Hichem Besbes
A Machine Learning Smartphone-based Sensing for Driver Behavior Classification
Feb 01, 2022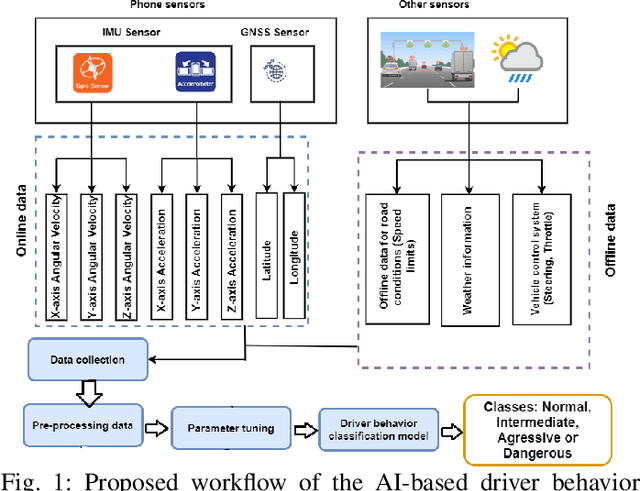

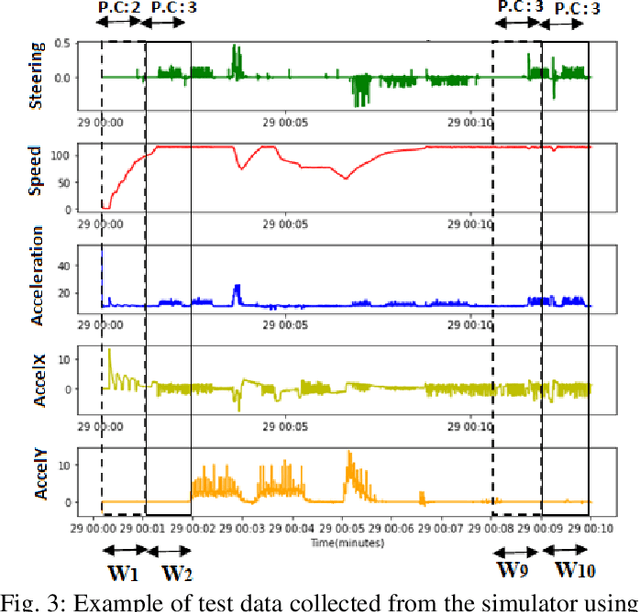
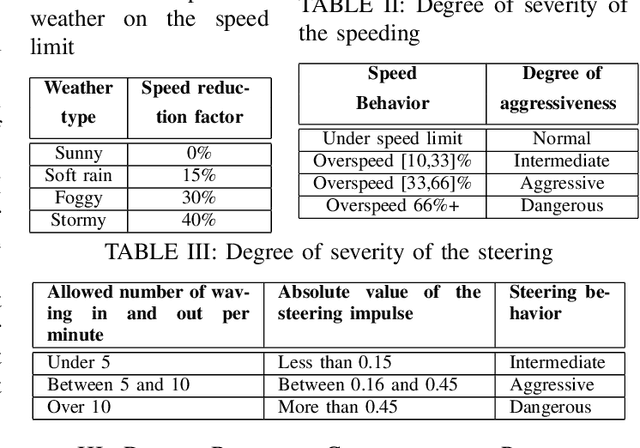
Abstract:Driver behavior profiling is one of the main issues in the insurance industries and fleet management, thus being able to classify the driver behavior with low-cost mobile applications remains in the spotlight of autonomous driving. However, using mobile sensors may face the challenge of security, privacy, and trust issues. To overcome those challenges, we propose to collect data sensors using Carla Simulator available in smartphones (Accelerometer, Gyroscope, GPS) in order to classify the driver behavior using speed, acceleration, direction, the 3-axis rotation angles (Yaw, Pitch, Roll) taking into account the speed limit of the current road and weather conditions to better identify the risky behavior. Secondly, after fusing inter-axial data from multiple sensors into a single file, we explore different machine learning algorithms for time series classification to evaluate which algorithm results in the highest performance.
Scalable and Secure Architecture for Distributed IoT Systems
Apr 20, 2020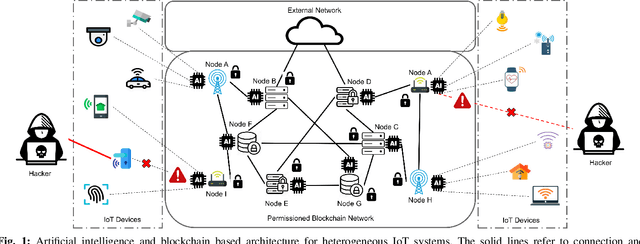
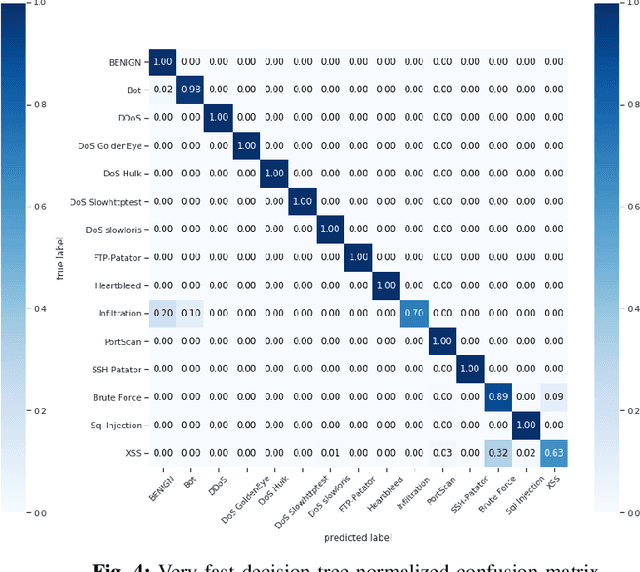

Abstract:Internet-of-things (IoT) is perpetually revolutionizing our daily life and rapidly transforming physical objects into an ubiquitous connected ecosystem. Due to their massive deployment and moderate security levels, those devices face a lot of security, management, and control challenges. Their classical centralized architecture is still cloaking vulnerabilities and anomalies that can be exploited by hackers for spying, eavesdropping, and taking control of the network. In this paper, we propose to improve the IoT architecture with additional security features using Artificial Intelligence (AI) and blockchain technology. We propose a novel architecture based on permissioned blockchain technology in order to build a scalable and decentralized end-to-end secure IoT system. Furthermore, we enhance the IoT system security with an AI-component at the gateway level to detect and classify suspected activities, malware, and cyber-attacks using machine learning techniques. Simulations and practical implementation show that the proposed architecture delivers high performance against cyber-attacks.
Autonomous UAV Navigation: A DDPG-based Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach
Mar 21, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, we propose an autonomous UAV path planning framework using deep reinforcement learning approach. The objective is to employ a self-trained UAV as a flying mobile unit to reach spatially distributed moving or static targets in a given three dimensional urban area. In this approach, a Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) with continuous action space is designed to train the UAV to navigate through or over the obstacles to reach its assigned target. A customized reward function is developed to minimize the distance separating the UAV and its destination while penalizing collisions. Numerical simulations investigate the behavior of the UAV in learning the environment and autonomously determining trajectories for different selected scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge