Flavio S. Correa da Silva
Population stratification for prediction of mortality in post-AKI patients
Oct 23, 2024

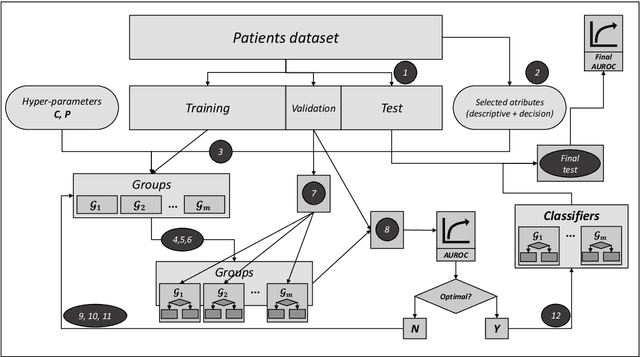

Abstract:Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a serious clinical condition that affects up to 20% of hospitalised patients. AKI is associated with short term unplanned hospital readmission and post-discharge mortality risk. Patient risk and healthcare expenditures can be minimised by followup planning grounded on predictive models and machine learning. Since AKI is multi-factorial, predictive models specialised in different categories of patients can increase accuracy of predictions. In the present article we present some results following this approach.
Towards a Transformer-Based Pre-trained Model for IoT Traffic Classification
Jul 26, 2024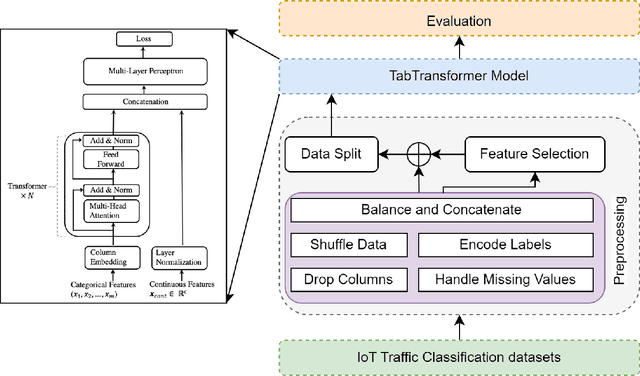
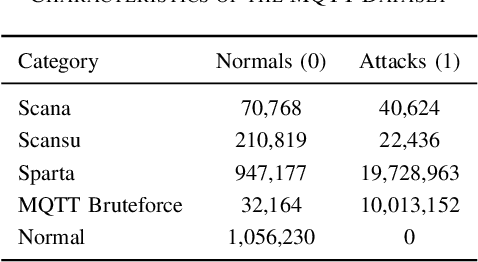
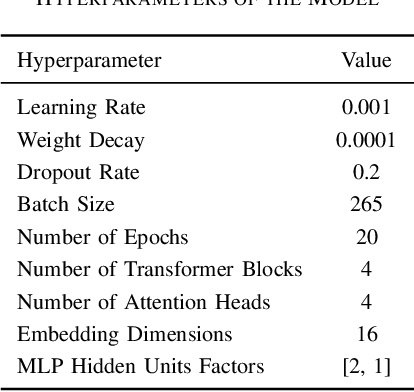
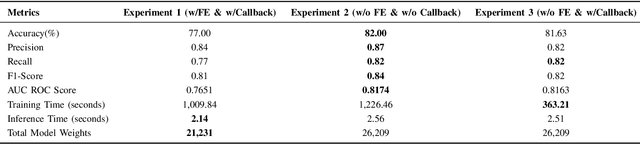
Abstract:The classification of IoT traffic is important to improve the efficiency and security of IoT-based networks. As the state-of-the-art classification methods are based on Deep Learning, most of the current results require a large amount of data to be trained. Thereby, in real-life situations, where there is a scarce amount of IoT traffic data, the models would not perform so well. Consequently, these models underperform outside their initial training conditions and fail to capture the complex characteristics of network traffic, rendering them inefficient and unreliable in real-world applications. In this paper, we propose IoT Traffic Classification Transformer (ITCT), a novel approach that utilizes the state-of-the-art transformer-based model named TabTransformer. ITCT, which is pre-trained on a large labeled MQTT-based IoT traffic dataset and may be fine-tuned with a small set of labeled data, showed promising results in various traffic classification tasks. Our experiments demonstrated that the ITCT model significantly outperforms existing models, achieving an overall accuracy of 82%. To support reproducibility and collaborative development, all associated code has been made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge