Harshit Agrawal
Ultrafast Deep Learning-Based Scatter Estimation in Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Purpose: Scatter artifacts drastically degrade the image quality of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans. Although deep learning-based methods show promise in estimating scatter from CBCT measurements, their deployment in mobile CBCT systems or edge devices is still limited due to the large memory footprint of the networks. This study addresses the issue by applying networks at varying resolutions and suggesting an optimal one, based on speed and accuracy. Methods: First, the reconstruction error in down-up sampling of CBCT scatter signal was examined at six resolutions by comparing four interpolation methods. Next, a recent state-of-the-art method was trained across five image resolutions and evaluated for the reductions in floating-point operations (FLOPs), inference times, and GPU memory requirements. Results: Reducing the input size and network parameters achieved a 78-fold reduction in FLOPs compared to the baseline method, while maintaining comarable performance in terms of mean-absolute-percentage-error (MAPE) and mean-square-error (MSE). Specifically, the MAPE decreased to 3.85% compared to 4.42%, and the MSE decreased to 1.34 \times 10^{-2} compared to 2.01 \times 10^{-2}. Inference time and GPU memory usage were reduced by factors of 16 and 12, respectively. Further experiments comparing scatter-corrected reconstructions on a large, simulated dataset and real CBCT scans from water and Sedentex CT phantoms clearly demonstrated the robustness of our method. Conclusion: This study highlights the underappreciated role of downsampling in deep learning-based scatter estimation. The substantial reduction in FLOPs and GPU memory requirements achieved by our method enables scatter correction in resource-constrained environments, such as mobile CBCT and edge devices.
Utilizing U-Net Architectures with Auxiliary Information for Scatter Correction in CBCT Across Different Field-of-View Settings
Feb 27, 2024Abstract:Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) has become a vital imaging technique in various medical fields but scatter artifacts are a major limitation in CBCT scanning. This challenge is exacerbated by the use of large flat panel 2D detectors. The scatter-to-primary ratio increases significantly with the increase in the size of FOV being scanned. Several deep learning methods, particularly U-Net architectures, have shown promising capabilities in estimating the scatter directly from the CBCT projections. However, the influence of varying FOV sizes on these deep learning models remains unexplored. Having a single neural network for the scatter estimation of varying FOV projections can be of significant importance towards real clinical applications. This study aims to train and evaluate the performance of a U-Net network on a simulated dataset with varying FOV sizes. We further propose a new method (Aux-Net) by providing auxiliary information, such as FOV size, to the U-Net encoder. We validate our method on 30 different FOV sizes and compare it with the U-Net. Our study demonstrates that providing auxiliary information to the network enhances the generalization capability of the U-Net. Our findings suggest that this novel approach outperforms the baseline U-Net, offering a significant step towards practical application in real clinical settings where CBCT systems are employed to scan a wide range of FOVs.
Metal artifact correction in cone beam computed tomography using synthetic X-ray data
Aug 17, 2022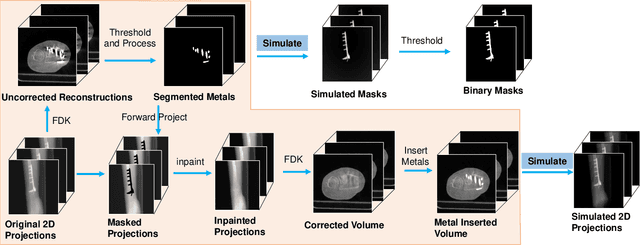
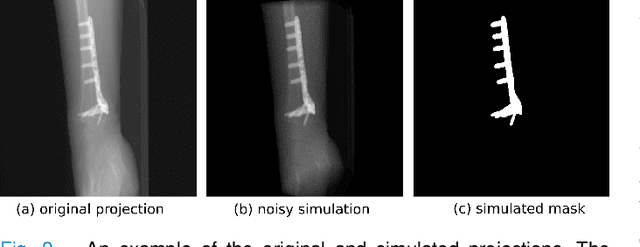
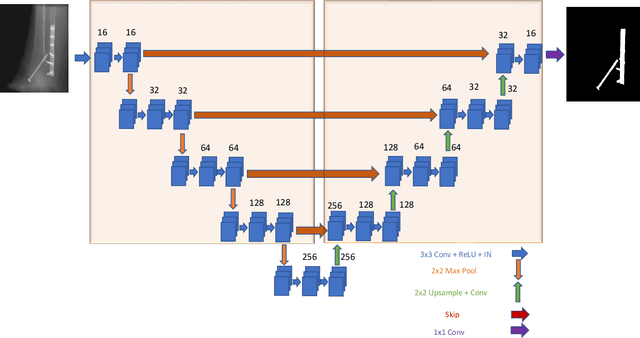
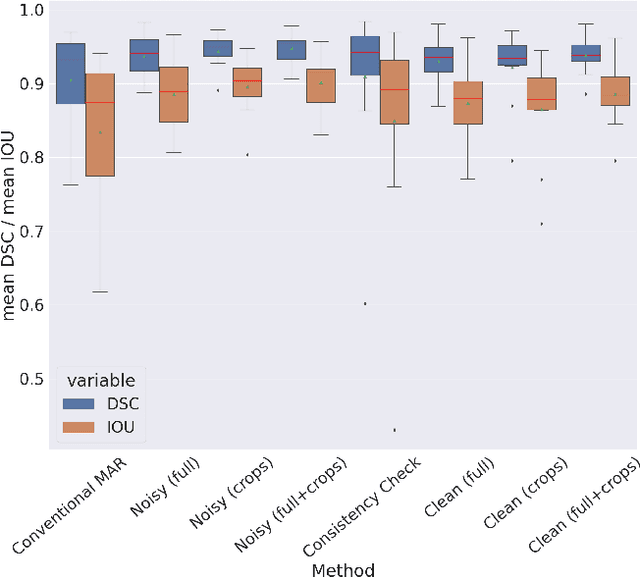
Abstract:Metal artifact correction is a challenging problem in cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scanning. Metal implants inserted into the anatomy cause severe artifacts in reconstructed images. Widely used inpainting-based metal artifact reduction (MAR) methods require segmentation of metal traces in the projections as a first step which is a challenging task. One approach is to use a deep learning method to segment metals in the projections. However, the success of deep learning methods is limited by the availability of realistic training data. It is challenging and time consuming to get reliable ground truth annotations due to unclear implant boundary and large number of projections. We propose to use X-ray simulations to generate synthetic metal segmentation training dataset from clinical CBCT scans. We compare the effect of simulations with different number of photons and also compare several training strategies to augment the available data. We compare our model's performance on real clinical scans with conventional threshold-based MAR and a recent deep learning method. We show that simulations with relatively small number of photons are suitable for the metal segmentation task and that training the deep learning model with full size and cropped projections together improves the robustness of the model. We show substantial improvement in the image quality affected by severe motion, voxel size under-sampling, and out-of-FOV metals. Our method can be easily implemented into the existing projection-based MAR pipeline to get improved image quality. This method can provide a novel paradigm to accurately segment metals in CBCT projections.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge