Gopal P. Sarma
Mammalian Value Systems
Jan 21, 2019Abstract:Characterizing human values is a topic deeply interwoven with the sciences, humanities, art, and many other human endeavors. In recent years, a number of thinkers have argued that accelerating trends in computer science, cognitive science, and related disciplines foreshadow the creation of intelligent machines which meet and ultimately surpass the cognitive abilities of human beings, thereby entangling an understanding of human values with future technological development. Contemporary research accomplishments suggest sophisticated AI systems becoming widespread and responsible for managing many aspects of the modern world, from preemptively planning users' travel schedules and logistics, to fully autonomous vehicles, to domestic robots assisting in daily living. The extrapolation of these trends has been most forcefully described in the context of a hypothetical "intelligence explosion," in which the capabilities of an intelligent software agent would rapidly increase due to the presence of feedback loops unavailable to biological organisms. The possibility of superintelligent agents, or simply the widespread deployment of sophisticated, autonomous AI systems, highlights an important theoretical problem: the need to separate the cognitive and rational capacities of an agent from the fundamental goal structure, or value system, which constrains and guides the agent's actions. The "value alignment problem" is to specify a goal structure for autonomous agents compatible with human values. In this brief article, we suggest that recent ideas from affective neuroscience and related disciplines aimed at characterizing neurological and behavioral universals in the mammalian class provide important conceptual foundations relevant to describing human values. We argue that the notion of "mammalian value systems" points to a potential avenue for fundamental research in AI safety and AI ethics.
* 12 pages
Integrative Biological Simulation, Neuropsychology, and AI Safety
Nov 07, 2018Abstract:We propose a biologically-inspired research agenda with parallel tracks aimed at AI and AI safety. The bottom-up component consists of building a sequence of biophysically realistic simulations of simple organisms such as the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster, and the zebrafish Danio rerio to serve as platforms for research into AI algorithms and system architectures. The top-down component consists of an approach to value alignment that grounds AI goal structures in neuropsychology. Our belief is that parallel pursuit of these tracks will inform the development of value-aligned AI systems that have been inspired by embodied organisms with sensorimotor integration. An important set of side benefits is that the research trajectories we describe here are grounded in long-standing intellectual traditions within existing research communities and funding structures. In addition, these research programs overlap with significant contemporary themes in the biological and psychological sciences such as data/model integration and reproducibility.
AI Safety and Reproducibility: Establishing Robust Foundations for the Neuropsychology of Human Values
Sep 08, 2018Abstract:We propose the creation of a systematic effort to identify and replicate key findings in neuropsychology and allied fields related to understanding human values. Our aim is to ensure that research underpinning the value alignment problem of artificial intelligence has been sufficiently validated to play a role in the design of AI systems.
* 5 pages
Brief Notes on Hard Takeoff, Value Alignment, and Coherent Extrapolated Volition
Apr 21, 2018Abstract:I make some basic observations about hard takeoff, value alignment, and coherent extrapolated volition, concepts which have been central in analyses of superintelligent AI systems.
Robust Computer Algebra, Theorem Proving, and Oracle AI
Dec 31, 2017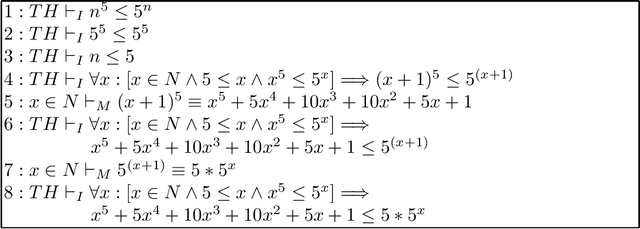

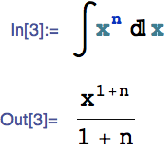
Abstract:In the context of superintelligent AI systems, the term "oracle" has two meanings. One refers to modular systems queried for domain-specific tasks. Another usage, referring to a class of systems which may be useful for addressing the value alignment and AI control problems, is a superintelligent AI system that only answers questions. The aim of this manuscript is to survey contemporary research problems related to oracles which align with long-term research goals of AI safety. We examine existing question answering systems and argue that their high degree of architectural heterogeneity makes them poor candidates for rigorous analysis as oracles. On the other hand, we identify computer algebra systems (CASs) as being primitive examples of domain-specific oracles for mathematics and argue that efforts to integrate computer algebra systems with theorem provers, systems which have largely been developed independent of one another, provide a concrete set of problems related to the notion of provable safety that has emerged in the AI safety community. We review approaches to interfacing CASs with theorem provers, describe well-defined architectural deficiencies that have been identified with CASs, and suggest possible lines of research and practical software projects for scientists interested in AI safety.
* 15 pages, 3 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge