Hamish Fraser
Bayesian Counterfactual Prediction Models for HIV Care Retention with Incomplete Outcome and Covariate Information
Oct 29, 2024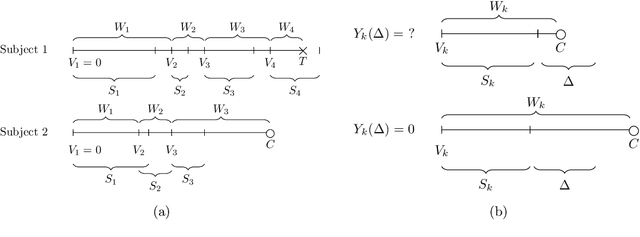
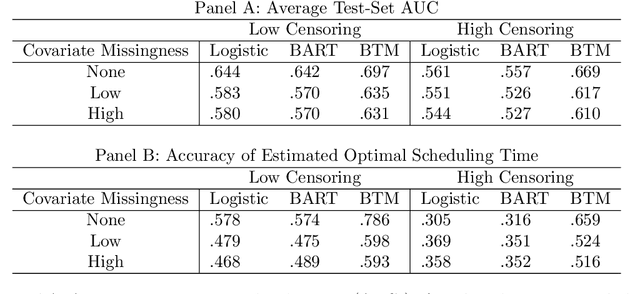
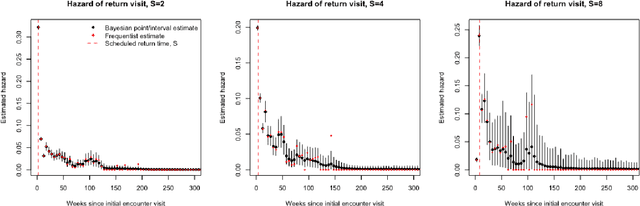
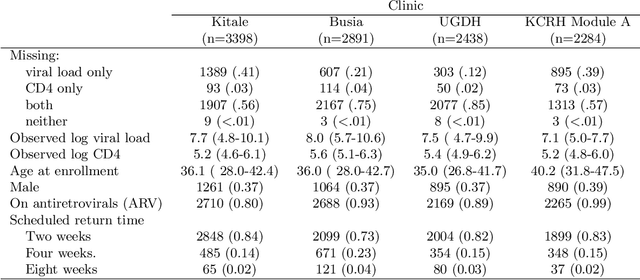
Abstract:Like many chronic diseases, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is managed over time at regular clinic visits. At each visit, patient features are assessed, treatments are prescribed, and a subsequent visit is scheduled. There is a need for data-driven methods for both predicting retention and recommending scheduling decisions that optimize retention. Prediction models can be useful for estimating retention rates across a range of scheduling options. However, training such models with electronic health records (EHR) involves several complexities. First, formal causal inference methods are needed to adjust for observed confounding when estimating retention rates under counterfactual scheduling decisions. Second, competing events such as death preclude retention, while censoring events render retention missing. Third, inconsistent monitoring of features such as viral load and CD4 count lead to covariate missingness. This paper presents an all-in-one approach for both predicting HIV retention and optimizing scheduling while accounting for these complexities. We formulate and identify causal retention estimands in terms of potential return-time under a hypothetical scheduling decision. Flexible Bayesian approaches are used to model the observed return-time distribution while accounting for competing and censoring events and form posterior point and uncertainty estimates for these estimands. We address the urgent need for data-driven decision support in HIV care by applying our method to EHR from the Academic Model Providing Access to Healthcare (AMPATH) - a consortium of clinics that treat HIV in Western Kenya.
DC3 -- A Diagnostic Case Challenge Collection for Clinical Decision Support
Aug 22, 2019



Abstract:In clinical care, obtaining a correct diagnosis is the first step towards successful treatment and, ultimately, recovery. Depending on the complexity of the case, the diagnostic phase can be lengthy and ridden with errors and delays. Such errors have a high likelihood to cause patients severe harm or even lead to their death and are estimated to cost the U.S. healthcare system several hundred billion dollars each year. To avoid diagnostic errors, physicians increasingly rely on diagnostic decision support systems drawing from heuristics, historic cases, textbooks, clinical guidelines and scholarly biomedical literature. The evaluation of such systems, however, is often conducted in an ad-hoc fashion, using non-transparent methodology, and proprietary data. This paper presents DC3, a collection of 31 extremely difficult diagnostic case challenges, manually compiled and solved by clinical experts. For each case, we present a number of temporally ordered physician-generated observations alongside the eventually confirmed true diagnosis. We additionally provide inferred dense relevance judgments for these cases among the PubMed collection of 27 million scholarly biomedical articles.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge