market Forecasting (EDSMF) Model. Our approach leverages the contextual capabilities of large language models alongside specialized agents designed to analyze the political and economic consequences of elections. By building on a state-of-the-art architecture, we demonstrate that EDSMF improves the predictive performance of the S&P 500 during this uniquely volatile day.
Popular News Always Compete for the User's Attention! POPK: Mitigating Popularity Bias via a Temporal-Counterfactual
Jul 13, 2024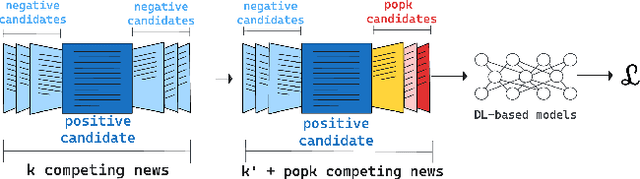
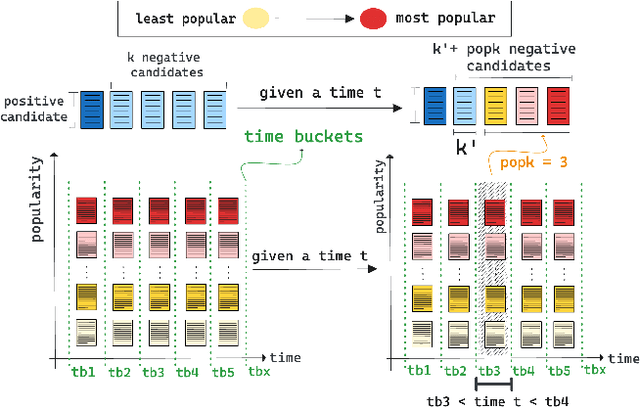
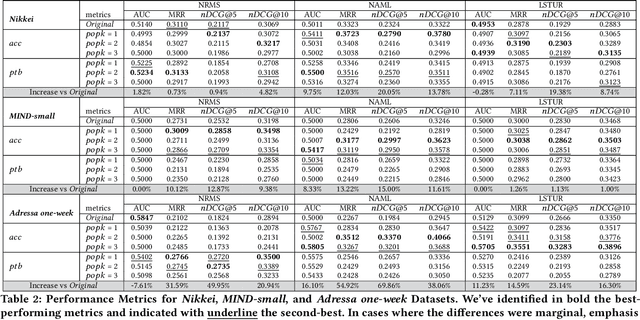
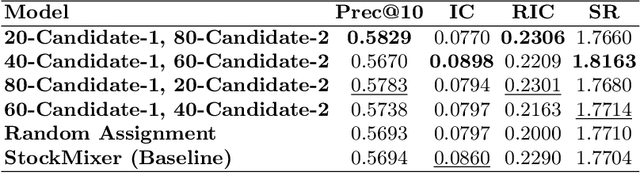
Abstract:In news recommendation systems, reducing popularity bias is essential for delivering accurate and diverse recommendations. This paper presents POPK, a new method that uses temporal-counterfactual analysis to mitigate the influence of popular news articles. By asking, "What if, at a given time $t$, a set of popular news articles were competing for the user's attention to be clicked?", POPK aims to improve recommendation accuracy and diversity. We tested POPK on three different language datasets (Japanese, English, and Norwegian) and found that it successfully enhances traditional methods. POPK offers flexibility for customization to enhance either accuracy or diversity, alongside providing distinct ways of measuring popularity. We argue that popular news articles always compete for attention, even if they are not explicitly present in the user's impression list. POPK systematically eliminates the implicit influence of popular news articles during each training step. We combine counterfactual reasoning with a temporal approach to adjust the negative sample space, refining understanding of user interests. Our findings underscore how POPK effectively enhances the accuracy and diversity of recommended articles while also tailoring the approach to specific needs.
A Look Into News Avoidance Through AWRS: An Avoidance-Aware Recommender System
Jul 12, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, journalists have expressed concerns about the increasing trend of news article avoidance, especially within specific domains. This issue has been exacerbated by the rise of recommender systems. Our research indicates that recommender systems should consider avoidance as a fundamental factor. We argue that news articles can be characterized by three principal elements: exposure, relevance, and avoidance, all of which are closely interconnected. To address these challenges, we introduce AWRS, an Avoidance-Aware Recommender System. This framework incorporates avoidance awareness when recommending news, based on the premise that news article avoidance conveys significant information about user preferences. Evaluation results on three news datasets in different languages (English, Norwegian, and Japanese) demonstrate that our method outperforms existing approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge