Hongliu Yang
Coherent False Seizure Prediction in Epilepsy, Coincidence or Providence?
Oct 26, 2021

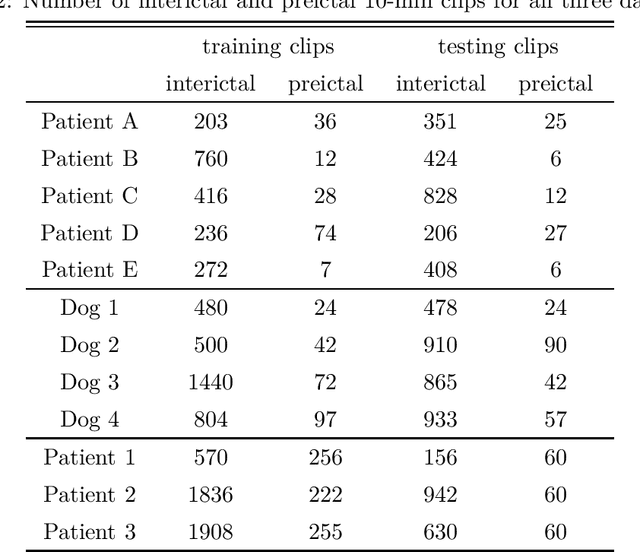

Abstract:Seizure forecasting using machine learning is possible, but the performance is far from ideal, as indicated by many false predictions and low specificity. Here, we examine false and missing alarms of two algorithms on long-term datasets to show that the limitations are less related to classifiers or features, but rather to intrinsic changes in the data. We evaluated two algorithms on three datasets by computing the correlation of false predictions and estimating the information transfer between both classification methods. For 9 out of 12 individuals both methods showed a performance better than chance. For all individuals we observed a positive correlation in predictions. For individuals with strong correlation in false predictions we were able to boost the performance of one method by excluding test samples based on the results of the second method. Substantially different algorithms exhibit a highly consistent performance and a strong coherency in false and missing alarms. Hence, changing the underlying hypothesis of a preictal state of fixed time length prior to each seizure to a proictal state is more helpful than further optimizing classifiers. The outcome is significant for the evaluation of seizure prediction algorithms on continuous data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge