Felix Weissberg
On the Role of Pre-trained Embeddings in Binary Code Analysis
Feb 12, 2025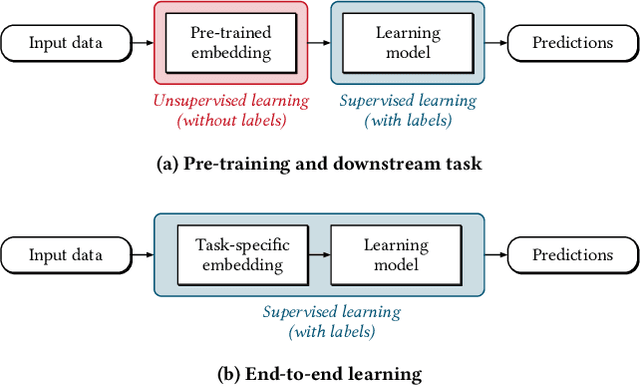

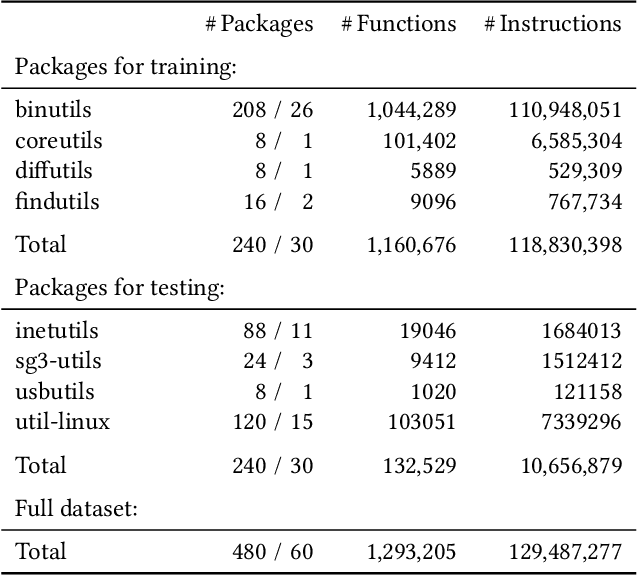
Abstract:Deep learning has enabled remarkable progress in binary code analysis. In particular, pre-trained embeddings of assembly code have become a gold standard for solving analysis tasks, such as measuring code similarity or recognizing functions. These embeddings are capable of learning a vector representation from unlabeled code. In contrast to natural language processing, however, label information is not scarce for many tasks in binary code analysis. For example, labeled training data for function boundaries, optimization levels, and argument types can be easily derived from debug information provided by a compiler. Consequently, the main motivation of embeddings does not transfer directly to binary code analysis. In this paper, we explore the role of pre-trained embeddings from a critical perspective. To this end, we systematically evaluate recent embeddings for assembly code on five downstream tasks using a corpus of 1.2 million functions from the Debian distribution. We observe that several embeddings perform similarly when sufficient labeled data is available, and that differences reported in prior work are hardly noticeable. Surprisingly, we find that end-to-end learning without pre-training performs best on average, which calls into question the need for specialized embeddings. By varying the amount of labeled data, we eventually derive guidelines for when embeddings offer advantages and when end-to-end learning is preferable for binary code analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge