Huaming Zhang
DatawiseAgent: A Notebook-Centric LLM Agent Framework for Automated Data Science
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:Data Science tasks are multifaceted, dynamic, and often domain-specific. Existing LLM-based approaches largely concentrate on isolated phases, neglecting the interdependent nature of many data science tasks and limiting their capacity for comprehensive end-to-end support. We propose DatawiseAgent, a notebook-centric LLM agent framework that unifies interactions among user, agent and the computational environment through markdown and executable code cells, supporting flexible and adaptive automated data science. Built on a Finite State Transducer(FST), DatawiseAgent orchestrates four stages, including DSF-like planning, incremental execution, self-debugging, and post-filtering. Specifically, the DFS-like planning stage systematically explores the solution space, while incremental execution harnesses real-time feedback and accommodates LLM's limited capabilities to progressively complete tasks. The self-debugging and post-filtering modules further enhance reliability by diagnosing and correcting errors and pruning extraneous information. Extensive experiments on diverse tasks, including data analysis, visualization, and data modeling, show that DatawiseAgent consistently outperforms or matches state-of-the-art methods across multiple model settings. These results highlight its potential to generalize across data science scenarios and lay the groundwork for more efficient, fully automated workflows.
Weighted Graph Nodes Clustering via Gumbel Softmax
Feb 22, 2021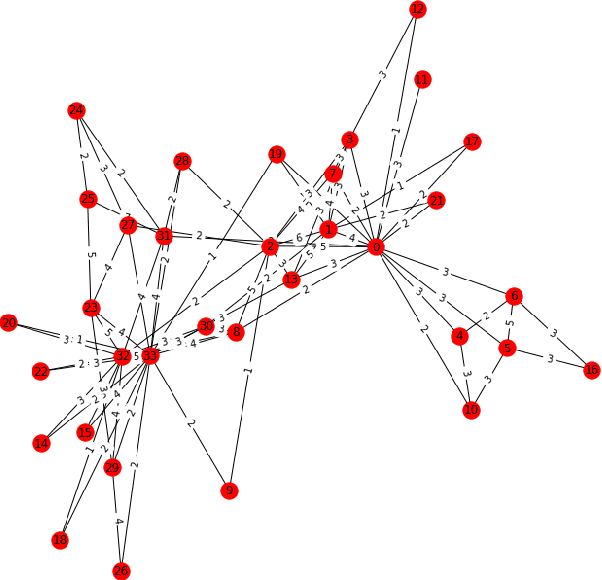
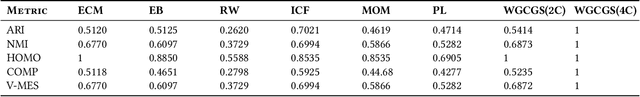
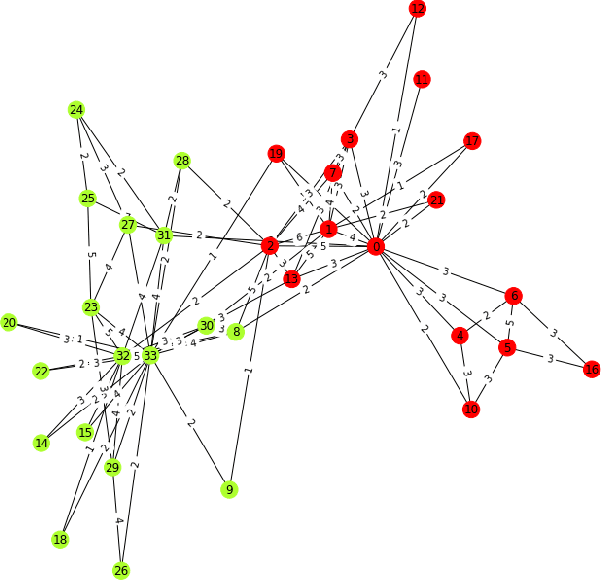
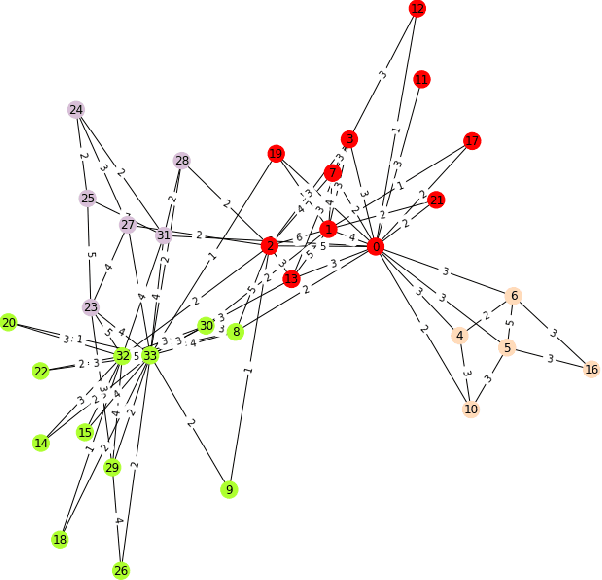
Abstract:Graph is a ubiquitous data structure in data science that is widely applied in social networks, knowledge representation graphs, recommendation systems, etc. When given a graph dataset consisting of one graph or more graphs, where the graphs are weighted in general, the first step is often to find clusters in the graphs. In this paper, we present some ongoing research results on graph clustering algorithms for clustering weighted graph datasets, which we name as Weighted Graph Node Clustering via Gumbel Softmax (WGCGS for short). We apply WGCGS on the Karate club weighted network dataset. Our experiments demonstrate that WGCGS can efficiently and effectively find clusters in the Karate club weighted network dataset. Our algorithm's effectiveness is demonstrated by (1) comparing the clustering result obtained from our algorithm and the given labels of the dataset; and (2) comparing various metrics between our clustering algorithm and other state-of-the-art graph clustering algorithms.
Community Detection Clustering via Gumbel Softmax
May 12, 2020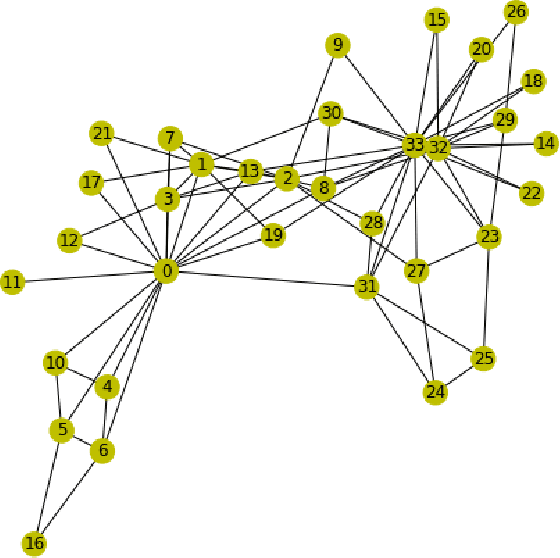
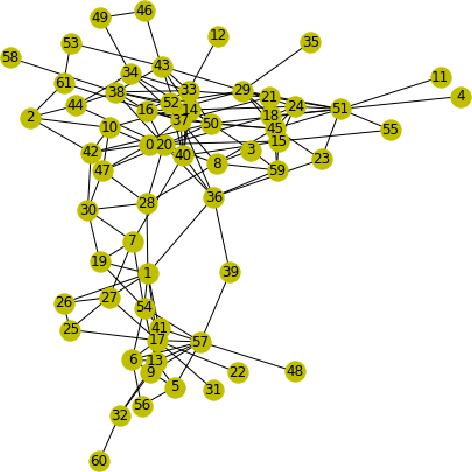
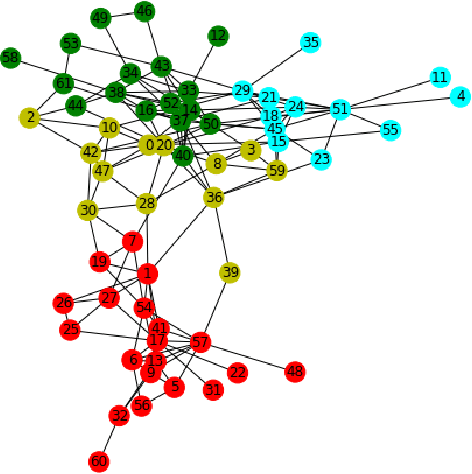
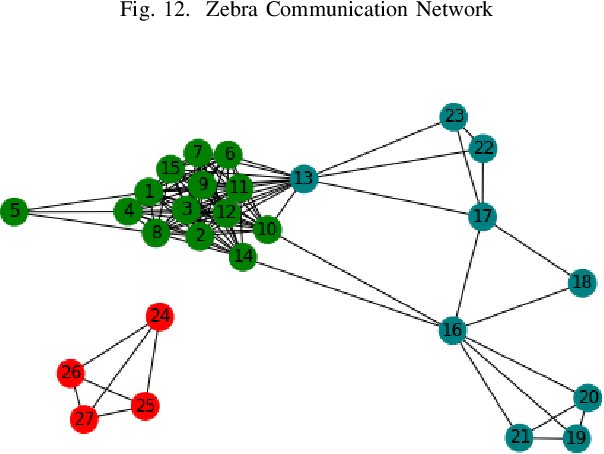
Abstract:Recently, in many systems such as speech recognition and visual processing, deep learning has been widely implemented. In this research, we are exploring the possibility of using deep learning in community detection among the graph datasets. Graphs have gained growing traction in different fields, including social networks, information graphs, the recommender system, and also life sciences. In this paper, we propose a method of community detection clustering the nodes of various graph datasets. We cluster different category datasets that belong to Affiliation networks, Animal networks, Human contact networks, Human social networks, Miscellaneous networks. The deep learning role in modeling the interaction between nodes in a network allows a revolution in the field of science relevant to graph network analysis. In this paper, we extend the gumbel softmax approach to graph network clustering. The experimental findings on specific graph datasets reveal that the new approach outperforms traditional clustering significantly, which strongly shows the efficacy of deep learning in graph community detection clustering. We do a series of experiments on our graph clustering algorithm, using various datasets: Zachary karate club, Highland Tribe, Train bombing, American Revolution, Dolphins, Zebra, Windsurfers, Les Mis\'erables, Political books.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge