Fuad Mahmud
Improving Cardiovascular Disease Prediction Through Comparative Analysis of Machine Learning Models: A Case Study on Myocardial Infarction
Nov 01, 2023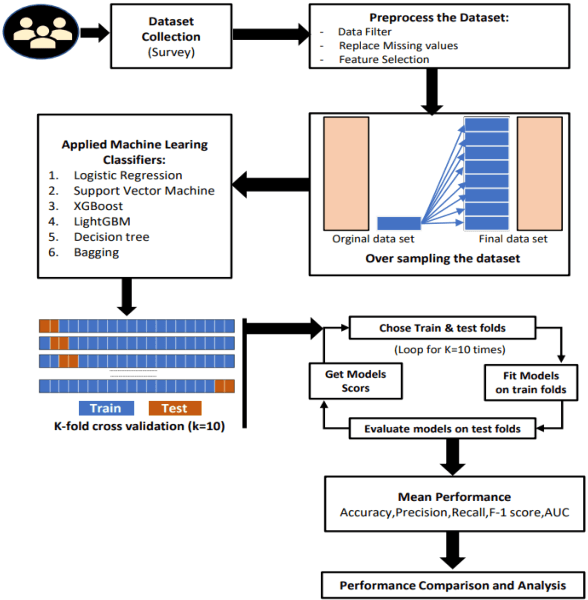
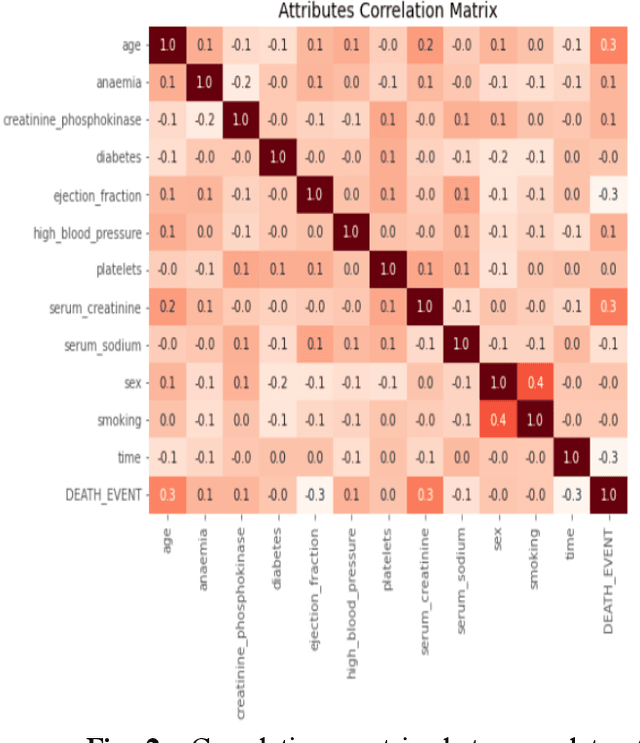
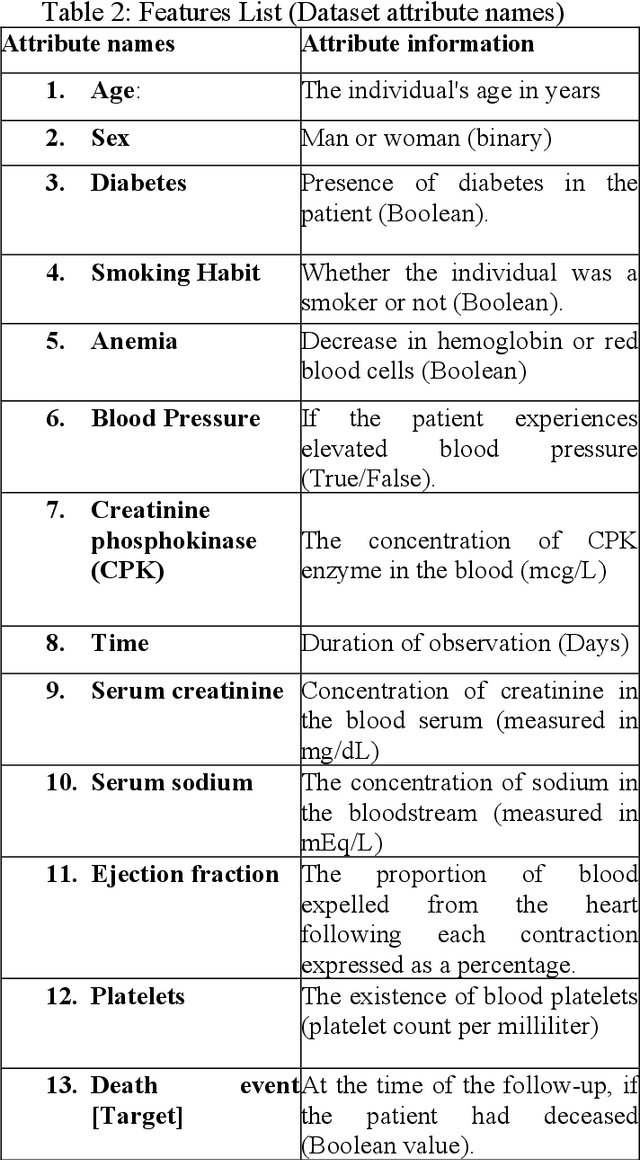
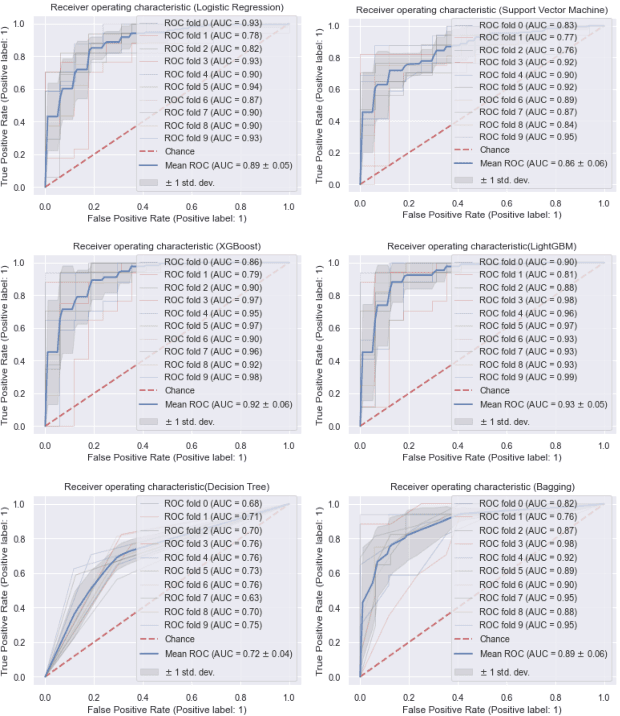
Abstract:Cardiovascular disease remains a leading cause of mortality in the contemporary world. Its association with smoking, elevated blood pressure, and cholesterol levels underscores the significance of these risk factors. This study addresses the challenge of predicting myocardial illness, a formidable task in medical research. Accurate predictions are pivotal for refining healthcare strategies. This investigation conducts a comparative analysis of six distinct machine learning models: Logistic Regression, Support Vector Machine, Decision Tree, Bagging, XGBoost, and LightGBM. The attained outcomes exhibit promise, with accuracy rates as follows: Logistic Regression (81.00%), Support Vector Machine (75.01%), XGBoost (92.72%), LightGBM (90.60%), Decision Tree (82.30%), and Bagging (83.01%). Notably, XGBoost emerges as the top-performing model. These findings underscore its potential to enhance predictive precision for coronary infarction. As the prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors persists, incorporating advanced machine learning techniques holds the potential to refine proactive medical interventions.
Advancing Brain Tumor Detection: A Thorough Investigation of CNNs, Clustering, and SoftMax Classification in the Analysis of MRI Images
Oct 26, 2023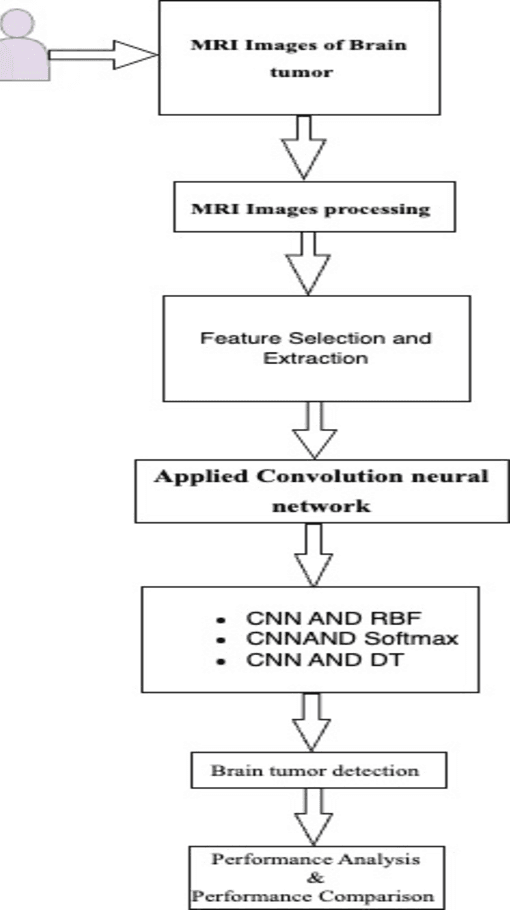
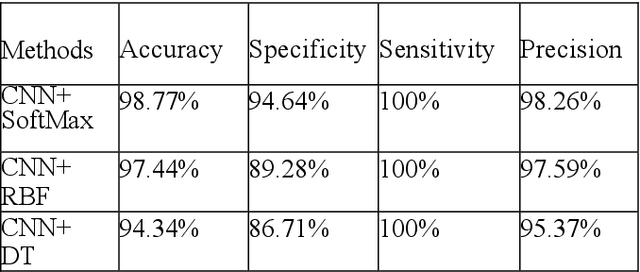
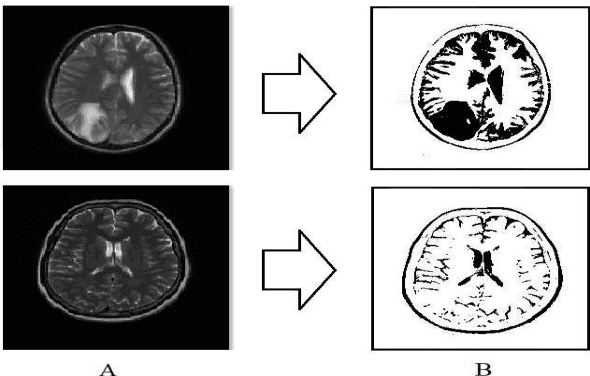
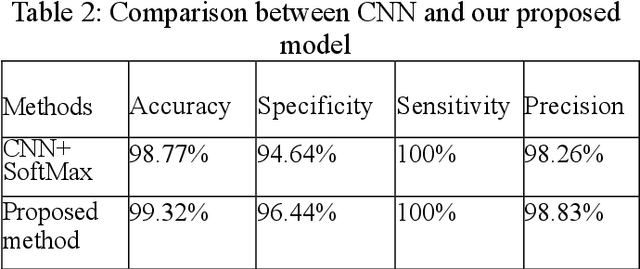
Abstract:Brain tumors pose a significant global health challenge due to their high prevalence and mortality rates across all age groups. Detecting brain tumors at an early stage is crucial for effective treatment and patient outcomes. This study presents a comprehensive investigation into the use of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for brain tumor detection using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) images. The dataset, consisting of MRI scans from both healthy individuals and patients with brain tumors, was processed and fed into the CNN architecture. The SoftMax Fully Connected layer was employed to classify the images, achieving an accuracy of 98%. To evaluate the CNN's performance, two other classifiers, Radial Basis Function (RBF) and Decision Tree (DT), were utilized, yielding accuracy rates of 98.24% and 95.64%, respectively. The study also introduced a clustering method for feature extraction, improving CNN's accuracy. Sensitivity, Specificity, and Precision were employed alongside accuracy to comprehensively evaluate the network's performance. Notably, the SoftMax classifier demonstrated the highest accuracy among the categorizers, achieving 99.52% accuracy on test data. The presented research contributes to the growing field of deep learning in medical image analysis. The combination of CNNs and MRI data offers a promising tool for accurately detecting brain tumors, with potential implications for early diagnosis and improved patient care.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge