I. Shimizu
KamNet: An Integrated Spatiotemporal Deep Neural Network for Rare Event Search in KamLAND-Zen
Mar 08, 2022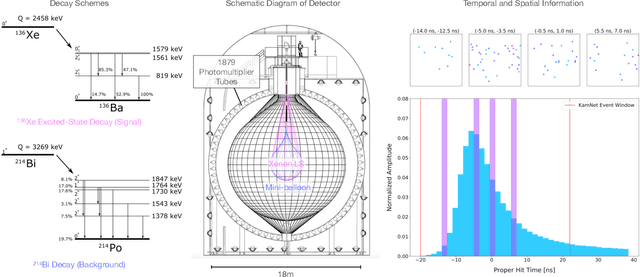
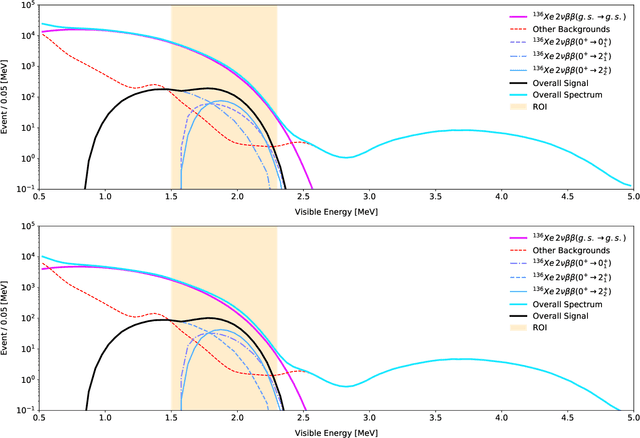
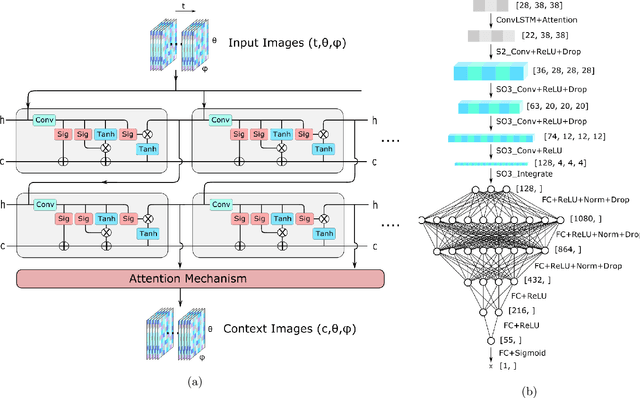
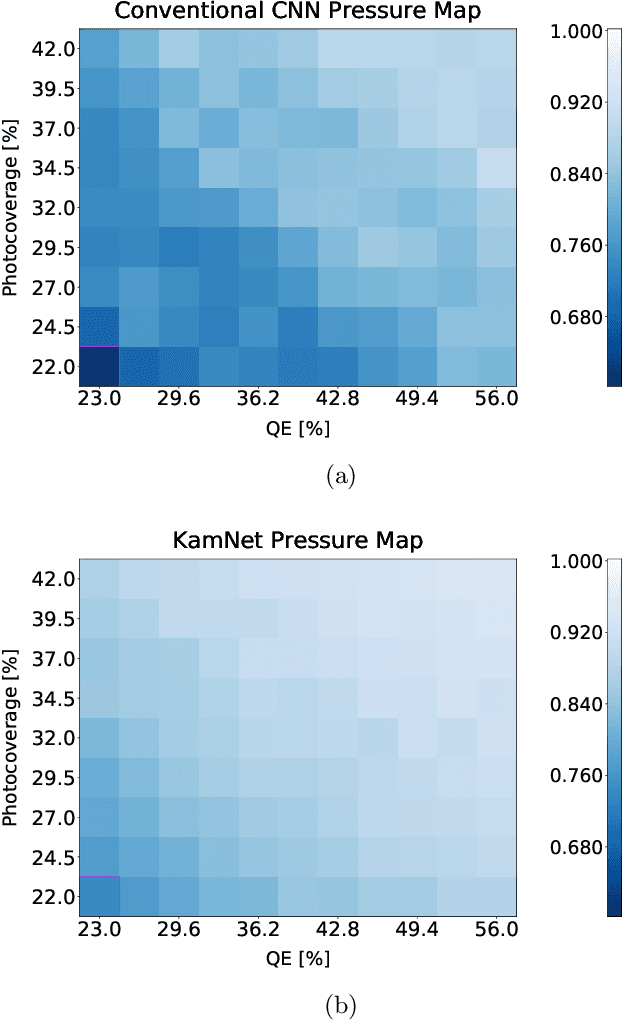
Abstract:Rare event searches allow us to search for new physics at energy scales inaccessible with other means by leveraging specialized large-mass detectors. Machine learning provides a new tool to maximize the information provided by these detectors. The information is sparse, which forces these algorithms to start from the lowest level data and exploit all symmetries in the detector to produce results. In this work we present KamNet which harnesses breakthroughs in geometric deep learning and spatiotemporal data analysis to maximize the physics reach of KamLAND-Zen, a kiloton scale spherical liquid scintillator detector searching for neutrinoless double beta decay ($0\nu\beta\beta$). Using a simplified background model for KamLAND we show that KamNet outperforms a conventional CNN on benchmarking MC simulations with an increasing level of robustness. Using simulated data, we then demonstrate KamNet's ability to increase KamLAND-Zen's sensitivity to $0\nu\beta\beta$ and $0\nu\beta\beta$ to excited states. A key component of this work is the addition of an attention mechanism to elucidate the underlying physics KamNet is using for the background rejection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge