Hasan Pourmahmood-Aghababa
For Kernel Range Spaces a Constant Number of Queries Are Sufficient
Jun 28, 2023

Abstract:We introduce the notion of an $\varepsilon$-cover for a kernel range space. A kernel range space concerns a set of points $X \subset \mathbb{R}^d$ and the space of all queries by a fixed kernel (e.g., a Gaussian kernel $K(p,\cdot) = \exp(-\|p-\cdot\|^2)$). For a point set $X$ of size $n$, a query returns a vector of values $R_p \in \mathbb{R}^n$, where the $i$th coordinate $(R_p)_i = K(p,x_i)$ for $x_i \in X$. An $\varepsilon$-cover is a subset of points $Q \subset \mathbb{R}^d$ so for any $p \in \mathbb{R}^d$ that $\frac{1}{n} \|R_p - R_q\|_1\leq \varepsilon$ for some $q \in Q$. This is a smooth analog of Haussler's notion of $\varepsilon$-covers for combinatorial range spaces (e.g., defined by subsets of points within a ball query) where the resulting vectors $R_p$ are in $\{0,1\}^n$ instead of $[0,1]^n$. The kernel versions of these range spaces show up in data analysis tasks where the coordinates may be uncertain or imprecise, and hence one wishes to add some flexibility in the notion of inside and outside of a query range. Our main result is that, unlike combinatorial range spaces, the size of kernel $\varepsilon$-covers is independent of the input size $n$ and dimension $d$. We obtain a bound of $(1/\varepsilon)^{\tilde O(1/\varepsilon^2)}$, where $\tilde{O}(f(1/\varepsilon))$ hides log factors in $(1/\varepsilon)$ that can depend on the kernel. This implies that by relaxing the notion of boundaries in range queries, eventually the curse of dimensionality disappears, and may help explain the success of machine learning in very high-dimensions. We also complement this result with a lower bound of almost $(1/\varepsilon)^{\Omega(1/\varepsilon)}$, showing the exponential dependence on $1/\varepsilon$ is necessary.
Classifying Spatial Trajectories
Sep 03, 2022
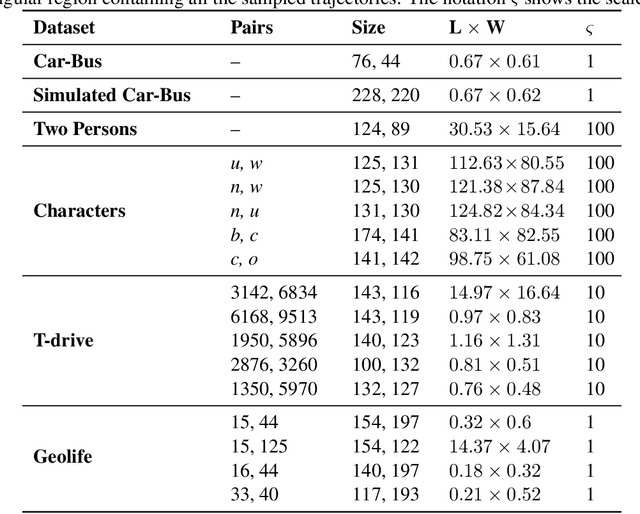
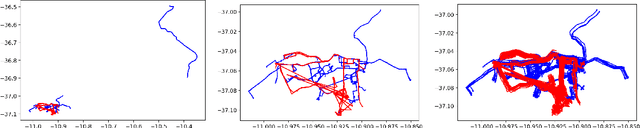
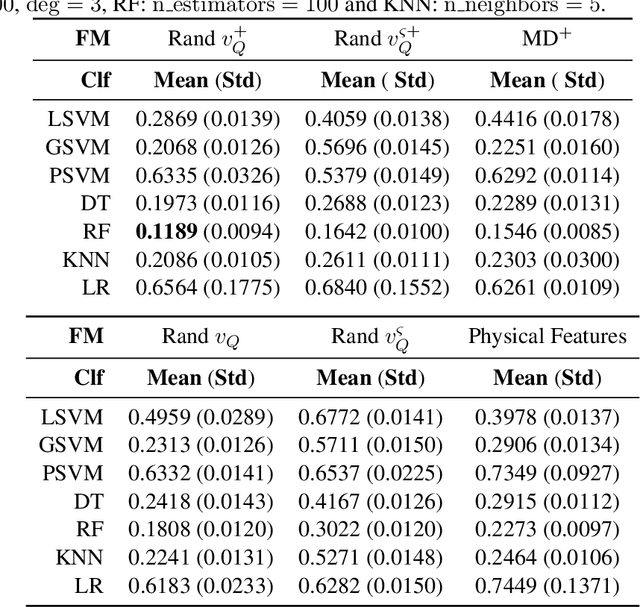
Abstract:We provide the first comprehensive study on how to classify trajectories using only their spatial representations, measured on 5 real-world data sets. Our comparison considers 20 distinct classifiers arising either as a KNN classifier of a popular distance, or as a more general type of classifier using a vectorized representation of each trajectory. We additionally develop new methods for how to vectorize trajectories via a data-driven method to select the associated landmarks, and these methods prove among the most effective in our study. These vectorized approaches are simple and efficient to use, and also provide state-of-the-art accuracy on an established transportation mode classification task. In all, this study sets the standard for how to classify trajectories, including introducing new simple techniques to achieve these results, and sets a rigorous standard for the inevitable future study on this topic.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge