Gursel Serpen
Wireless Sensor Networks as Parallel and Distributed Hardware Platform for Artificial Neural Networks
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:We are proposing fully parallel and maximally distributed hardware realization of a generic neuro-computing system. More specifically, the proposal relates to the wireless sensor networks technology to serve as a massively parallel and fully distributed hardware platform to implement and realize artificial neural network (ANN) algorithms. A parallel and distributed (PDP) hardware realization of ANNs makes it possible to have real time computation of large-scale (and complex) problems in a highly robust framework. We will demonstrate how a network of hundreds of thousands of processing nodes (or motes of a wireless sensor network), which have on-board processing and wireless communication features, can be used to implement fully parallel and massively distributed computation of artificial neural network algorithms for solution of truly large-scale problems in real time. The realization of artificial neural network algorithms in a massively parallel and fully distributed hardware has been the goal of neural network computing researchers. This is because a parallel and distributed computation of artificial neural network algorithms could not have been achieved against all the advancements in silicon- or optics-based computing. Accordingly, artificial neural networks could not be applied to very large-scale problems for real time computation of solutions. This hindered the development of neural algorithms for affordable and practical solutions of challenging problems since often special-purpose computing approaches in hardware, software or hybrid (non-neural) had to be developed for and fine-tuned to specific problems that are very large-scale and highly complex. Successful implementation is likely to revolutionize computing as we know it by making it possible to solve very large scale scientific, engineering or technical problems in real time.
Empirical Investigation into Configuring Echo State Networks for Representative Benchmark Problem Domains
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:This paper examines Echo State Network, a reservoir computer, performance using four different benchmark problems, then proposes heuristics or rules of thumb for configuring the architecture, as well as the selection of parameters and their values, which are applicable to problems within the same domain, to help serve to fill the experience gap needed by those entering this field of study. The influence of various parameter selections and their value adjustments, as well as architectural changes made to an Echo State Network, a powerful recurrent neural network configured as a reservoir computer, can be challenging to fully comprehend without experience in the field, and even some hyperparameter optimization algorithms may have difficulty adjusting parameter values without proper manual selections made first. Therefore, it is imperative to understand the effects of parameters and their value selection on Echo State Network architecture performance for a successful build. Thus, to address the requirement for an extensive background in Echo State Network architecture, as well as examine how Echo State Network performance is affected with respect to variations in architecture, design, and parameter selection and values, a series of benchmark tasks representing different problem domains, including time series prediction, pattern generation, chaotic system prediction, and time series classification, were modeled and experimented on to show the impact on the performance of Echo State Network.
Ensemble Classifier Design Tuned to Dataset Characteristics for Network Intrusion Detection
May 08, 2022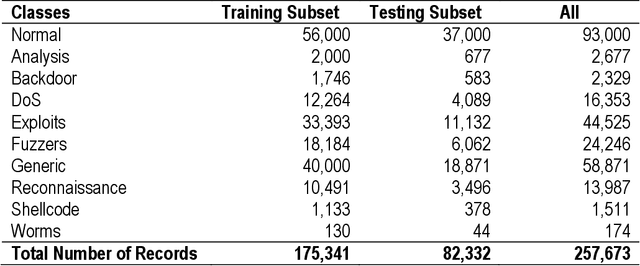
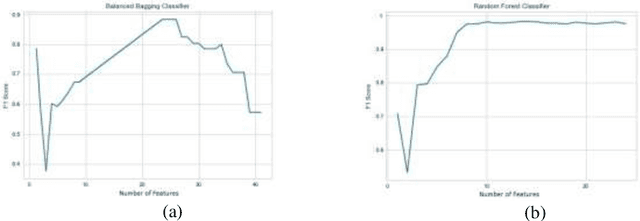
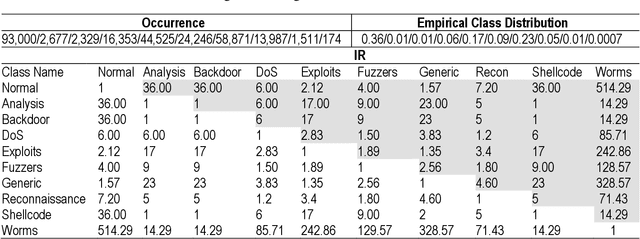

Abstract:Machine Learning-based supervised approaches require highly customized and fine-tuned methodologies to deliver outstanding performance. This paper presents a dataset-driven design and performance evaluation of a machine learning classifier for the network intrusion dataset UNSW-NB15. Analysis of the dataset suggests that it suffers from class representation imbalance and class overlap in the feature space. We employed ensemble methods using Balanced Bagging (BB), eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), and Random Forest empowered by Hellinger Distance Decision Tree (RF-HDDT). BB and XGBoost are tuned to handle the imbalanced data, and Random Forest (RF) classifier is supplemented by the Hellinger metric to address the imbalance issue. Two new algorithms are proposed to address the class overlap issue in the dataset. These two algorithms are leveraged to help improve the performance of the testing dataset by modifying the final classification decision made by three base classifiers as part of the ensemble classifier which employs a majority vote combiner. The proposed design is evaluated for both binary and multi-category classification. Comparing the proposed model to those reported on the same dataset in the literature demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms others by a significant margin for both binary and multi-category classification cases.
Host-based anomaly detection using Eigentraces feature extraction and one-class classification on system call trace data
Nov 25, 2019



Abstract:This paper proposes a methodology for host-based anomaly detection using a semi-supervised algorithm namely one-class classifier combined with a PCA-based feature extraction technique called Eigentraces on system call trace data. The one-class classification is based on generating a set of artificial data using a reference distribution and combining the target class probability function with artificial class density function to estimate the target class density function through the Bayes formulation. The benchmark dataset, ADFA-LD, is employed for the simulation study. ADFA-LD dataset contains thousands of system call traces collected during various normal and attack processes for the Linux operating system environment. In order to pre-process and to extract features, windowing on the system call trace data followed by the principal component analysis which is named as Eigentraces is implemented. The target class probability function is modeled separately by Radial Basis Function neural network and Random Forest machine learners for performance comparison purposes. The simulation study showed that the proposed intrusion detection system offers high performance for detecting anomalies and normal activities with respect to a set of well-accepted metrics including detection rate, accuracy, and missed and false alarm rates.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge