Hendrik Šuvalov
MedMine: Examining Pre-trained Language Models on Medication Mining
Aug 08, 2023
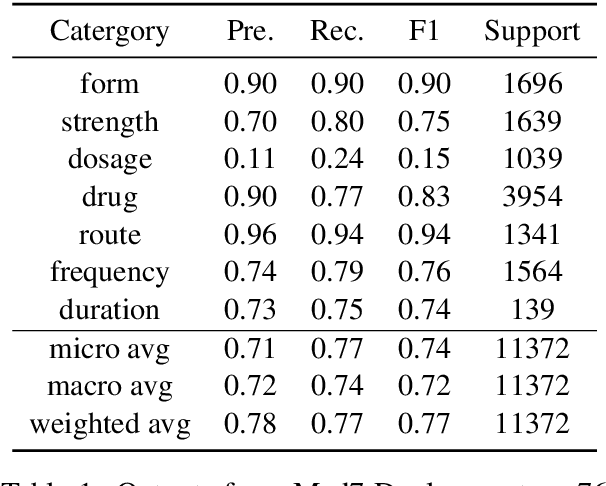
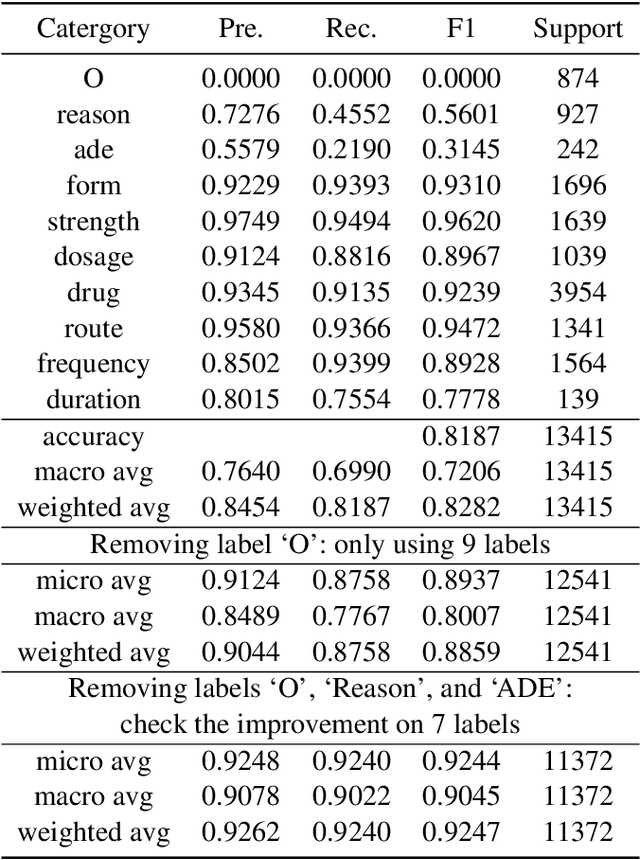
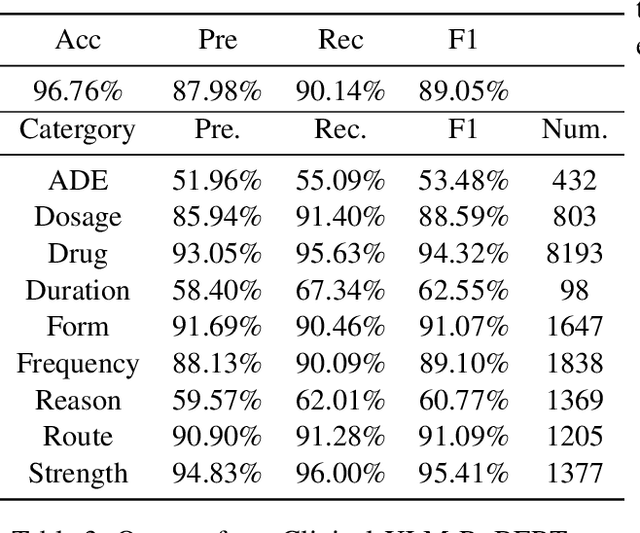
Abstract:Automatic medication mining from clinical and biomedical text has become a popular topic due to its real impact on healthcare applications and the recent development of powerful language models (LMs). However, fully-automatic extraction models still face obstacles to be overcome such that they can be deployed directly into clinical practice for better impacts. Such obstacles include their imbalanced performances on different entity types and clinical events. In this work, we examine current state-of-the-art pre-trained language models (PLMs) on such tasks, via fine-tuning including the monolingual model Med7 and multilingual large language model (LLM) XLM-RoBERTa. We compare their advantages and drawbacks using historical medication mining shared task data sets from n2c2-2018 challenges. We report the findings we get from these fine-tuning experiments such that they can facilitate future research on addressing them, for instance, how to combine their outputs, merge such models, or improve their overall accuracy by ensemble learning and data augmentation. MedMine is part of the M3 Initiative \url{https://github.com/HECTA-UoM/M3}
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge