Hitesh Sapkota
Reinforced Compressive Neural Architecture Search for Versatile Adversarial Robustness
Jun 10, 2024



Abstract:Prior neural architecture search (NAS) for adversarial robustness works have discovered that a lightweight and adversarially robust neural network architecture could exist in a non-robust large teacher network, generally disclosed by heuristic rules through statistical analysis and neural architecture search, generally disclosed by heuristic rules from neural architecture search. However, heuristic methods cannot uniformly handle different adversarial attacks and "teacher" network capacity. To solve this challenge, we propose a Reinforced Compressive Neural Architecture Search (RC-NAS) for Versatile Adversarial Robustness. Specifically, we define task settings that compose datasets, adversarial attacks, and teacher network information. Given diverse tasks, we conduct a novel dual-level training paradigm that consists of a meta-training and a fine-tuning phase to effectively expose the RL agent to diverse attack scenarios (in meta-training), and making it adapt quickly to locate a sub-network (in fine-tuning) for any previously unseen scenarios. Experiments show that our framework could achieve adaptive compression towards different initial teacher networks, datasets, and adversarial attacks, resulting in more lightweight and adversarially robust architectures.
Balancing Bias and Variance for Active Weakly Supervised Learning
Jun 12, 2022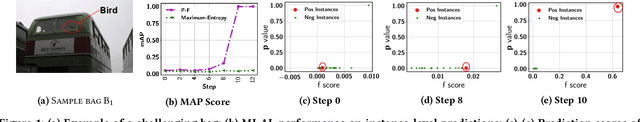
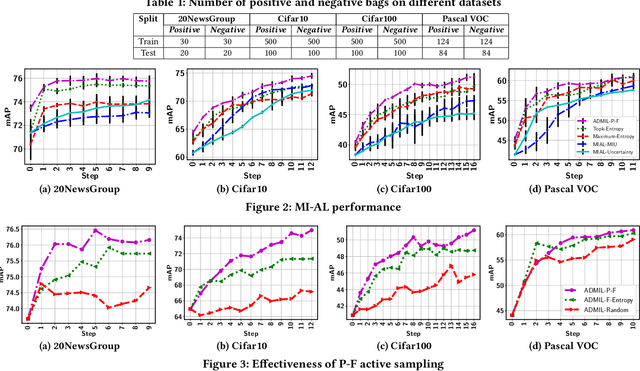
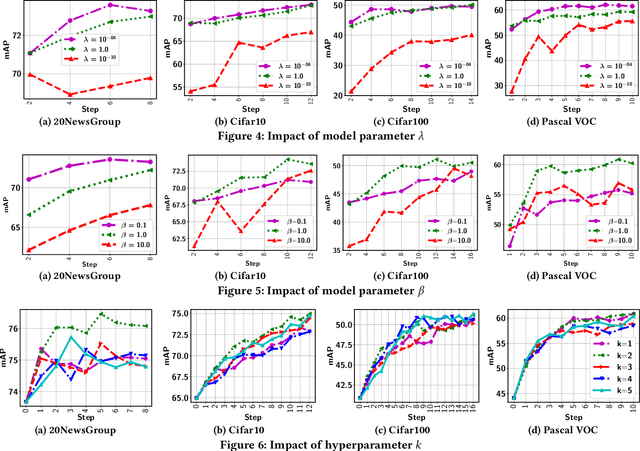

Abstract:As a widely used weakly supervised learning scheme, modern multiple instance learning (MIL) models achieve competitive performance at the bag level. However, instance-level prediction, which is essential for many important applications, remains largely unsatisfactory. We propose to conduct novel active deep multiple instance learning that samples a small subset of informative instances for annotation, aiming to significantly boost the instance-level prediction. A variance regularized loss function is designed to properly balance the bias and variance of instance-level predictions, aiming to effectively accommodate the highly imbalanced instance distribution in MIL and other fundamental challenges. Instead of directly minimizing the variance regularized loss that is non-convex, we optimize a distributionally robust bag level likelihood as its convex surrogate. The robust bag likelihood provides a good approximation of the variance based MIL loss with a strong theoretical guarantee. It also automatically balances bias and variance, making it effective to identify the potentially positive instances to support active sampling. The robust bag likelihood can be naturally integrated with a deep architecture to support deep model training using mini-batches of positive-negative bag pairs. Finally, a novel P-F sampling function is developed that combines a probability vector and predicted instance scores, obtained by optimizing the robust bag likelihood. By leveraging the key MIL assumption, the sampling function can explore the most challenging bags and effectively detect their positive instances for annotation, which significantly improves the instance-level prediction. Experiments conducted over multiple real-world datasets clearly demonstrate the state-of-the-art instance-level prediction achieved by the proposed model.
Bayesian Nonparametric Submodular Video Partition for Robust Anomaly Detection
Mar 24, 2022
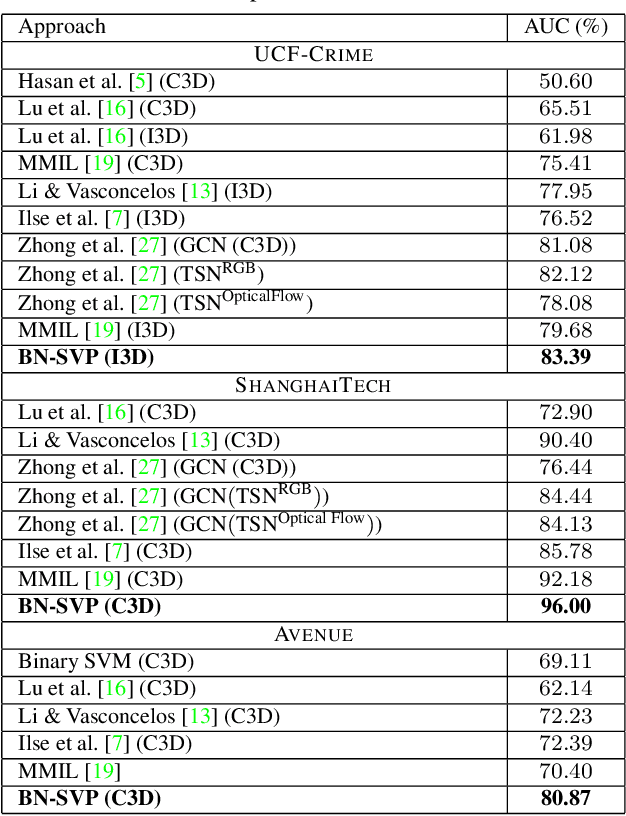
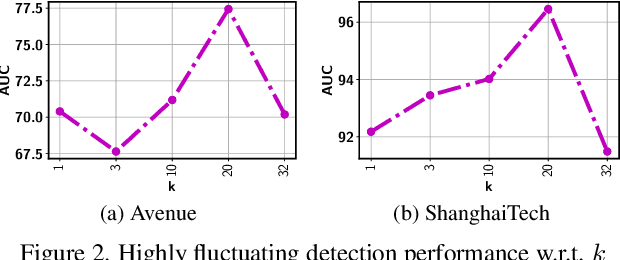
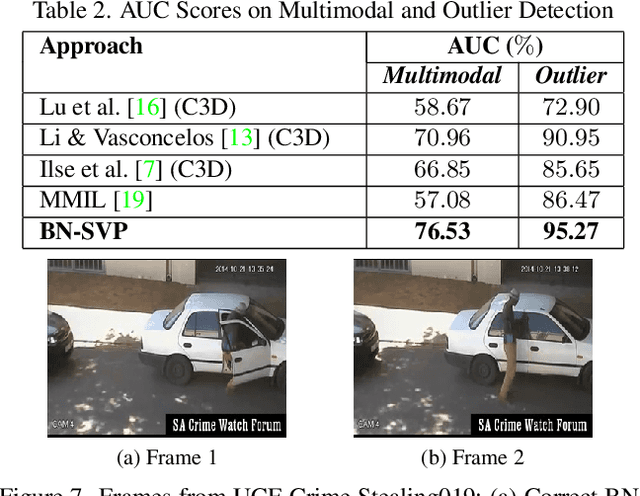
Abstract:Multiple-instance learning (MIL) provides an effective way to tackle the video anomaly detection problem by modeling it as a weakly supervised problem as the labels are usually only available at the video level while missing for frames due to expensive labeling cost. We propose to conduct novel Bayesian non-parametric submodular video partition (BN-SVP) to significantly improve MIL model training that can offer a highly reliable solution for robust anomaly detection in practical settings that include outlier segments or multiple types of abnormal events. BN-SVP essentially performs dynamic non-parametric hierarchical clustering with an enhanced self-transition that groups segments in a video into temporally consistent and semantically coherent hidden states that can be naturally interpreted as scenes. Each segment is assumed to be generated through a non-parametric mixture process that allows variations of segments within the same scenes to accommodate the dynamic and noisy nature of many real-world surveillance videos. The scene and mixture component assignment of BN-SVP also induces a pairwise similarity among segments, resulting in non-parametric construction of a submodular set function. Integrating this function with an MIL loss effectively exposes the model to a diverse set of potentially positive instances to improve its training. A greedy algorithm is developed to optimize the submodular function and support efficient model training. Our theoretical analysis ensures a strong performance guarantee of the proposed algorithm. The effectiveness of the proposed approach is demonstrated over multiple real-world anomaly video datasets with robust detection performance.
Deep Reinforced Attention Regression for Partial Sketch Based Image Retrieval
Nov 21, 2021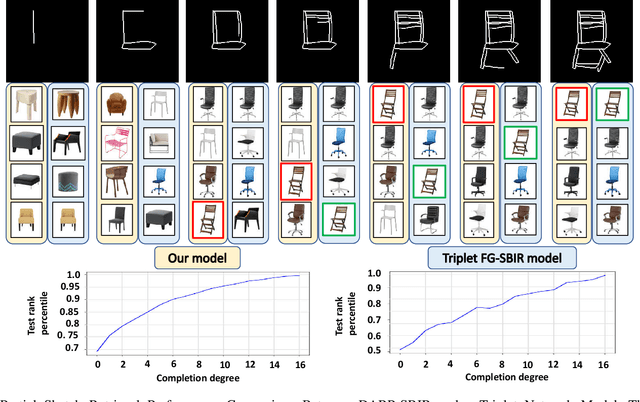
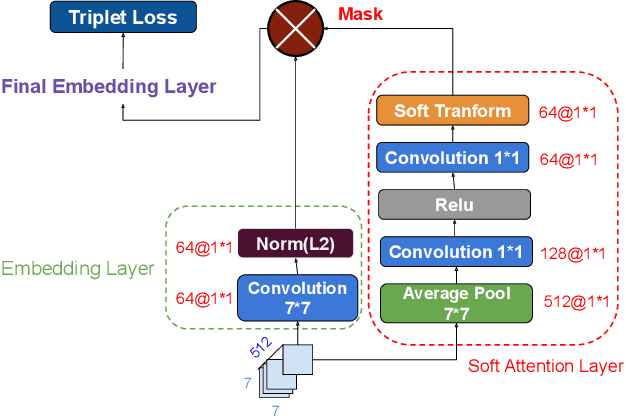
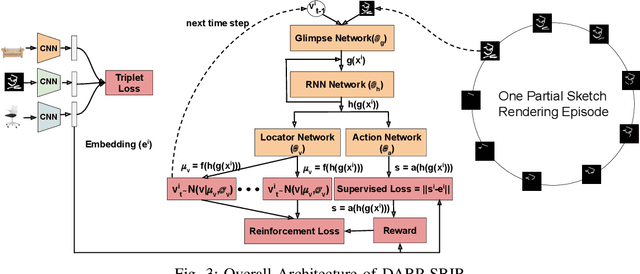
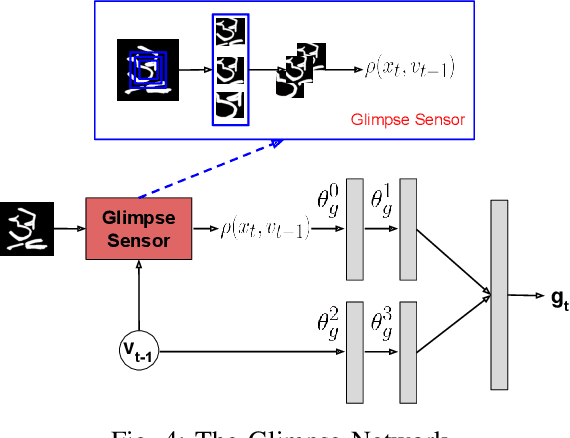
Abstract:Fine-Grained Sketch-Based Image Retrieval (FG-SBIR) aims at finding a specific image from a large gallery given a query sketch. Despite the widespread applicability of FG-SBIR in many critical domains (e.g., crime activity tracking), existing approaches still suffer from a low accuracy while being sensitive to external noises such as unnecessary strokes in the sketch. The retrieval performance will further deteriorate under a more practical on-the-fly setting, where only a partially complete sketch with only a few (noisy) strokes are available to retrieve corresponding images. We propose a novel framework that leverages a uniquely designed deep reinforcement learning model that performs a dual-level exploration to deal with partial sketch training and attention region selection. By enforcing the model's attention on the important regions of the original sketches, it remains robust to unnecessary stroke noises and improve the retrieval accuracy by a large margin. To sufficiently explore partial sketches and locate the important regions to attend, the model performs bootstrapped policy gradient for global exploration while adjusting a standard deviation term that governs a locator network for local exploration. The training process is guided by a hybrid loss that integrates a reinforcement loss and a supervised loss. A dynamic ranking reward is developed to fit the on-the-fly image retrieval process using partial sketches. The extensive experimentation performed on three public datasets shows that our proposed approach achieves the state-of-the-art performance on partial sketch based image retrieval.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge