Heather Knight
Uncovering implementable dormant pruning decisions from three different stakeholder perspectives
May 07, 2024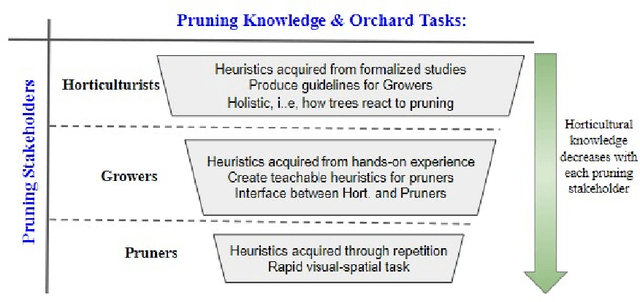
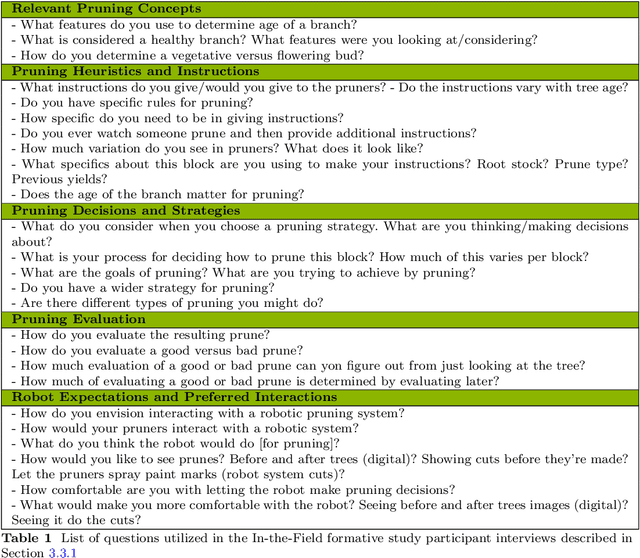
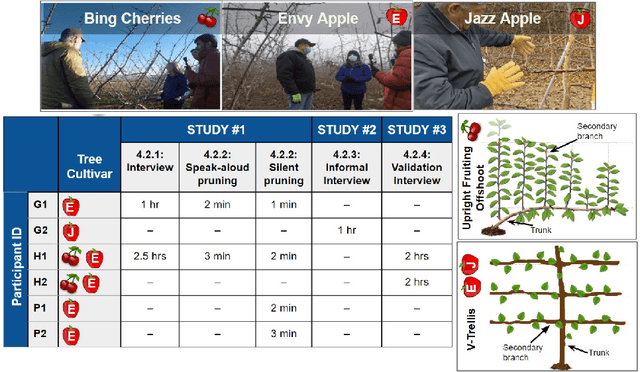

Abstract:Dormant pruning, or the removal of unproductive portions of a tree while a tree is not actively growing, is an important orchard task to help maintain yield, requiring years to build expertise. Because of long training periods and an increasing labor shortage in agricultural jobs, pruning could benefit from robotic automation. However, to program robots to prune branches, we first need to understand how pruning decisions are made, and what variables in the environment (e.g., branch size and thickness) we need to capture. Working directly with three pruning stakeholders -- horticulturists, growers, and pruners -- we find that each group of human experts approaches pruning decision-making differently. To capture this knowledge, we present three studies and two extracted pruning protocols from field work conducted in Prosser, Washington in January 2022 and 2023. We interviewed six stakeholders (two in each group) and observed pruning across three cultivars -- Bing Cherries, Envy Apples, and Jazz Apples -- and two tree architectures -- Upright Fruiting Offshoot and V-Trellis. Leveraging participant interviews and video data, this analysis uses grounded coding to extract pruning terminology, discover horticultural contexts that influence pruning decisions, and find implementable pruning heuristics for autonomous systems. The results include a validated terminology set, which we offer for use by both pruning stakeholders and roboticists, to communicate general pruning concepts and heuristics. The results also highlight seven pruning heuristics utilizing this terminology set that would be relevant for use by future autonomous robot pruning systems, and characterize three discovered horticultural contexts (i.e., environmental management, crop-load management, and replacement wood) across all three cultivars.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge