Haruya Ishikawa
BoundMatch: Boundary detection applied to semi-supervised segmentation for urban-driving scenes
Mar 30, 2025Abstract:Semi-supervised semantic segmentation (SS-SS) aims to mitigate the heavy annotation burden of dense pixel labeling by leveraging abundant unlabeled images alongside a small labeled set. While current teacher-student consistency regularization methods achieve strong results, they often overlook a critical challenge: the precise delineation of object boundaries. In this paper, we propose BoundMatch, a novel multi-task SS-SS framework that explicitly integrates semantic boundary detection into the consistency regularization pipeline. Our core mechanism, Boundary Consistency Regularized Multi-Task Learning (BCRM), enforces prediction agreement between teacher and student models on both segmentation masks and detailed semantic boundaries. To further enhance performance and sharpen contours, BoundMatch incorporates two lightweight fusion modules: Boundary-Semantic Fusion (BSF) injects learned boundary cues into the segmentation decoder, while Spatial Gradient Fusion (SGF) refines boundary predictions using mask gradients, leading to higher-quality boundary pseudo-labels. This framework is built upon SAMTH, a strong teacher-student baseline featuring a Harmonious Batch Normalization (HBN) update strategy for improved stability. Extensive experiments on diverse datasets including Cityscapes, BDD100K, SYNTHIA, ADE20K, and Pascal VOC show that BoundMatch achieves competitive performance against state-of-the-art methods while significantly improving boundary-specific evaluation metrics. We also demonstrate its effectiveness in realistic large-scale unlabeled data scenarios and on lightweight architectures designed for mobile deployment.
PCT: Perspective Cue Training Framework for Multi-Camera BEV Segmentation
Mar 19, 2024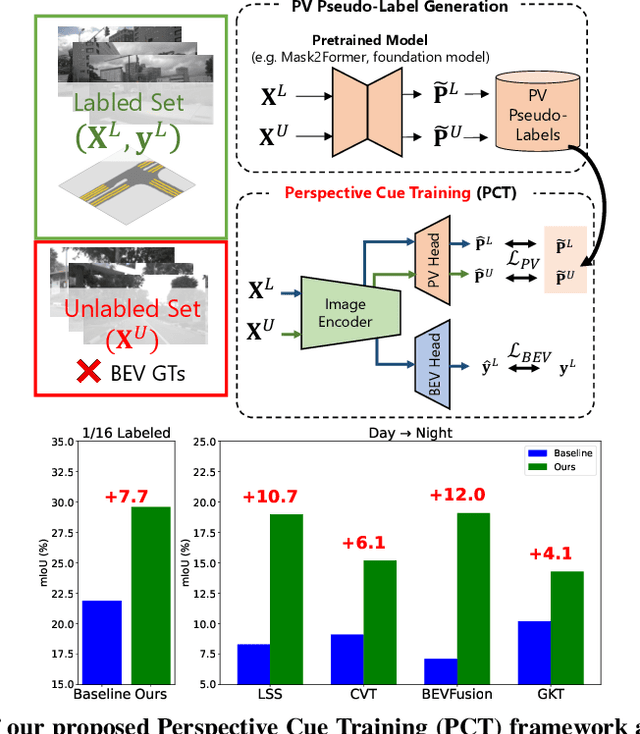
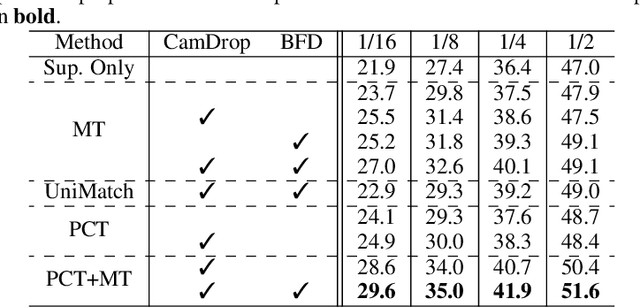
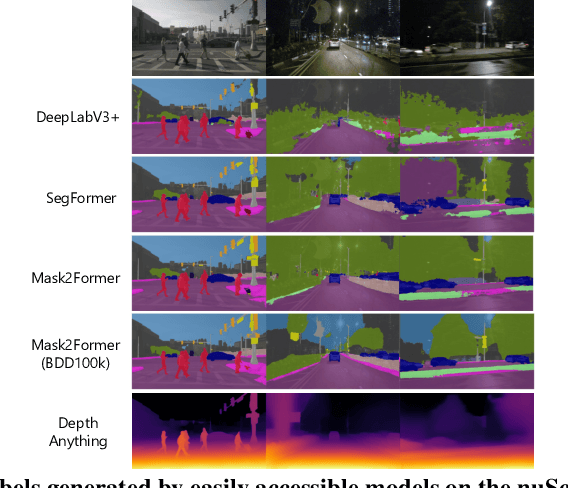
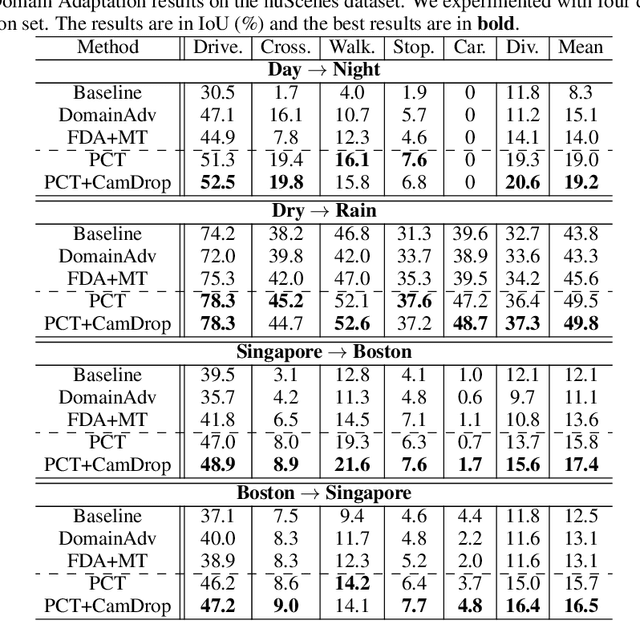
Abstract:Generating annotations for bird's-eye-view (BEV) segmentation presents significant challenges due to the scenes' complexity and the high manual annotation cost. In this work, we address these challenges by leveraging the abundance of unlabeled data available. We propose the Perspective Cue Training (PCT) framework, a novel training framework that utilizes pseudo-labels generated from unlabeled perspective images using publicly available semantic segmentation models trained on large street-view datasets. PCT applies a perspective view task head to the image encoder shared with the BEV segmentation head, effectively utilizing the unlabeled data to be trained with the generated pseudo-labels. Since image encoders are present in nearly all camera-based BEV segmentation architectures, PCT is flexible and applicable to various existing BEV architectures. PCT can be applied to various settings where unlabeled data is available. In this paper, we applied PCT for semi-supervised learning (SSL) and unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA). Additionally, we introduce strong input perturbation through Camera Dropout (CamDrop) and feature perturbation via BEV Feature Dropout (BFD), which are crucial for enhancing SSL capabilities using our teacher-student framework. Our comprehensive approach is simple and flexible but yields significant improvements over various baselines for SSL and UDA, achieving competitive performances even against the current state-of-the-art.
Boosting Semantic Segmentation with Semantic Boundaries
Apr 19, 2023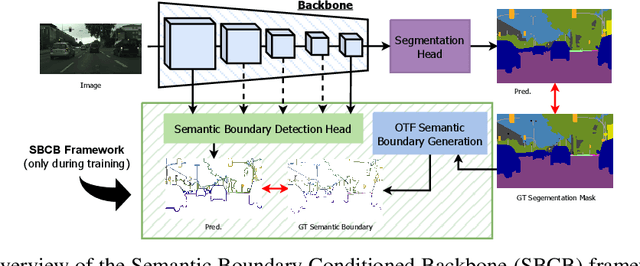
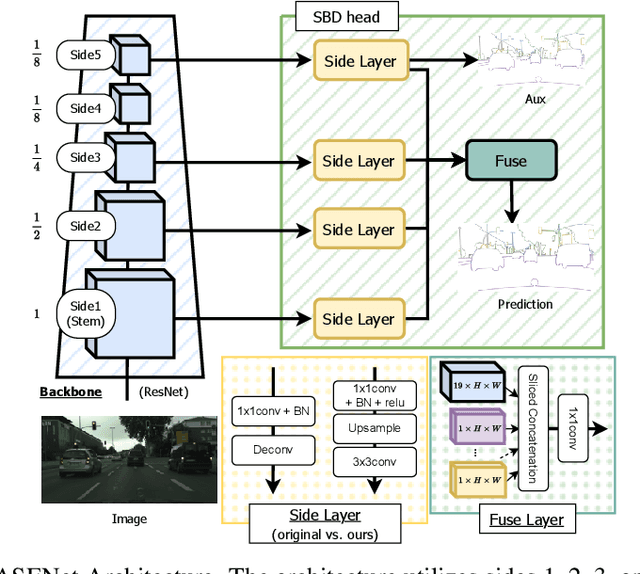
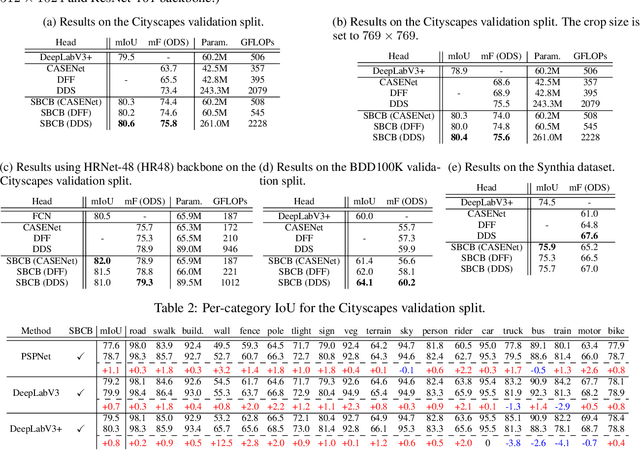
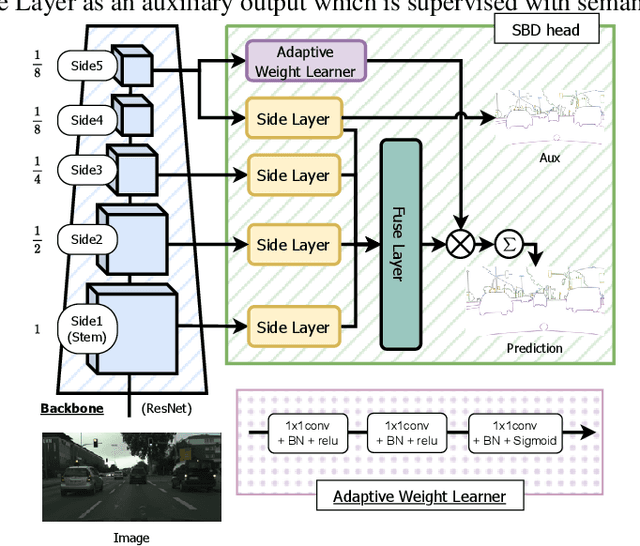
Abstract:In this paper, we present the Semantic Boundary Conditioned Backbone (SBCB) framework, a simple yet effective training framework that is model-agnostic and boosts segmentation performance, especially around the boundaries. Motivated by the recent development in improving semantic segmentation by incorporating boundaries as auxiliary tasks, we propose a multi-task framework that uses semantic boundary detection (SBD) as an auxiliary task. The SBCB framework utilizes the nature of the SBD task, which is complementary to semantic segmentation, to improve the backbone of the segmentation head. We apply an SBD head that exploits the multi-scale features from the backbone, where the model learns low-level features in the earlier stages, and high-level semantic understanding in the later stages. This head perfectly complements the common semantic segmentation architectures where the features from the later stages are used for classification. We can improve semantic segmentation models without additional parameters during inference by only conditioning the backbone. Through extensive evaluations, we show the effectiveness of the SBCB framework by improving various popular segmentation heads and backbones by 0.5% ~ 3.0% IoU on the Cityscapes dataset and gains 1.6% ~ 4.1% in boundary Fscores. We also apply this framework on customized backbones and the emerging vision transformer models and show the effectiveness of the SBCB framework.
FindView: Precise Target View Localization Task for Look Around Agents
Mar 16, 2023Abstract:With the increase in demands for service robots and automated inspection, agents need to localize in its surrounding environment to achieve more natural communication with humans by shared contexts. In this work, we propose a novel but straightforward task of precise target view localization for look around agents called the FindView task. This task imitates the movements of PTZ cameras or user interfaces for 360 degree mediums, where the observer must "look around" to find a view that exactly matches the target. To solve this task, we introduce a rule-based agent that heuristically finds the optimal view and a policy learning agent that employs reinforcement learning to learn by interacting with the 360 degree scene. Through extensive evaluations and benchmarks, we conclude that learned methods have many advantages, in particular precise localization that is robust to corruption and can be easily deployed in novel scenes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge