Hans Fangohr
Machine learning-based spin structure detection
Mar 24, 2023



Abstract:One of the most important magnetic spin structure is the topologically stabilised skyrmion quasi-particle. Its interesting physical properties make them candidates for memory and efficient neuromorphic computation schemes. For the device operation, detection of the position, shape, and size of skyrmions is required and magnetic imaging is typically employed. A frequently used technique is magneto-optical Kerr microscopy where depending on the samples material composition, temperature, material growing procedures, etc., the measurements suffer from noise, low-contrast, intensity gradients, or other optical artifacts. Conventional image analysis packages require manual treatment, and a more automatic solution is required. We report a convolutional neural network specifically designed for segmentation problems to detect the position and shape of skyrmions in our measurements. The network is tuned using selected techniques to optimize predictions and in particular the number of detected classes is found to govern the performance. The results of this study shows that a well-trained network is a viable method of automating data pre-processing in magnetic microscopy. The approach is easily extendable to other spin structures and other magnetic imaging methods.
Unsupervised learning approaches to characterize heterogeneous samples using X-ray single particle imaging
Sep 13, 2021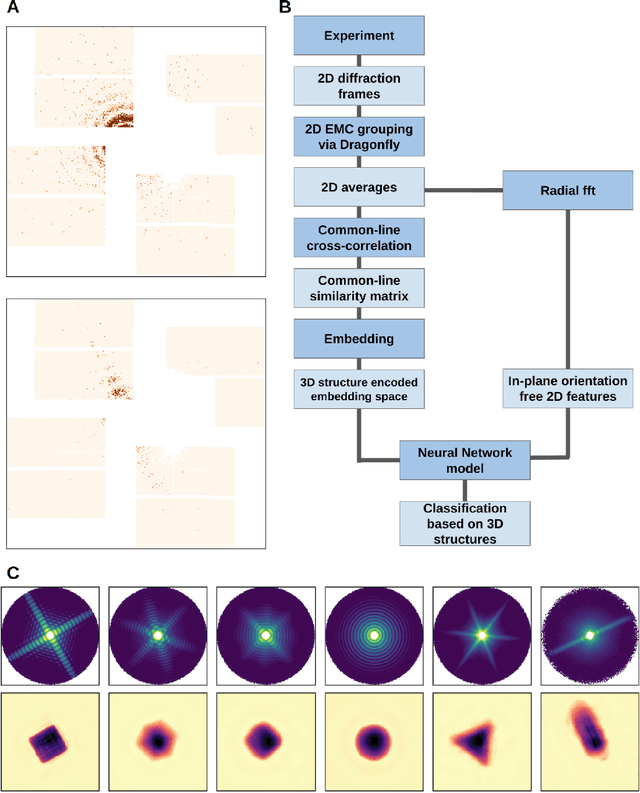
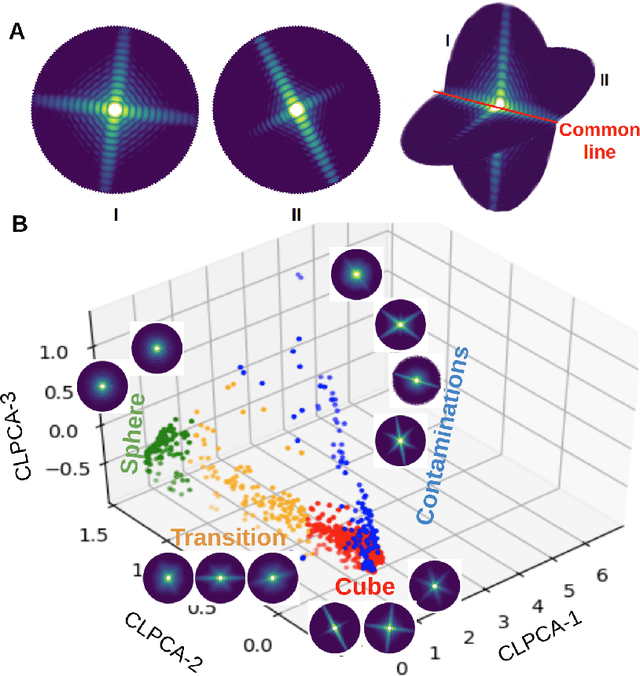
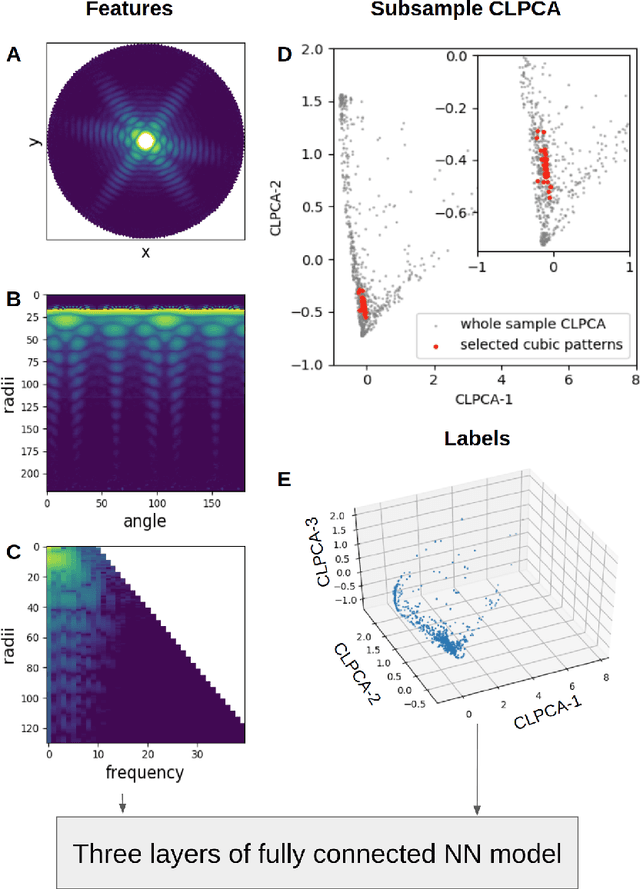
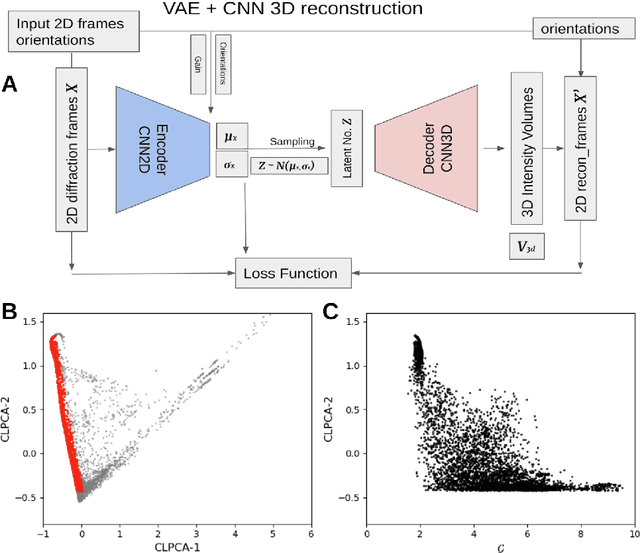
Abstract:One of the outstanding analytical problems in X-ray single particle imaging (SPI) is the classification of structural heterogeneity, which is especially difficult given the low signal-to-noise ratios of individual patterns and that even identical objects can yield patterns that vary greatly when orientation is taken into consideration. We propose two methods which explicitly account for this orientation-induced variation and can robustly determine the structural landscape of a sample ensemble. The first, termed common-line principal component analysis (PCA) provides a rough classification which is essentially parameter-free and can be run automatically on any SPI dataset. The second method, utilizing variation auto-encoders (VAEs) can generate 3D structures of the objects at any point in the structural landscape. We implement both these methods in combination with the noise-tolerant expand-maximize-compress (EMC) algorithm and demonstrate its utility by applying it to an experimental dataset from gold nanoparticles with only a few thousand photons per pattern and recover both discrete structural classes as well as continuous deformations. These developments diverge from previous approaches of extracting reproducible subsets of patterns from a dataset and open up the possibility to move beyond studying homogeneous sample sets and study open questions on topics such as nanocrystal growth and dynamics as well as phase transitions which have not been externally triggered.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge