H. Sun
Brain-like Functional Organization within Large Language Models
Oct 25, 2024Abstract:The human brain has long inspired the pursuit of artificial intelligence (AI). Recently, neuroimaging studies provide compelling evidence of alignment between the computational representation of artificial neural networks (ANNs) and the neural responses of the human brain to stimuli, suggesting that ANNs may employ brain-like information processing strategies. While such alignment has been observed across sensory modalities--visual, auditory, and linguistic--much of the focus has been on the behaviors of artificial neurons (ANs) at the population level, leaving the functional organization of individual ANs that facilitates such brain-like processes largely unexplored. In this study, we bridge this gap by directly coupling sub-groups of artificial neurons with functional brain networks (FBNs), the foundational organizational structure of the human brain. Specifically, we extract representative patterns from temporal responses of ANs in large language models (LLMs), and use them as fixed regressors to construct voxel-wise encoding models to predict brain activity recorded by functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). This framework links the AN sub-groups to FBNs, enabling the delineation of brain-like functional organization within LLMs. Our findings reveal that LLMs (BERT and Llama 1-3) exhibit brain-like functional architecture, with sub-groups of artificial neurons mirroring the organizational patterns of well-established FBNs. Notably, the brain-like functional organization of LLMs evolves with the increased sophistication and capability, achieving an improved balance between the diversity of computational behaviors and the consistency of functional specializations. This research represents the first exploration of brain-like functional organization within LLMs, offering novel insights to inform the development of artificial general intelligence (AGI) with human brain principles.
Graphene-based Distributed 3D Sensing Electrodes for Mapping Spatiotemporal Auricular Physiological Signals
Jul 10, 2021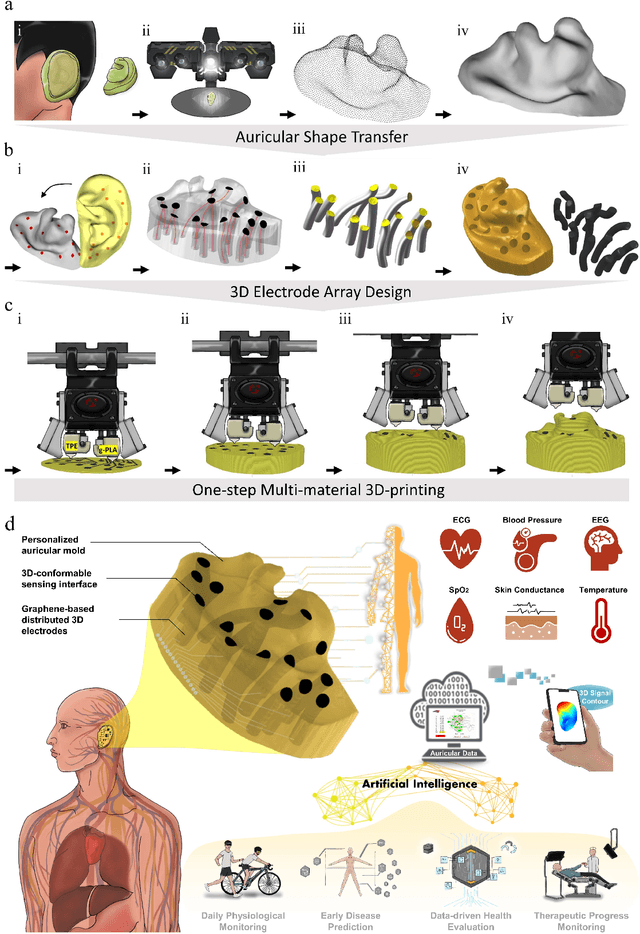
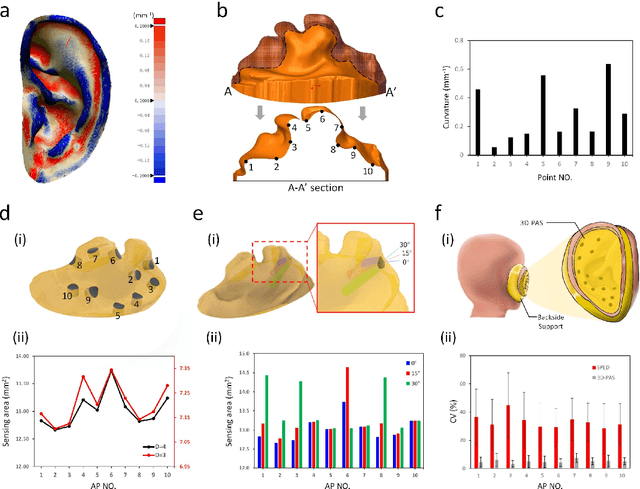
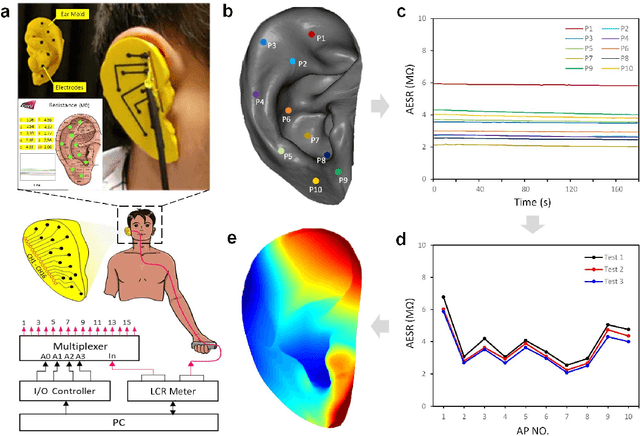
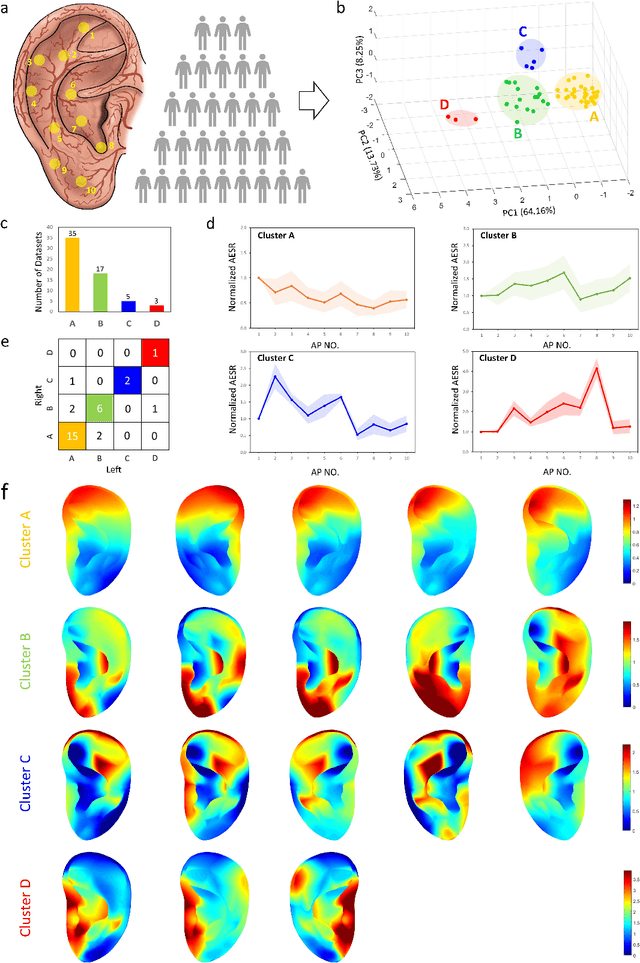
Abstract:Underneath the ear skin there are richly branching vascular and neural networks that ultimately connecting to our heart and brain. Hence, the three-dimensional (3D) mapping of auricular electrophysiological signals could provide a new perspective for biomedical studies such as diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases and neurological disorders. However, it is still extremely challenging for current sensing techniques to cover the entire ultra-curved auricle. Here, we report a graphene-based ear-conformable sensing device with embedded and distributed 3D electrodes which enable full-auricle physiological monitoring. The sensing device, which incorporates programable 3D electrode thread array and personalized auricular mold, has 3D-conformable sensing interfaces with curved auricular skin, and was developed using one-step multi-material 3D-printing process. As a proof-of-concept, spatiotemporal auricular electrical skin resistance (AESR) mapping was demonstrated. For the first time, 3D AESR contours were generated and human subject-specific AESR distributions among a population were observed. From the data of 17 volunteers, the auricular region-specific AESR changes after cycling exercise were observed in 98% of the tests and were validated via machine learning techniques. Correlations of AESR with heart rate and blood pressure were also studied using statistical analysis. This 3D electronic platform and AESR-based new biometrical findings show promising biomedical applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge