Federica Paganelli Azza
Neural-based Control for CubeSat Docking Maneuvers
Oct 16, 2024
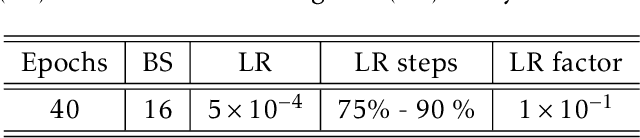
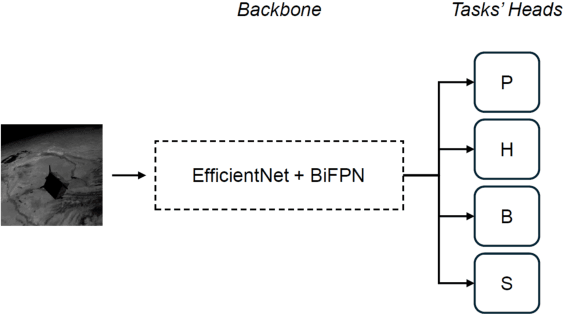
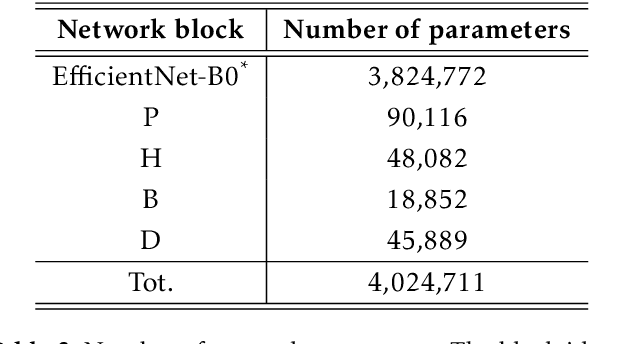
Abstract:Autonomous Rendezvous and Docking (RVD) have been extensively studied in recent years, addressing the stringent requirements of spacecraft dynamics variations and the limitations of GNC systems. This paper presents an innovative approach employing Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) trained through Reinforcement Learning (RL) for autonomous spacecraft guidance and control during the final phase of the rendezvous maneuver. The proposed strategy is easily implementable onboard and offers fast adaptability and robustness to disturbances by learning control policies from experience rather than relying on predefined models. Extensive Monte Carlo simulations within a relevant environment are conducted in 6DoF settings to validate our approach, along with hardware tests that demonstrate deployment feasibility. Our findings highlight the efficacy of RL in assuring the adaptability and efficiency of spacecraft RVD, offering insights into future mission expectations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge