Gustavo A. Nunez Segura
Distributed DoS Attack Detection in SDN: Trade offs in Resource Constrained Wireless Networks
Mar 25, 2021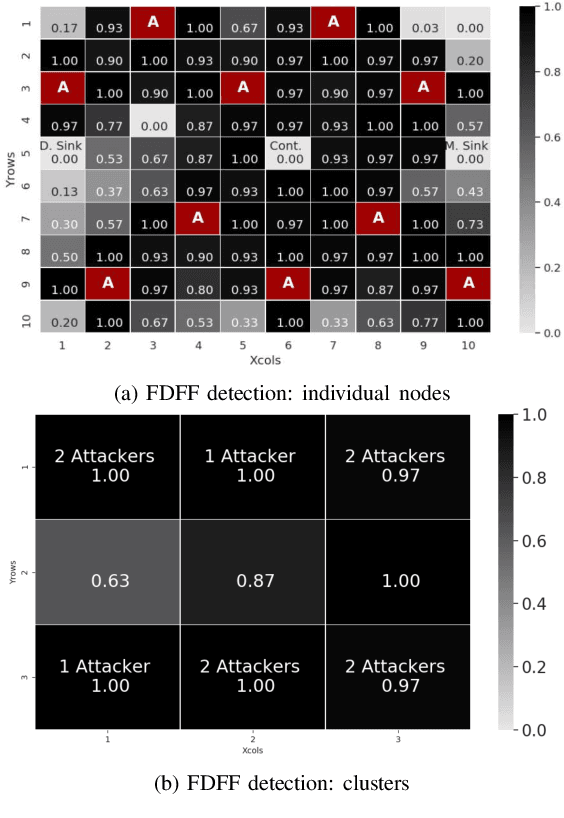
Abstract:The Software-defined networking(SDN) paradigm centralizes control decisions to improve programmability and simplify network management. However, this centralization turns the network vulnerable to denial of service (DoS) attacks, and in the case of resource constrained networks, the vulnerabilities escalate. The main shortcoming in current security solutions is the trade off between detection rate and complexity. In this work, we propose a DoS attack detection algorithm for SDN resource constrained networks, based on recent results on non-parametric real-time change point detection, and lightweight enough to run on individual resource constrained devices. Our experiment results show detection rates and attacker identification probabilities equal or over 0.93.
Centralized and Distributed Intrusion Detection for Resource Constrained Wireless SDN Networks
Mar 01, 2021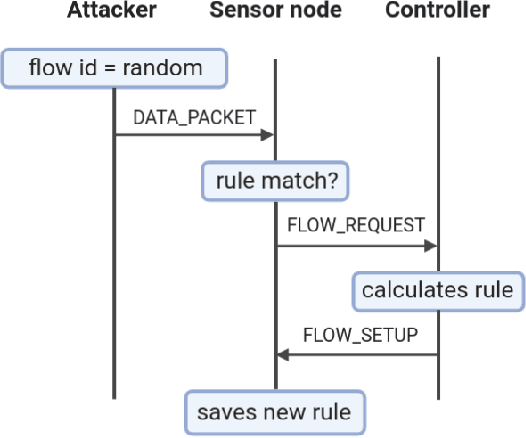
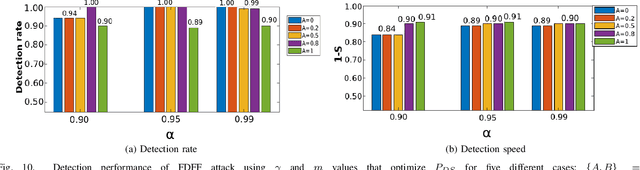
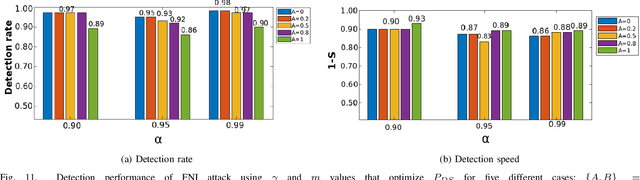
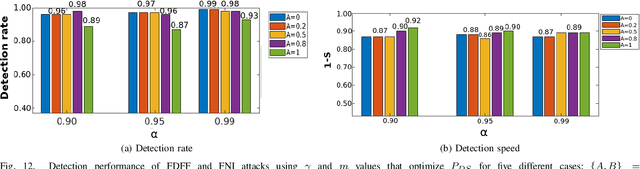
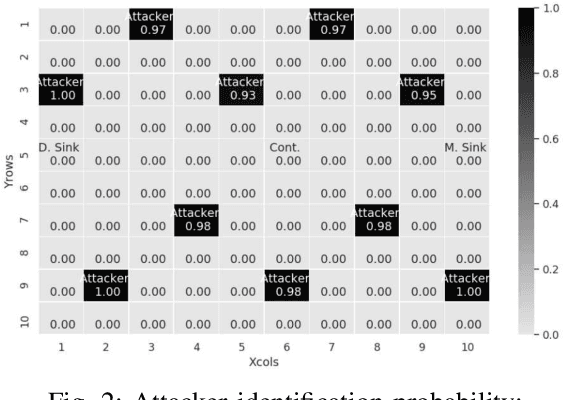
Abstract:Software-defined networking (SDN) was devised to simplify network management and automate infrastructure sharing in wired networks. These benefits motivated the application of SDN in wireless sensor networks to leverage solutions for complex applications. However, some of the core SDN traits turn the networks prone to denial of service attacks (DoS). There are proposals in the literature to detect DoS in wireless SDN networks, however, not without shortcomings: there is little focus on resource constraints, high detection rates have been reported only for small networks, and the detection is disengaged from the identification of the type of the attack or the attacker. Our work targets these shortcomings by introducing a lightweight, online change point detector to monitor performance metrics that are impacted when the network is under attack. A key novelty is that the proposed detector is able to operate in either centralized or distributed mode. The centralized detector has very high detection rates and can further distinguish the type of the attack (from a list of known attacks). On the other hand, the distributed detector provides information that allows to identify the nodes launching the attack. Our proposal is tested over IEEE 802.15.4 networks. The results show detection rates exceeding $96\%$ in networks of 36 and 100 nodes and identification of the type of the attack with a probability exceeding $0.89$ when using the centralized approach. Additionally, for some types of attack it was possible to pinpoint the attackers with an identification probability over $0.93$ when using distributed detectors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge