Huawei Tian
Acceleration of Histogram-Based Contrast Enhancement via Selective Downsampling
Nov 20, 2017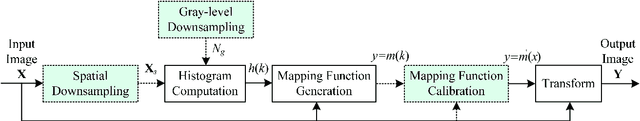
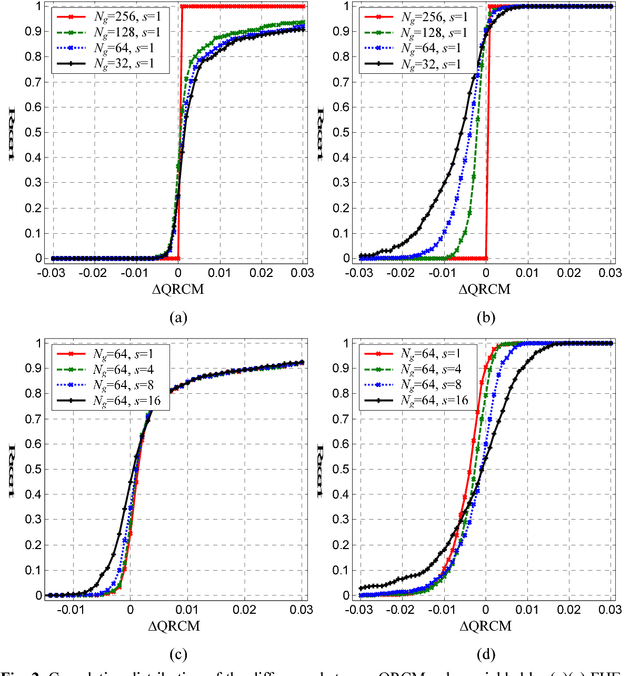

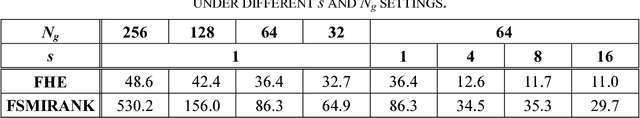
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a general framework to accelerate the universal histogram-based image contrast enhancement (CE) algorithms. Both spatial and gray-level selective down- sampling of digital images are adopted to decrease computational cost, while the visual quality of enhanced images is still preserved and without apparent degradation. Mapping function calibration is novelly proposed to reconstruct the pixel mapping on the gray levels missed by downsampling. As two case studies, accelerations of histogram equalization (HE) and the state-of-the-art global CE algorithm, i.e., spatial mutual information and PageRank (SMIRANK), are presented detailedly. Both quantitative and qualitative assessment results have verified the effectiveness of our proposed CE acceleration framework. In typical tests, computational efficiencies of HE and SMIRANK have been speeded up by about 3.9 and 13.5 times, respectively.
Contrast Enhancement of Brightness-Distorted Images by Improved Adaptive Gamma Correction
Sep 13, 2017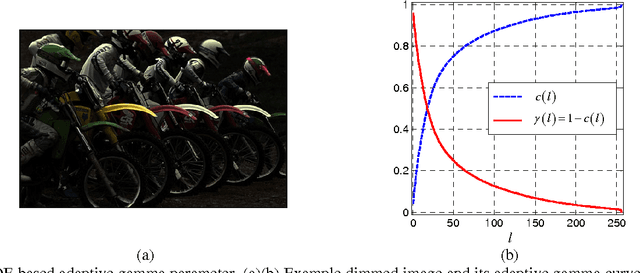

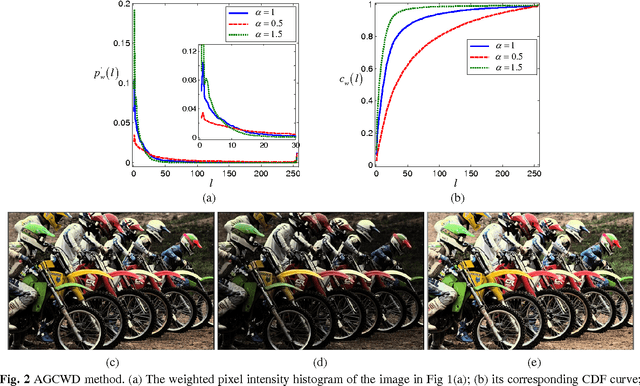
Abstract:As an efficient image contrast enhancement (CE) tool, adaptive gamma correction (AGC) was previously proposed by relating gamma parameter with cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the pixel gray levels within an image. ACG deals well with most dimmed images, but fails for globally bright images and the dimmed images with local bright regions. Such two categories of brightness-distorted images are universal in real scenarios, such as improper exposure and white object regions. In order to attenuate such deficiencies, here we propose an improved AGC algorithm. The novel strategy of negative images is used to realize CE of the bright images, and the gamma correction modulated by truncated CDF is employed to enhance the dimmed ones. As such, local over-enhancement and structure distortion can be alleviated. Both qualitative and quantitative experimental results show that our proposed method yields consistently good CE results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge