Goksenin Yuksel
Remining Hard Negatives for Generative Pseudo Labeled Domain Adaptation
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:Dense retrievers have demonstrated significant potential for neural information retrieval; however, they exhibit a lack of robustness to domain shifts, thereby limiting their efficacy in zero-shot settings across diverse domains. A state-of-the-art domain adaptation technique is Generative Pseudo Labeling (GPL). GPL uses synthetic query generation and initially mined hard negatives to distill knowledge from cross-encoder to dense retrievers in the target domain. In this paper, we analyze the documents retrieved by the domain-adapted model and discover that these are more relevant to the target queries than those of the non-domain-adapted model. We then propose refreshing the hard-negative index during the knowledge distillation phase to mine better hard negatives. Our remining R-GPL approach boosts ranking performance in 13/14 BEIR datasets and 9/12 LoTTe datasets. Our contributions are (i) analyzing hard negatives returned by domain-adapted and non-domain-adapted models and (ii) applying the GPL training with and without hard-negative re-mining in LoTTE and BEIR datasets.
Interpretability Analysis of Domain Adapted Dense Retrievers
Jan 24, 2025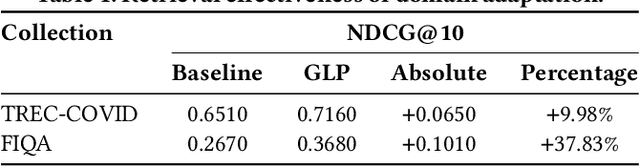
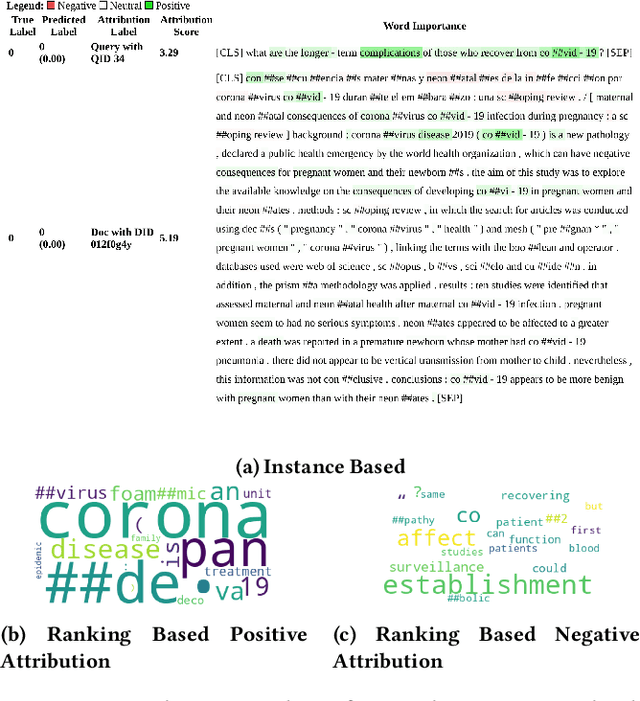
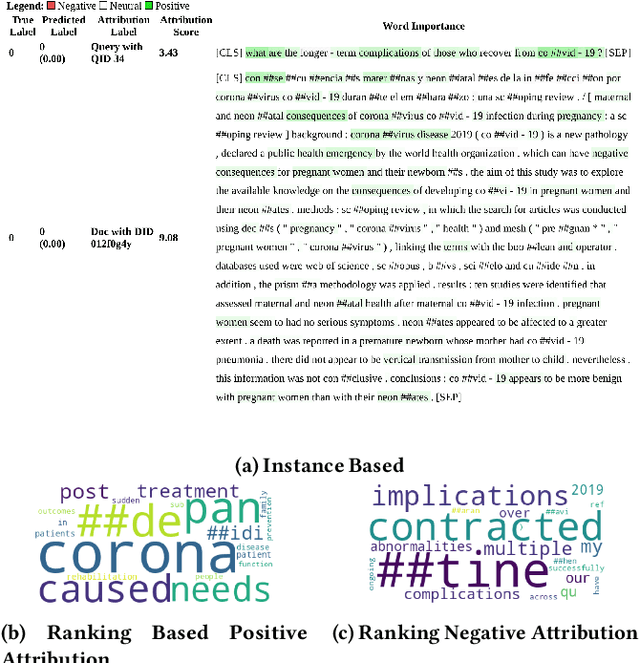
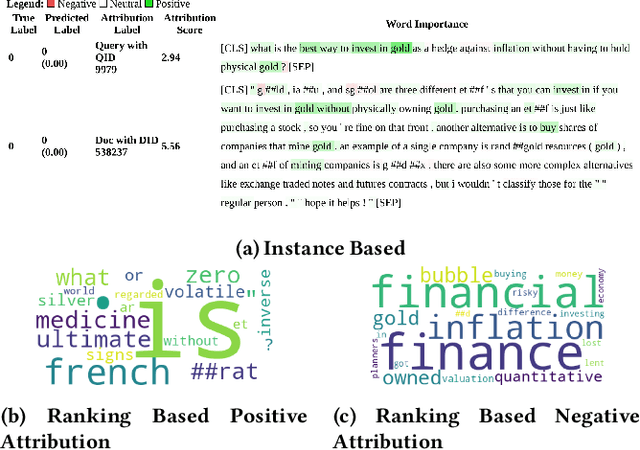
Abstract:Dense retrievers have demonstrated significant potential for neural information retrieval; however, they exhibit a lack of robustness to domain shifts, thereby limiting their efficacy in zero-shot settings across diverse domains. Previous research has investigated unsupervised domain adaptation techniques to adapt dense retrievers to target domains. However, these studies have not focused on explainability analysis to understand how such adaptations alter the model's behavior. In this paper, we propose utilizing the integrated gradients framework to develop an interpretability method that provides both instance-based and ranking-based explanations for dense retrievers. To generate these explanations, we introduce a novel baseline that reveals both query and document attributions. This method is used to analyze the effects of domain adaptation on input attributions for query and document tokens across two datasets: the financial question answering dataset (FIQA) and the biomedical information retrieval dataset (TREC-COVID). Our visualizations reveal that domain-adapted models focus more on in-domain terminology compared to non-adapted models, exemplified by terms such as "hedge," "gold," "corona," and "disease." This research addresses how unsupervised domain adaptation techniques influence the behavior of dense retrievers when adapted to new domains. Additionally, we demonstrate that integrated gradients are a viable choice for explaining and analyzing the internal mechanisms of these opaque neural models.
On Correlating Factors for Domain Adaptation Performance
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:Dense retrievers have demonstrated significant potential for neural information retrieval; however, they lack robustness to domain shifts, limiting their efficacy in zero-shot settings across diverse domains. In this paper, we set out to analyze the possible factors that lead to successful domain adaptation of dense retrievers. We include domain similarity proxies between generated queries to test and source domains. Furthermore, we conduct a case study comparing two powerful domain adaptation techniques. We find that generated query type distribution is an important factor, and generating queries that share a similar domain to the test documents improves the performance of domain adaptation methods. This study further emphasizes the importance of domain-tailored generated queries.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge