Gen Kudo
Risk-Aware Coverage Path Planning for Lunar Micro-Rovers Leveraging Global and Local Environmental Data
Apr 29, 2024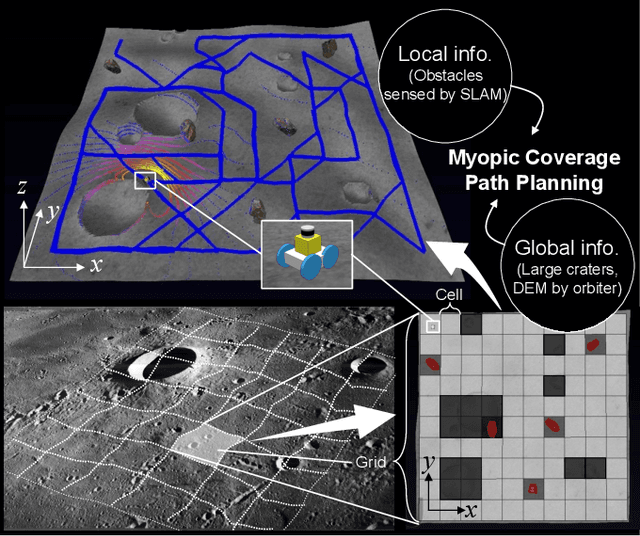
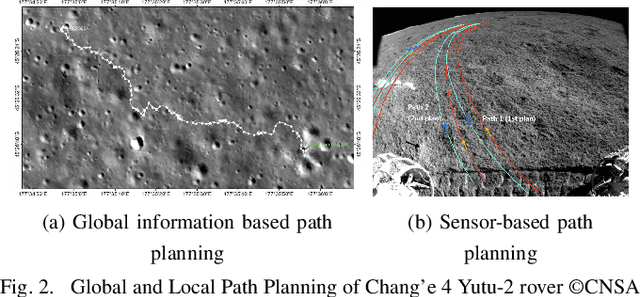
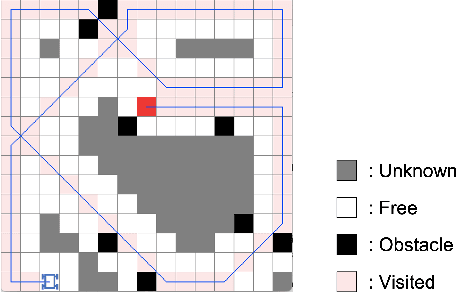
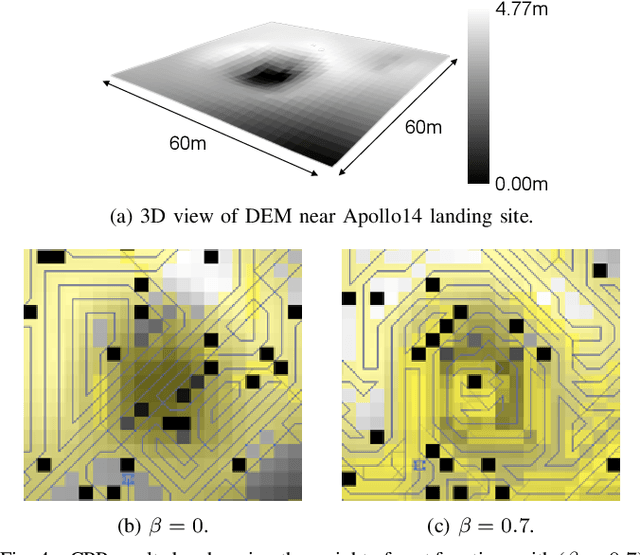
Abstract:This paper presents a novel 3D myopic coverage path planning algorithm for lunar micro-rovers that can explore unknown environments with limited sensing and computational capabilities. The algorithm expands upon traditional non-graph path planning methods to accommodate the complexities of lunar terrain, utilizing global data with local topographic features into motion cost calculations. The algorithm also integrates localization and mapping to update the rover's pose and map the environment. The resulting environment map's accuracy is evaluated and tested in a 3D simulator. Outdoor field tests were conducted to validate the algorithm's efficacy in sim-to-real scenarios. The results showed that the algorithm could achieve high coverage with low energy consumption and computational cost, while incrementally exploring the terrain and avoiding obstacles. This study contributes to the advancement of path planning methodologies for space exploration, paving the way for efficient, scalable and autonomous exploration of lunar environments by small rovers.
Enabling Faster Locomotion of Planetary Rovers with a Mechanically-Hybrid Suspension
Jul 10, 2023



Abstract:The exploration of the lunar poles and the collection of samples from the martian surface are characterized by shorter time windows demanding increased autonomy and speeds. Autonomous mobile robots must intrinsically cope with a wider range of disturbances. Faster off-road navigation has been explored for terrestrial applications but the combined effects of increased speeds and reduced gravity fields are yet to be fully studied. In this paper, we design and demonstrate a novel fully passive suspension design for wheeled planetary robots, which couples a high-range passive rocker with elastic in-wheel coil-over shock absorbers. The design was initially conceived and verified in a reduced-gravity (1.625 m/s$^2$) simulated environment, where three different passive suspension configurations were evaluated against a set of challenges--climbing steep slopes and surmounting unexpected obstacles like rocks and outcrops--and later prototyped and validated in a series of field tests. The proposed mechanically-hybrid suspension proves to mitigate more effectively the negative effects (high-frequency/high-amplitude vibrations and impact loads) of faster locomotion (>1 m/s) over unstructured terrains under varied gravity fields. This lowers the demand on navigation and control systems, impacting the efficiency of exploration missions in the years to come.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge