Grace Diehl
GRAPE-S: Near Real-Time Coalition Formation for Multiple Service Collectives
Oct 19, 2023
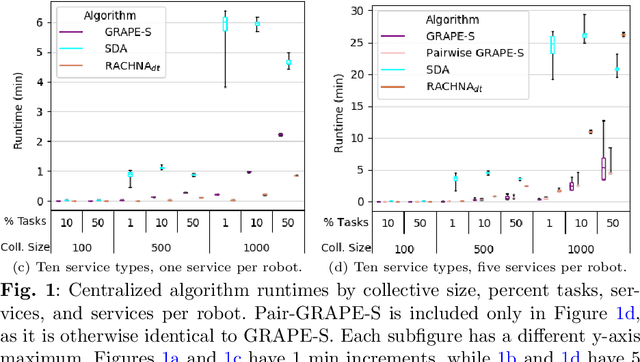
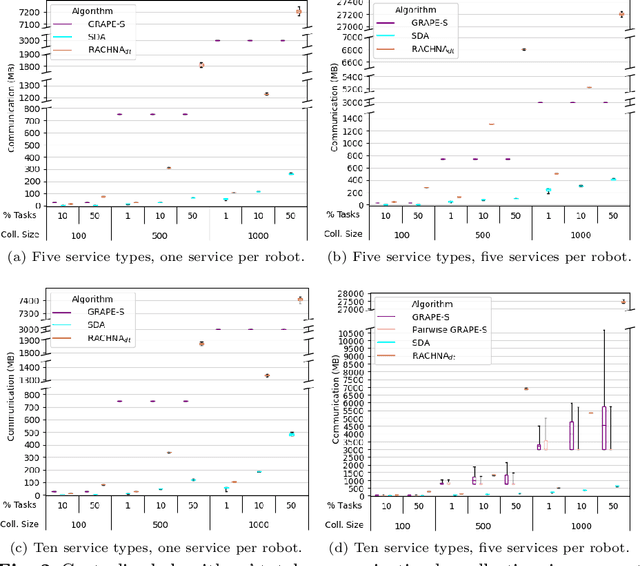
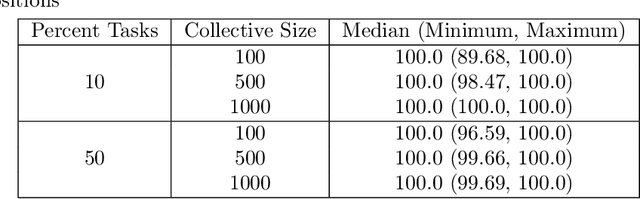
Abstract:Robotic collectives for military and disaster response applications require coalition formation algorithms to partition robots into appropriate task teams. Collectives' missions will often incorporate tasks that require multiple high-level robot behaviors or services, which coalition formation must accommodate. The highly dynamic and unstructured application domains also necessitate that coalition formation algorithms produce near optimal solutions (i.e., >95% utility) in near real-time (i.e., <5 minutes) with very large collectives (i.e., hundreds of robots). No previous coalition formation algorithm satisfies these requirements. An initial evaluation found that traditional auction-based algorithms' runtimes are too long, even though the centralized simulator incorporated ideal conditions unlikely to occur in real-world deployments (i.e., synchronization across robots and perfect, instantaneous communication). The hedonic game-based GRAPE algorithm can produce solutions in near real-time, but cannot be applied to multiple service collectives. This manuscript integrates GRAPE and a services model, producing GRAPE-S and Pair-GRAPE-S. These algorithms and two auction baselines were evaluated using a centralized simulator with up to 1000 robots, and via the largest distributed coalition formation simulated evaluation to date, with up to 500 robots. The evaluations demonstrate that auctions transfer poorly to distributed collectives, resulting in excessive runtimes and low utility solutions. GRAPE-S satisfies the target domains' coalition formation requirements, producing near optimal solutions in near real-time, and Pair-GRAPE-S more than satisfies the domain requirements, producing optimal solutions in near real-time. GRAPE-S and Pair-GRAPE-S are the first algorithms demonstrated to support near real-time coalition formation for very large, distributed collectives with multiple services.
The Viability of Domain Constrained Coalition Formation for Robotic Collectives
Jun 08, 2023Abstract:Applications, such as military and disaster response, can benefit from robotic collectives' ability to perform multiple cooperative tasks (e.g., surveillance, damage assessments) efficiently across a large spatial area. Coalition formation algorithms can potentially facilitate collective robots' assignment to appropriate task teams; however, most coalition formation algorithms were designed for smaller multiple robot systems (i.e., 2-50 robots). Collectives' scale and domain-relevant constraints (i.e., distribution, near real-time, minimal communication) make coalition formation more challenging. This manuscript identifies the challenges inherent to designing coalition formation algorithms for very large collectives (e.g., 1000 robots). A survey of multiple robot coalition formation algorithms finds that most are unable to transfer directly to collectives, due to the identified system differences; however, auctions and hedonic games may be the most transferable. A simulation-based evaluation of three auction and hedonic game algorithms, applied to homogeneous and heterogeneous collectives, demonstrates that there are collective compositions for which no existing algorithm is viable; however, the experimental results and literature survey suggest paths forward.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge