Gabriel Maciá-Fernández
Leveraging a Probabilistic PCA Model to Understand the Multivariate Statistical Network Monitoring Framework for Network Security Anomaly Detection
Feb 02, 2023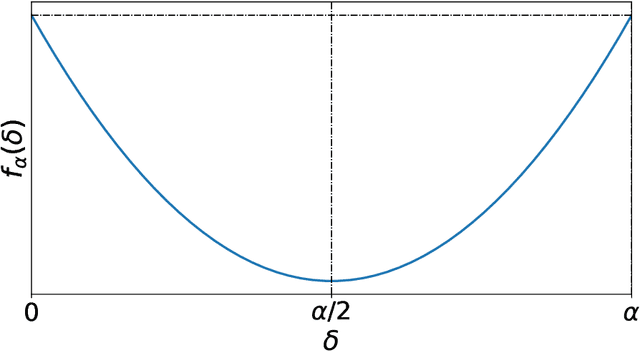
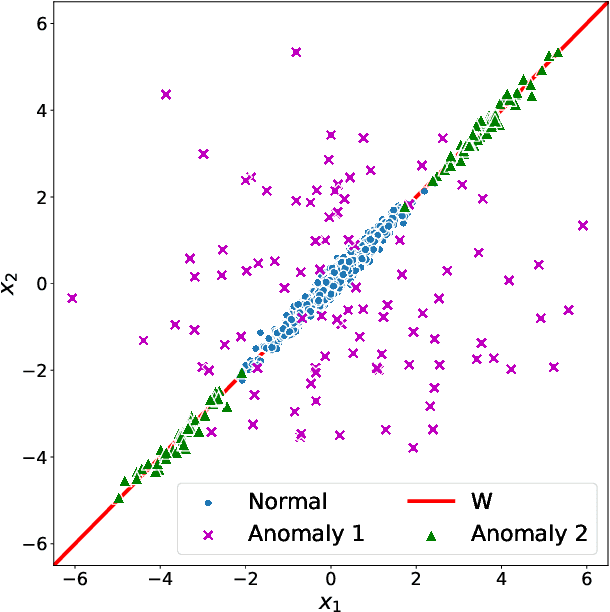
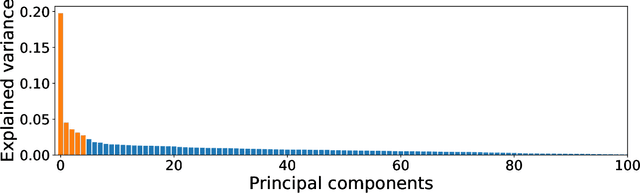
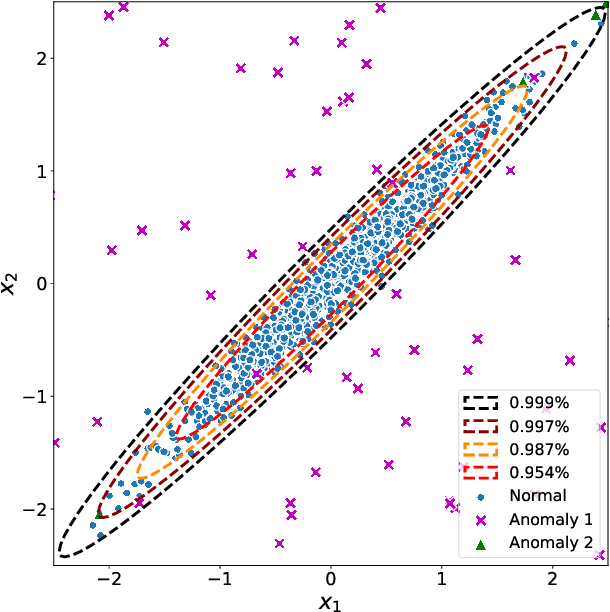
Abstract:Network anomaly detection is a very relevant research area nowadays, especially due to its multiple applications in the field of network security. The boost of new models based on variational autoencoders and generative adversarial networks has motivated a reevaluation of traditional techniques for anomaly detection. It is, however, essential to be able to understand these new models from the perspective of the experience attained from years of evaluating network security data for anomaly detection. In this paper, we revisit anomaly detection techniques based on PCA from a probabilistic generative model point of view, and contribute a mathematical model that relates them. Specifically, we start with the probabilistic PCA model and explain its connection to the Multivariate Statistical Network Monitoring (MSNM) framework. MSNM was recently successfully proposed as a means of incorporating industrial process anomaly detection experience into the field of networking. We have evaluated the mathematical model using two different datasets. The first, a synthetic dataset created to better understand the analysis proposed, and the second, UGR'16, is a specifically designed real-traffic dataset for network security anomaly detection. We have drawn conclusions that we consider to be useful when applying generative models to network security detection.
Multivariate Big Data Analysis for Intrusion Detection: 5 steps from the haystack to the needle
Jun 27, 2019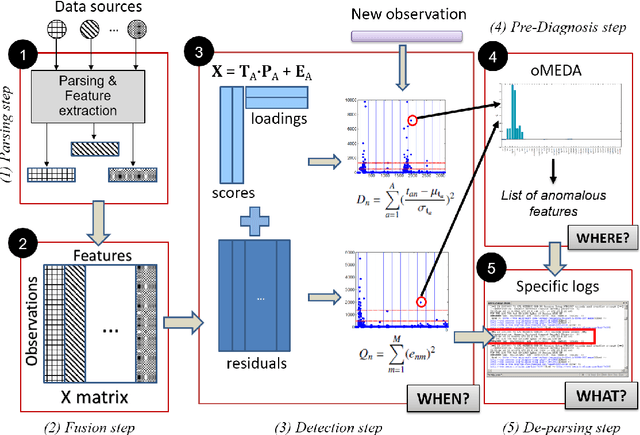
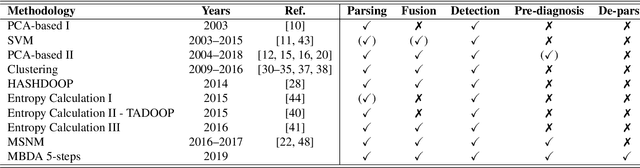
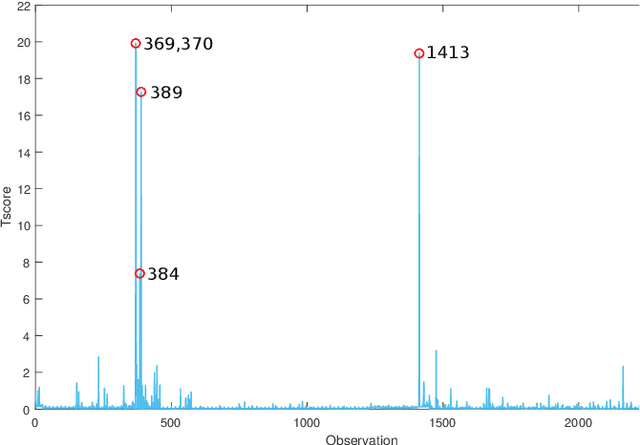
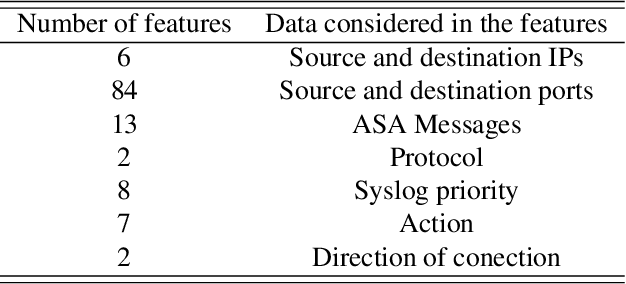
Abstract:The research literature on cybersecurity incident detection & response is very rich in automatic detection methodologies, in particular those based on the anomaly detection paradigm. However, very little attention has been devoted to the diagnosis ability of the methods, aimed to provide useful information on the causes of a given detected anomaly. This information is of utmost importance for the security team to reduce the time from detection to response. In this paper, we present Multivariate Big Data Analysis (MBDA), a complete intrusion detection approach based on 5 steps to effectively handle massive amounts of disparate data sources. The approach has been designed to deal with the main characteristics of Big Data, that is, the high volume, velocity and variety. The core of the approach is the Multivariate Statistical Network Monitoring (MSNM) technique proposed in a recent paper. Unlike in state of the art machine learning methodologies applied to the intrusion detection problem, when an anomaly is identified in MBDA the output of the system includes the detail of the logs of raw information associated to this anomaly, so that the security team can use this information to elucidate its root causes. MBDA is based in two open software packages available in Github: the MEDA Toolbox and the FCParser. We illustrate our approach with two case studies. The first one demonstrates the application of MBDA to semistructured sources of information, using the data from the VAST 2012 mini challenge 2. This complete case study is supplied in a virtual machine available for download. In the second case study we show the Big Data capabilities of the approach in data collected from a real network with labeled attacks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge