Hendrik Pretorius
Learning to estimate a surrogate respiratory signal from cardiac motion by signal-to-signal translation
Jul 20, 2022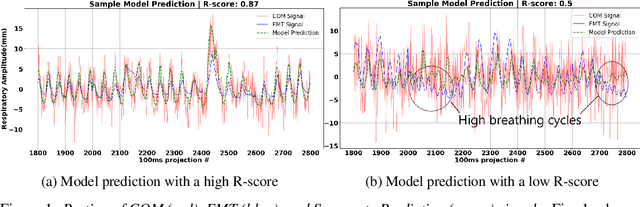
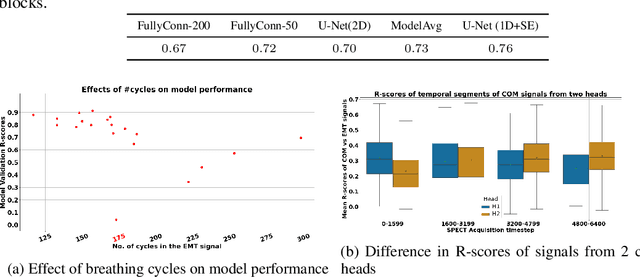
Abstract:In this work, we develop a neural network-based method to convert a noisy motion signal generated from segmenting rebinned list-mode cardiac SPECT images, to that of a high-quality surrogate signal, such as those seen from external motion tracking systems (EMTs). This synthetic surrogate will be used as input to our pre-existing motion correction technique developed for EMT surrogate signals. In our method, we test two families of neural networks to translate noisy internal motion to external surrogate: 1) fully connected networks and 2) convolutional neural networks. Our dataset consists of cardiac perfusion SPECT acquisitions for which cardiac motion was estimated (input: center-of-count-mass - COM signals) in conjunction with a respiratory surrogate motion signal acquired using a commercial Vicon Motion Tracking System (GT: EMT signals). We obtained an average R-score of 0.76 between the predicted surrogate and the EMT signal. Our goal is to lay a foundation to guide the optimization of neural networks for respiratory motion correction from SPECT without the need for an EMT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge