German Terrazas
University of Nottingham
Exploring Programmable Self-Assembly in Non-DNA based Molecular Computing
Sep 25, 2013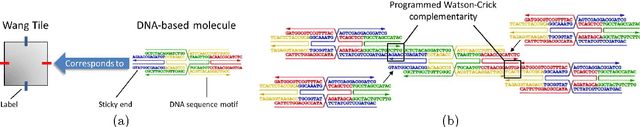
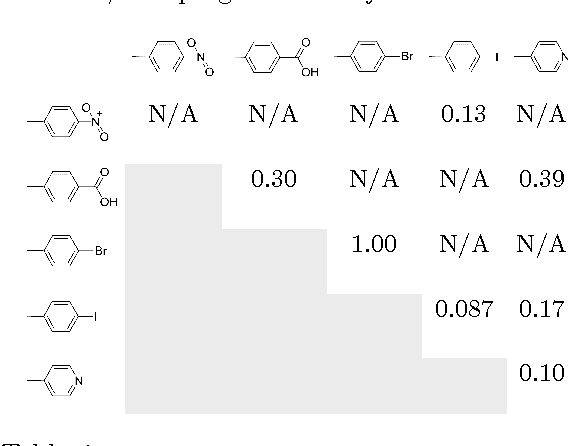
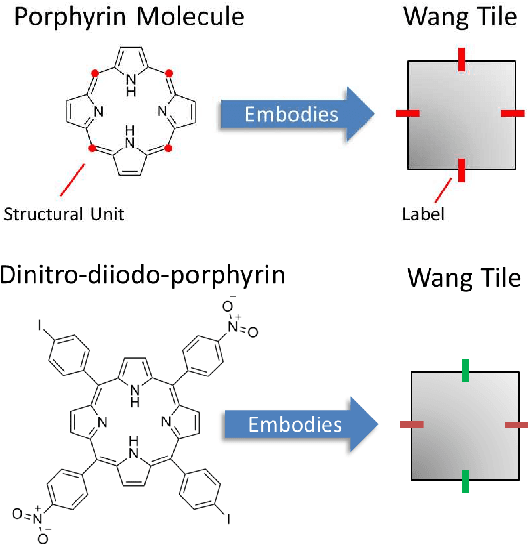
Abstract:Self-assembly is a phenomenon observed in nature at all scales where autonomous entities build complex structures, without external influences nor centralised master plan. Modelling such entities and programming correct interactions among them is crucial for controlling the manufacture of desired complex structures at the molecular and supramolecular scale. This work focuses on a programmability model for non DNA-based molecules and complex behaviour analysis of their self-assembled conformations. In particular, we look into modelling, programming and simulation of porphyrin molecules self-assembly and apply Kolgomorov complexity-based techniques to classify and assess simulation results in terms of information content. The analysis focuses on phase transition, clustering, variability and parameter discovery which as a whole pave the way to the notion of complex systems programmability.
Towards the Design of Heuristics by Means of Self-Assembly
Jun 09, 2010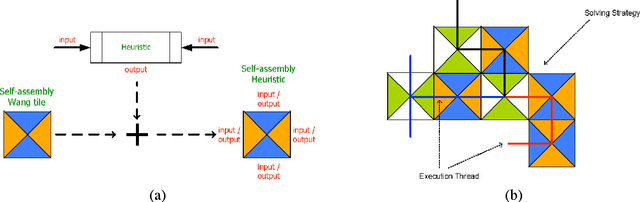
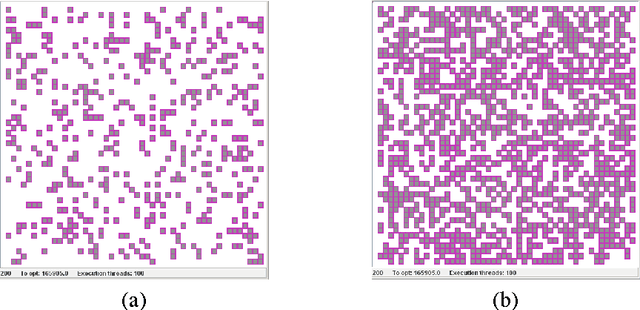
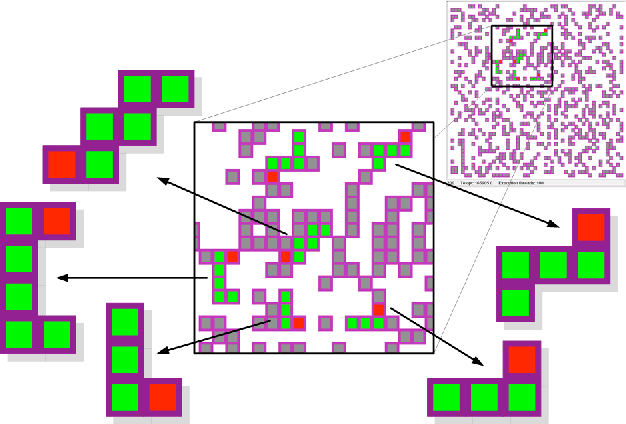
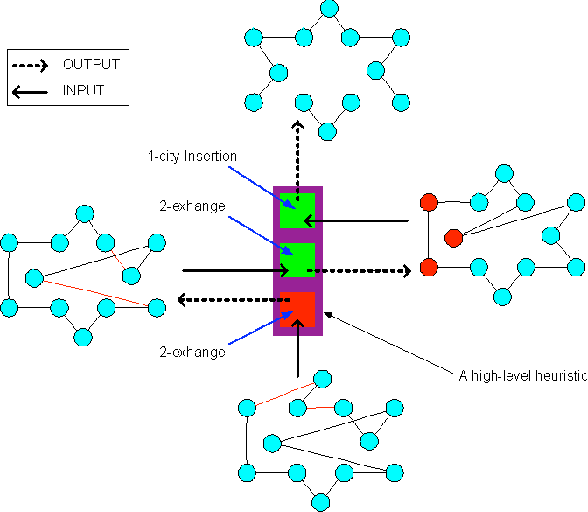
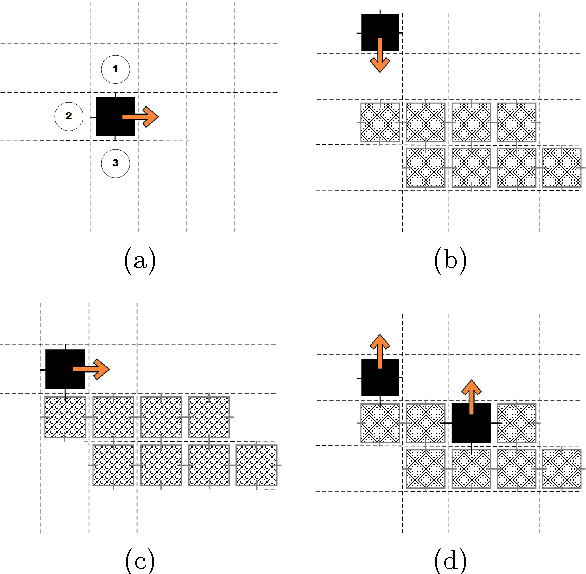
Abstract:The current investigations on hyper-heuristics design have sprung up in two different flavours: heuristics that choose heuristics and heuristics that generate heuristics. In the latter, the goal is to develop a problem-domain independent strategy to automatically generate a good performing heuristic for the problem at hand. This can be done, for example, by automatically selecting and combining different low-level heuristics into a problem specific and effective strategy. Hyper-heuristics raise the level of generality on automated problem solving by attempting to select and/or generate tailored heuristics for the problem at hand. Some approaches like genetic programming have been proposed for this. In this paper, we explore an elegant nature-inspired alternative based on self-assembly construction processes, in which structures emerge out of local interactions between autonomous components. This idea arises from previous works in which computational models of self-assembly were subject to evolutionary design in order to perform the automatic construction of user-defined structures. Then, the aim of this paper is to present a novel methodology for the automated design of heuristics by means of self-assembly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge