Floriano De Rango
Optimal In-Network Distribution of Learning Functions for a Secure-by-Design Programmable Data Plane of Next-Generation Networks
Nov 27, 2024



Abstract:The rise of programmable data plane (PDP) and in-network computing (INC) paradigms paves the way for the development of network devices (switches, network interface cards, etc.) capable of performing advanced computing tasks. This allows to execute algorithms of various nature, including machine learning ones, within the network itself to support user and network services. In particular, this paper delves into the issue of implementing in-network learning models to support distributed intrusion detection systems (IDS). It proposes a model that optimally distributes the IDS workload, resulting from the subdivision of a "Strong Learner" (SL) model into lighter distributed "Weak Learner" (WL) models, among data plane devices; the objective is to ensure complete network security without excessively burdening their normal operations. Furthermore, a meta-heuristic approach is proposed to reduce the long computational time required by the exact solution provided by the mathematical model, and its performance is evaluated. The analysis conducted and the results obtained demonstrate the enormous potential of the proposed new approach to the creation of intelligent data planes that effectively act as a first line of defense against cyber attacks, with minimal additional workload on network devices.
Self-adaptive decision-making mechanisms to balance the execution of multiple tasks for a multi-robots team
Mar 27, 2019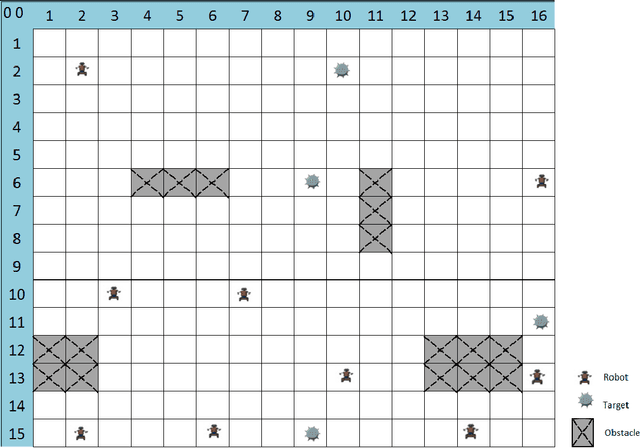
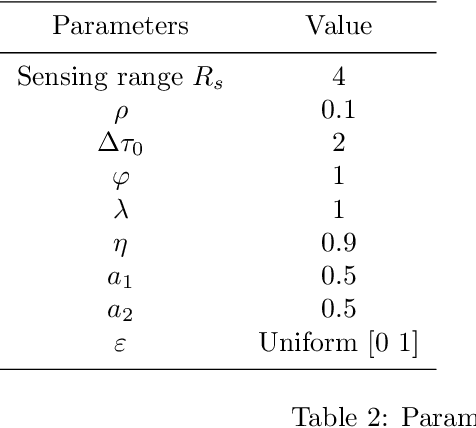
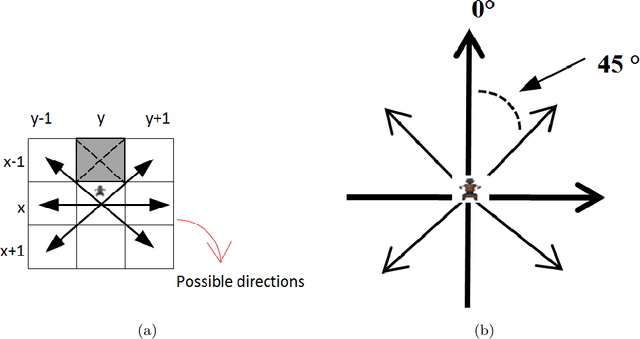
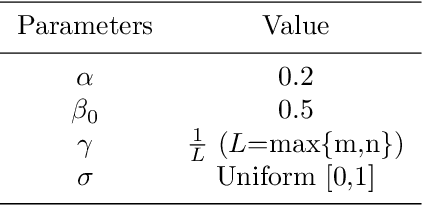
Abstract:This work addresses the coordination problem of multiple robots with the goal of finding specific hazardous targets in an unknown area and dealing with them cooperatively. The desired behaviour for the robotic system entails multiple requirements, which may also be conflicting. The paper presents the problem as a constrained bi-objective optimization problem in which mobile robots must perform two specific tasks of exploration and at same time cooperation and coordination for disarming the hazardous targets. These objectives are opposed goals, in which one may be favored, but only at the expense of the other. Therefore, a good trade-off must be found. For this purpose, a nature-inspired approach and an analytical mathematical model to solve this problem considering a single equivalent weighted objective function are presented. The results of proposed coordination model, simulated in a two dimensional terrain, are showed in order to assess the behaviour of the proposed solution to tackle this problem. We have analyzed the performance of the approach and the influence of the weights of the objective function under different conditions: static and dynamic. In this latter situation, the robots may fail under the stringent limited budget of energy or for hazardous events. The paper concludes with a critical discussion of the experimental results.
* 40 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge