Gianmarco Gabrieli
Interleaving Text and Number Embeddings to Solve Mathemathics Problems
Oct 25, 2024Abstract:Integrating text and numbers effectively is a crucial step towards enhancing Large Language Models (LLMs) capabilities in assisting in scientific tasks. While most current approaches rely on discrete tokenization of numbers, for instance, conversion to scientific notation or base 10-decomposition, a recent approach proposed a continuous numerical encoding as an inductive bias. In this paper, we build upon this approach by introducing more expressive numerical embeddings. Our method addresses key shortcomings, including the elimination of numerical artefacts and the ability to handle a wide range of magnitudes without clipping. Our work presents two key contributions. First, we employ an MLP to assign distinct directions in the embedding space to different numbers. Our second contribution is the introduction of a routing layer that differentiates between numerical and text embeddings. We hypothesise that this combined approach enables the model to distinguish between text and number distributions while maintaining its capacity for arithmetic operations. Using only a 45 M parameter encoder-decoder architecture our method achieves a $R^2$=0.9988 over a wide range of magnitude ($10^{-3},10^{8}$). In addition, we empirically observe a reduction of the numerical artefacts and biases observed compared to the baselines.
A reconfigurable integrated electronic tongue and its use in accelerated analysis of juices and wines
May 27, 2022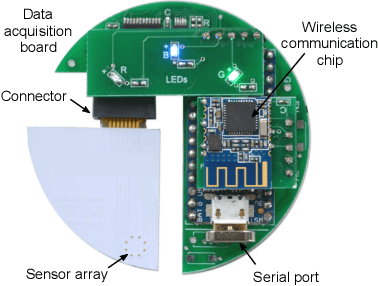
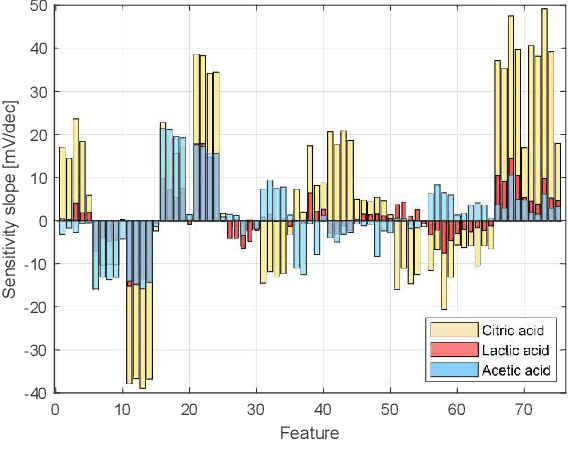
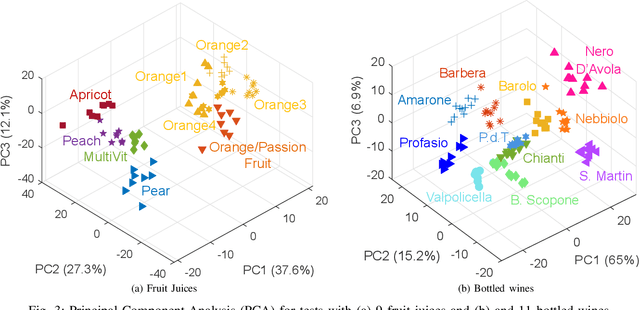
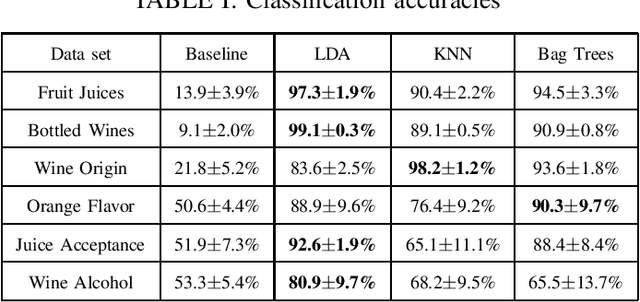
Abstract:Potentiometric electronic tongues (ETs) leveraging trends in miniaturization and internet of things (IoT) bear promise for facile mobile chemical analysis of complex multicomponent liquids, such as beverages. In this work, hand-crafted feature extraction from the transient potentiometric response of an array of low-selective miniaturized polymeric sensors is combined with a data pipeline for deployment of trained machine learning models on a cloud back-end or edge device. The sensor array demonstrated sensitivity to different organic acids and exhibited interesting performance for the fingerprinting of fruit juices and wines, including differentiation of samples through supervised learning based on sensory descriptors and prediction of consumer acceptability of aged juice samples. Product authentication, quality control and support of sensory evaluation are some of the applications that are expected to benefit from integrated electronic tongues that facilitate the characterization of complex properties of multi-component liquids.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge