Graham Tierney
Author Clustering and Topic Estimation for Short Texts
Jun 15, 2021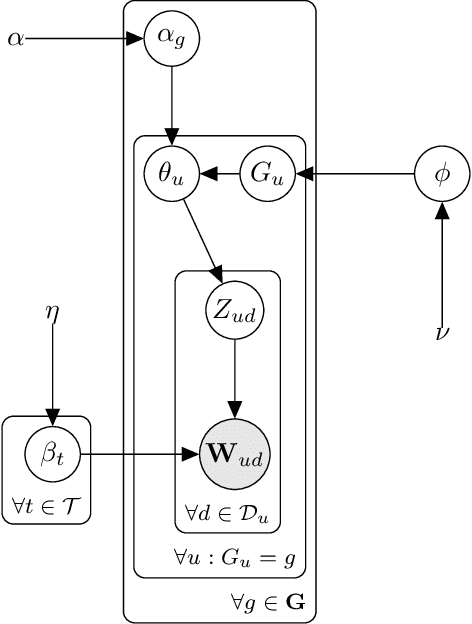
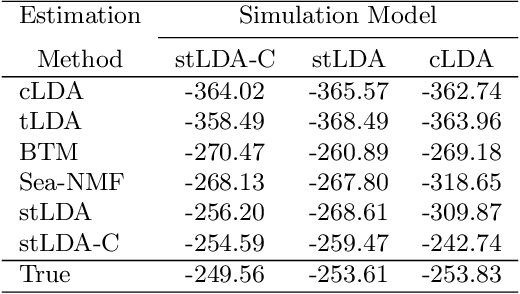
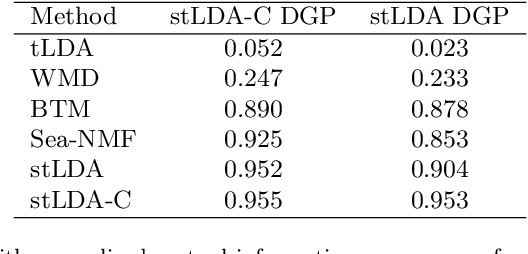
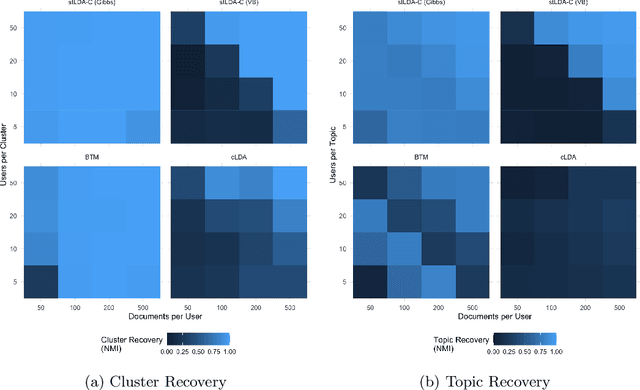
Abstract:Analysis of short text, such as social media posts, is extremely difficult because it relies on observing many document-level word co-occurrence pairs. Beyond topic distributions, a common downstream task of the modeling is grouping the authors of these documents for subsequent analyses. Traditional models estimate the document groupings and identify user clusters with an independent procedure. We propose a novel model that expands on the Latent Dirichlet Allocation by modeling strong dependence among the words in the same document, with user-level topic distributions. We also simultaneously cluster users, removing the need for post-hoc cluster estimation and improving topic estimation by shrinking noisy user-level topic distributions towards typical values. Our method performs as well as -- or better -- than traditional approaches to problems arising in short text, and we demonstrate its usefulness on a dataset of tweets from United States Senators, recovering both meaningful topics and clusters that reflect partisan ideology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge