Hongbin Chen
Service Provisioning and Path Planning with Obstacle Avoidance for Low-Altitude Wireless Networks
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This paper investigates the three-dimensional (3D) deployment of uncrewed aerial vehicles (UAVs) as aerial base stations in heterogeneous communication networks under constraints imposed by diverse ground obstacles. Given the diverse data demands of user equipments (UEs), a user satisfaction model is developed to provide personalized services. In particular, when a UE is located within a ground obstacle, the UAV must approach the obstacle boundary to ensure reliable service quality. Considering constraints such as UAV failures due to battery depletion, heterogeneous UEs, and obstacles, we aim to maximize overall user satisfaction by jointly optimizing the 3D trajectories of UAVs, transmit beamforming vectors, and binary association indicators between UAVs and UEs. To address the complexity and dynamics of the problem, a block coordinate descent method is adopted to decompose it into two subproblems. The beamforming subproblem is efficiently addressed via a bisection-based water-filling algorithm. For the trajectory and association subproblem, we design a deep reinforcement learning algorithm based on proximal policy optimization to learn an adaptive control policy. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed scheme outperforms baseline schemes in terms of convergence speed and overall system performance. Moreover, it achieves efficient association and accurate obstacle avoidance.
Label Smoothing and Adversarial Robustness
Sep 17, 2020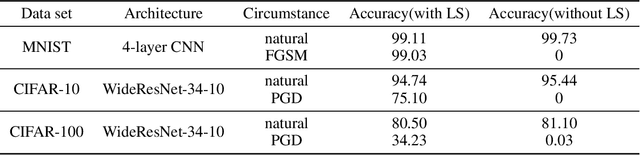
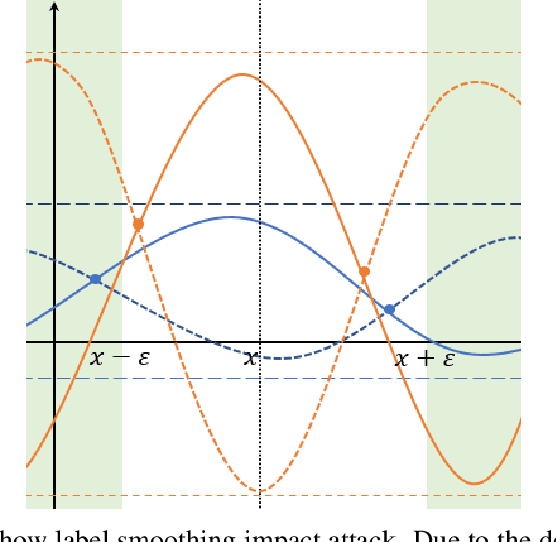
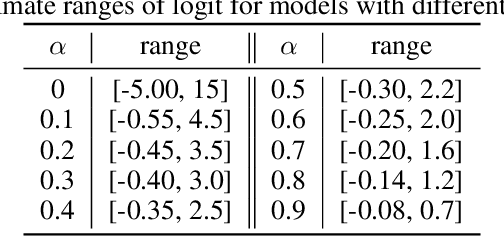
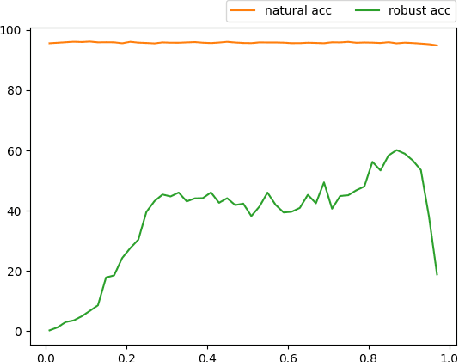
Abstract:Recent studies indicate that current adversarial attack methods are flawed and easy to fail when encountering some deliberately designed defense. Sometimes even a slight modification in the model details will invalidate the attack. We find that training model with label smoothing can easily achieve striking accuracy under most gradient-based attacks. For instance, the robust accuracy of a WideResNet model trained with label smoothing on CIFAR-10 achieves 75% at most under PGD attack. To understand the reason underlying the subtle robustness, we investigate the relationship between label smoothing and adversarial robustness. Through theoretical analysis about the characteristics of the network trained with label smoothing and experiment verification of its performance under various attacks. We demonstrate that the robustness produced by label smoothing is incomplete based on the fact that its defense effect is volatile, and it cannot defend attacks transferred from a naturally trained model. Our study enlightens the research community to rethink how to evaluate the model's robustness appropriately.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge