Gonçalo Hora de Carvalho
Show, Don't Tell: Evaluating Large Language Models Beyond Textual Understanding with ChildPlay
Jul 12, 2024Abstract:We explore the hypothesis that LLMs, such as GPT-3.5 and GPT-4, possess broader cognitive functions, particularly in non-linguistic domains. Our approach extends beyond standard linguistic benchmarks by incorporating games like Tic-Tac-Toe, Connect Four, and Battleship, encoded via ASCII, to assess strategic thinking and decision-making. To evaluate the models' ability to generalize beyond their training data, we introduce two additional games. The first game, LEGO Connect Language (LCL), tests the models' capacity to understand spatial logic and follow assembly instructions. The second game, the game of shapes, challenges the models to identify shapes represented by 1s within a matrix of zeros, further testing their spatial reasoning skills. This "show, don't tell" strategy uses games instead of simply querying the models. Our results show that despite their proficiency on standard benchmarks, GPT-3.5 and GPT-4's abilities to play and reason about fully observable games without pre-training is mediocre. Both models fail to anticipate losing moves in Tic-Tac-Toe and Connect Four, and they are unable to play Battleship correctly. While GPT-4 shows some success in the game of shapes, both models fail at the assembly tasks presented in the LCL game. These results suggest that while GPT models can emulate conversational proficiency and basic rule comprehension, their performance in strategic gameplay and spatial reasoning tasks is very limited. Importantly, this reveals a blind spot in current LLM benchmarks that we highlight with our gameplay benchmark suite ChildPlay (https://github.com/child-play-neurips/child-play). Our findings provide a cautionary tale about claims of emergent intelligence and reasoning capabilities of LLMs that are roughly the size of GPT-3.5 and GPT-4.
C-Causal Blindness An experimental computational framework on the isomorphic relationship between biological computation, artificial computation, and logic using weighted hidden Markov models
Aug 19, 2022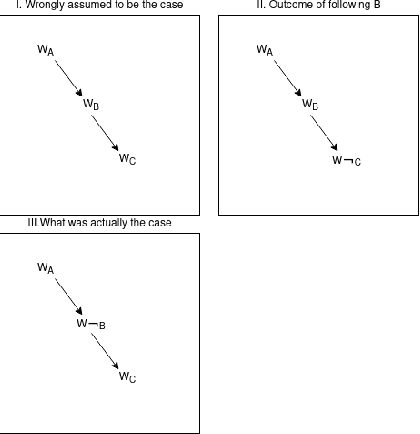
Abstract:This text concerns a particular flavor of cognitive blindness referred to as C-Causal Blindness, or C-CB. A blindness where the policy to obtain the objective leads to the state to be avoided. A literal example of C-CB would be Kurt G\"odel's decision to starve for "fear of being poisoned" - take this to be premise A. The objective being "to avoid being poisoned (so as to not die)": C, the plan or policy being "don't eat": B, and the actual outcome having been "dying": not C - the state that G\"odel wanted to avoid to begin with. Like many, G\"odel pursued a strategy that caused the result he wanted to avoid. An experimental computational framework is proposed to show the isomorphic relationship between C-CB in brain computations, logic, and computer computations using hidden Markov models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge