Frédéric Docquier
Using an interpretable Machine Learning approach to study the drivers of International Migration
Jun 05, 2020

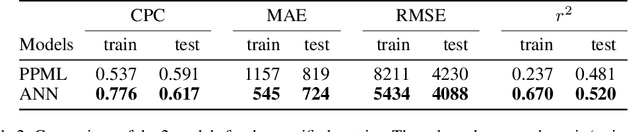
Abstract:Globally increasing migration pressures call for new modelling approaches in order to design effective policies. It is important to have not only efficient models to predict migration flows but also to understand how specific parameters influence these flows. In this paper, we propose an artificial neural network (ANN) to model international migration. Moreover, we use a technique for interpreting machine learning models, namely Partial Dependence Plots (PDP), to show that one can well study the effects of drivers behind international migration. We train and evaluate the model on a dataset containing annual international bilateral migration from $1960$ to $2010$ from $175$ origin countries to $33$ mainly OECD destinations, along with the main determinants as identified in the migration literature. The experiments carried out confirm that: 1) the ANN model is more efficient w.r.t. a traditional model, and 2) using PDP we are able to gain additional insights on the specific effects of the migration drivers. This approach provides much more information than only using the feature importance information used in previous works.
An aggregate learning approach for interpretable semi-supervised population prediction and disaggregation using ancillary data
Jun 29, 2019



Abstract:Census data provide detailed information about population characteristics at a coarse resolution. Nevertheless, fine-grained, high-resolution mappings of population counts are increasingly needed to characterize population dynamics and to assess the consequences of climate shocks, natural disasters, investments in infrastructure, development policies, etc. Dissagregating these census is a complex machine learning, and multiple solutions have been proposed in past research. We propose in this paper to view the problem in the context of the aggregate learning paradigm, where the output value for all training points is not known, but where it is only known for aggregates of the points (i.e. in this context, for regions of pixels where a census is available). We demonstrate with a very simple and interpretable model that this method is on par, and even outperforms on some metrics, the state-of-the-art, despite its simplicity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge