Hamid Hekmatian
Conf-Net: Predicting Depth Completion Error-Map For High-Confidence Dense 3D Point-Cloud
Jul 29, 2019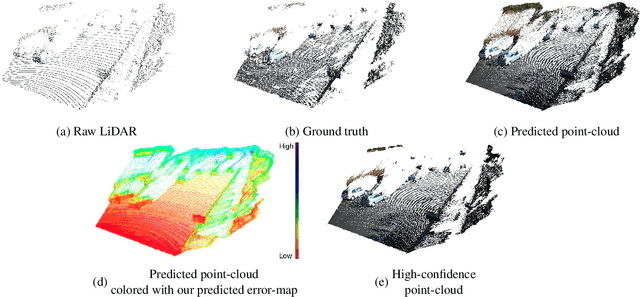
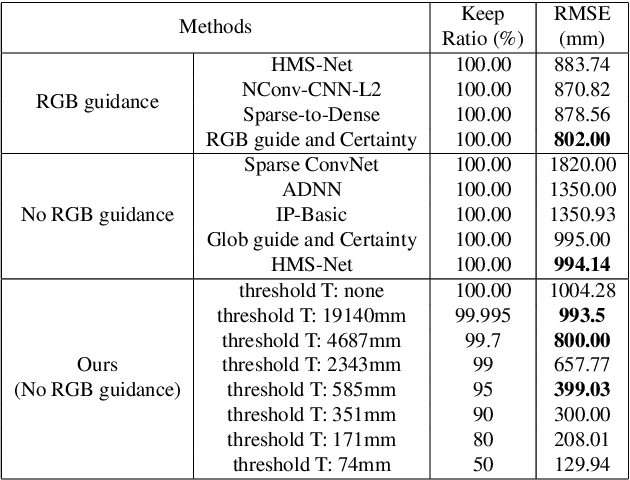

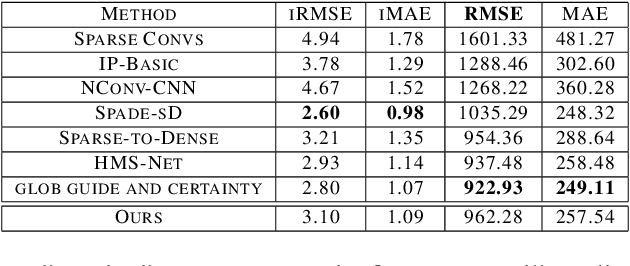
Abstract:This work proposes a new method for depth completion of sparse LiDAR data using a convolutional neural network which learns to generate almost full 3D point-clouds with significantly lower root mean squared error (RMSE) over state-of-the-art methods. An almost dense high-confidence/low-variance point-cloud is more valuable for safety-critical applications specifically real-world autonomous driving than a dense point-cloud with high error rate and high variance. We examine the error of the standard depth completion methods and demonstrate that the error exhibits a long tail distribution which can be significantly reduced if a small portion of the generated depth points can be identified and removed. We add a purging step to our neural network and present a novel end-to-end algorithm that learns to predict a high-quality error-map of its prediction. Using our predicted error map, we demonstrate that by up-filling a LiDAR point cloud from 18,000 points to 285,000 points, versus 300,000 points for full depth, we can reduce the RMSE error from 1004 to 399. This error is approximately 60% less than the state-of-the-art and 50% less than the state-of-the-art with RGB guidance. We only need to remove 0.3% of the predicted points to get comparable results with the state-of-the-art which has RGB guidance. Our post-processing step takes the output of a standard encoder-decoder network, to generate high resolution 360 degrees dense point-cloud. In addition to analyzing our results on Kitti depth completion dataset, we demonstrate the real-world performance of our algorithm using data gathered with a Velodyne VLP-32C LiDAR mounted on our vehicle to verify the effectiveness and real-time performance of our algorithm for autonomous driving. Codes and demo videos are available at http://github.com/hekmak/Conf-net.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge