Hanan Hamza
Malayalam Sign Language Identification using Finetuned YOLOv8 and Computer Vision Techniques
May 08, 2024
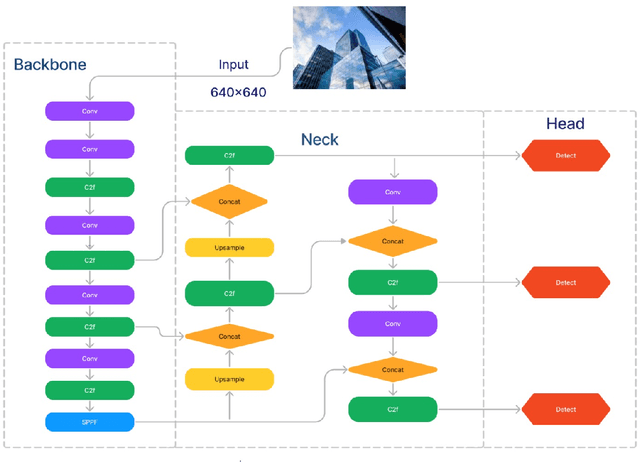


Abstract:Technological advancements and innovations are advancing our daily life in all the ways possible but there is a larger section of society who are deprived of accessing the benefits due to their physical inabilities. To reap the real benefits and make it accessible to society, these talented and gifted people should also use such innovations without any hurdles. Many applications developed these days address these challenges, but localized communities and other constrained linguistic groups may find it difficult to use them. Malayalam, a Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala is one of the twenty-two scheduled languages in India. Recent years have witnessed a surge in the development of systems and tools in Malayalam, addressing the needs of Kerala, but many of them are not empathetically designed to cater to the needs of hearing-impaired people. One of the major challenges is the limited or no availability of sign language data for the Malayalam language and sufficient efforts are not made in this direction. In this connection, this paper proposes an approach for sign language identification for the Malayalam language using advanced deep learning and computer vision techniques. We start by developing a labeled dataset for Malayalam letters and for the identification we use advanced deep learning techniques such as YOLOv8 and computer vision. Experimental results show that the identification accuracy is comparable to other sign language identification systems and other researchers in sign language identification can use the model as a baseline to develop advanced models.
EmoDiarize: Speaker Diarization and Emotion Identification from Speech Signals using Convolutional Neural Networks
Oct 19, 2023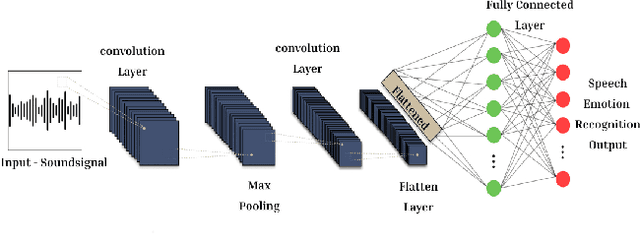
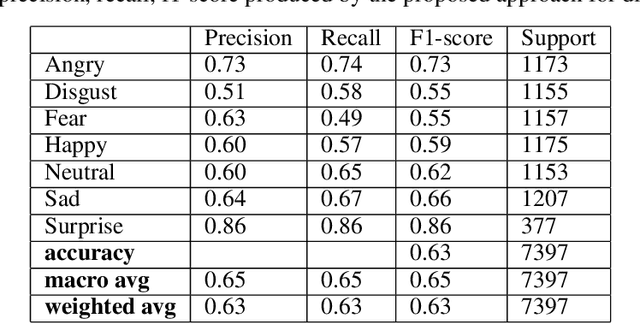
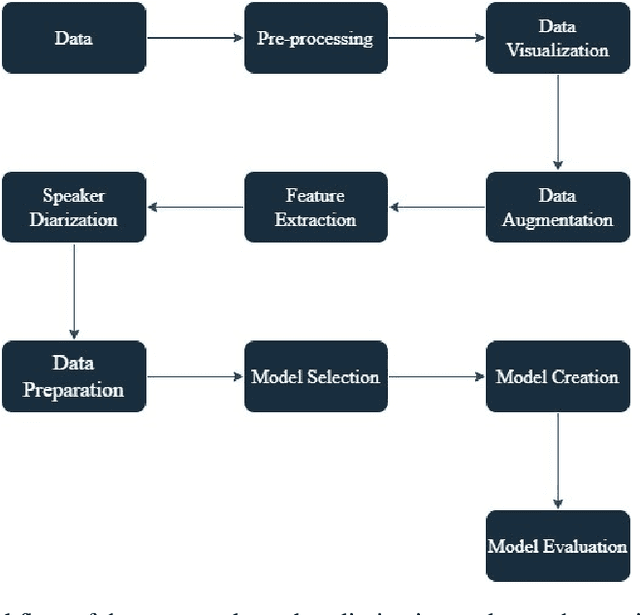
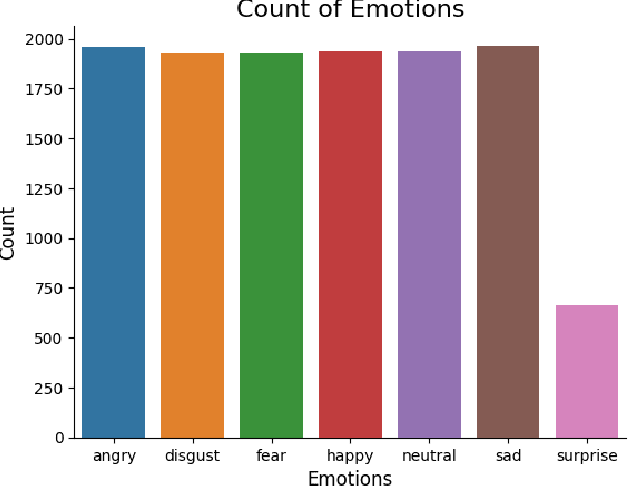
Abstract:In the era of advanced artificial intelligence and human-computer interaction, identifying emotions in spoken language is paramount. This research explores the integration of deep learning techniques in speech emotion recognition, offering a comprehensive solution to the challenges associated with speaker diarization and emotion identification. It introduces a framework that combines a pre-existing speaker diarization pipeline and an emotion identification model built on a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to achieve higher precision. The proposed model was trained on data from five speech emotion datasets, namely, RAVDESS, CREMA-D, SAVEE, TESS, and Movie Clips, out of which the latter is a speech emotion dataset created specifically for this research. The features extracted from each sample include Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC), Zero Crossing Rate (ZCR), Root Mean Square (RMS), and various data augmentation algorithms like pitch, noise, stretch, and shift. This feature extraction approach aims to enhance prediction accuracy while reducing computational complexity. The proposed model yields an unweighted accuracy of 63%, demonstrating remarkable efficiency in accurately identifying emotional states within speech signals.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge