François Hamon
Deep Learning-Accelerated 3D Carbon Storage Reservoir Pressure Forecasting Based on Data Assimilation Using Surface Displacement from InSAR
Jan 27, 2022



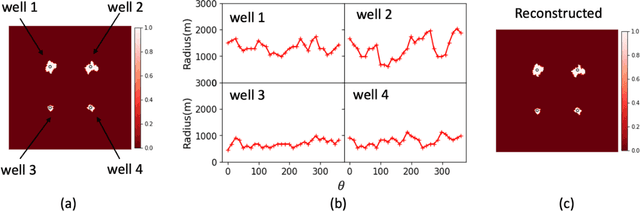
Abstract:Fast forecasting of reservoir pressure distribution in geologic carbon storage (GCS) by assimilating monitoring data is a challenging problem. Due to high drilling cost, GCS projects usually have spatially sparse measurements from wells, leading to high uncertainties in reservoir pressure prediction. To address this challenge, we propose to use low-cost Interferometric Synthetic-Aperture Radar (InSAR) data as monitoring data to infer reservoir pressure build up. We develop a deep learning-accelerated workflow to assimilate surface displacement maps interpreted from InSAR and to forecast dynamic reservoir pressure. Employing an Ensemble Smoother Multiple Data Assimilation (ES-MDA) framework, the workflow updates three-dimensional (3D) geologic properties and predicts reservoir pressure with quantified uncertainties. We use a synthetic commercial-scale GCS model with bimodally distributed permeability and porosity to demonstrate the efficacy of the workflow. A two-step CNN-PCA approach is employed to parameterize the bimodal fields. The computational efficiency of the workflow is boosted by two residual U-Net based surrogate models for surface displacement and reservoir pressure predictions, respectively. The workflow can complete data assimilation and reservoir pressure forecasting in half an hour on a personal computer.
A Deep Learning-Accelerated Data Assimilation and Forecasting Workflow for Commercial-Scale Geologic Carbon Storage
May 09, 2021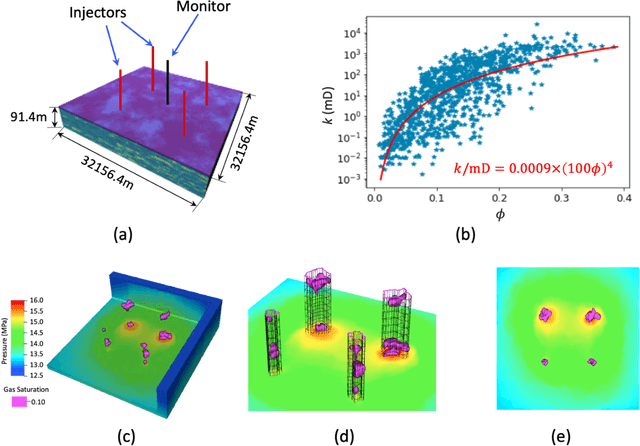

Abstract:Fast assimilation of monitoring data to update forecasts of pressure buildup and carbon dioxide (CO2) plume migration under geologic uncertainties is a challenging problem in geologic carbon storage. The high computational cost of data assimilation with a high-dimensional parameter space impedes fast decision-making for commercial-scale reservoir management. We propose to leverage physical understandings of porous medium flow behavior with deep learning techniques to develop a fast history matching-reservoir response forecasting workflow. Applying an Ensemble Smoother Multiple Data Assimilation framework, the workflow updates geologic properties and predicts reservoir performance with quantified uncertainty from pressure history and CO2 plumes interpreted through seismic inversion. As the most computationally expensive component in such a workflow is reservoir simulation, we developed surrogate models to predict dynamic pressure and CO2 plume extents under multi-well injection. The surrogate models employ deep convolutional neural networks, specifically, a wide residual network and a residual U-Net. The workflow is validated against a flat three-dimensional reservoir model representative of a clastic shelf depositional environment. Intelligent treatments are applied to bridge between quantities in a true-3D reservoir model and those in a single-layer reservoir model. The workflow can complete history matching and reservoir forecasting with uncertainty quantification in less than one hour on a mainstream personal workstation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge