Fabrizio Borgia
DiFiLiLe
Customization and modifications of SignWriting by LIS users
Apr 24, 2020



Abstract:Historically, the various sign languages (SL) have not developed an own writing system; nevertheless, some systems exist, among which the SignWriting (SW) is a powerful and flexible one. In this paper, we present the mechanisms adopted by signers of the Italian Sign Language (LIS), expert users of SW, to modify the standard SW glyphs and increase their writing skills and/or represent peculiar linguistic phenomena. We identify these glyphs and show which characteristics make them "acceptable" by the expert community. Eventually, we analyze the potentialities of these glyphs in hand writing and in computer-assisted writing, focusing on SWift, a software designed to allow the electronic writing-down of user-modified glyphs.
A concrete example of inclusive design: deaf-oriented accessibility
Nov 27, 2019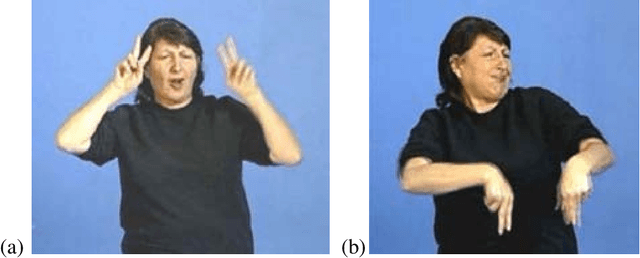

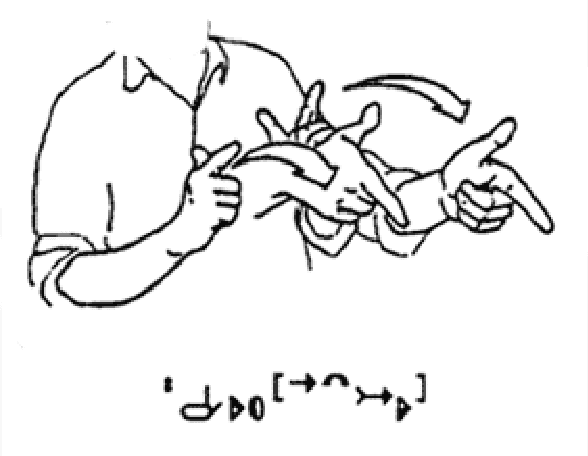
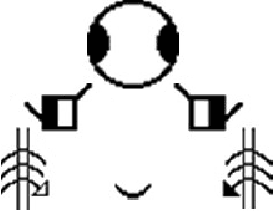
Abstract:One of the continuing challenges of Human Computer Interaction research is the full inclusion of people with special needs into the digital world. In particular, this crucial category includes people that experiences some kind of limitation in exploiting traditional information communication channels. One immediately thinks about blind people, and several researches aim at addressing their needs. On the contrary, limitations suffered by deaf people are often underestimated. This often the result of a kind of ignorance or misunderstanding of the real nature of their communication difficulties. This chapter aims at both increasing the awareness of deaf problems in the digital world, and at proposing the project of a comprehensive solution for their better inclusion. As for the former goal, we will provide a bird's-eye presentation of history and evolution of understanding of deafness issues, and of strategies to address them. As for the latter, we will present the design, implementation and evaluation of the first nucleus of a comprehensive digital framework to facilitate the access of deaf people into the digital world.
* SCOPUS - ISI?
Towards improving the e-learning experience for deaf students: e-LUX
Nov 27, 2019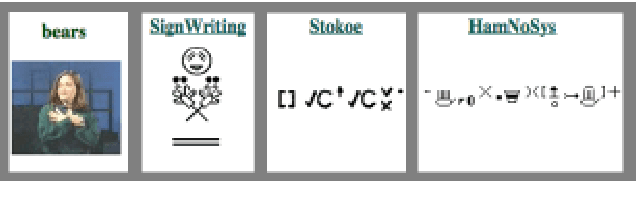
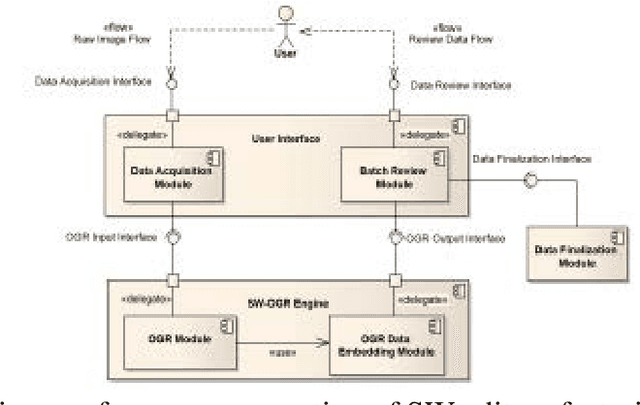
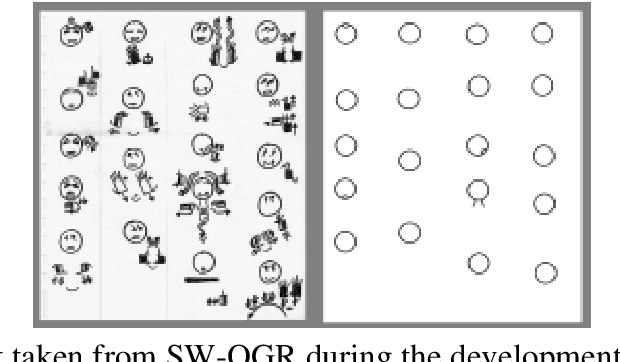
Abstract:Deaf people are more heavily affected by the digital divide than many would expect. Moreover, most accessibility guidelines addressing their needs just deal with captioning and audio-content transcription. However, this approach to the problem does not consider that deaf people have big troubles with vocal languages, even in their written form. At present, only a few organizations, like W3C, produced guidelines dealing with one of their most distinctive expressions: Sign Language (SL). SL is, in fact, the visual-gestural language used by many deaf people to communicate with each other. The present work aims at supporting e-learning user experience (e-LUX) for these specific users by enhancing the accessibility of content and container services. In particular, we propose preliminary solutions to tailor activities which can be more fruitful when performed in one's own "native" language, which for most deaf people, especially younger ones, is represented by national SL.
* anche ISBN 978-3-319-07436-9
SWift -- A SignWriting improved fast transcriber
Nov 25, 2019
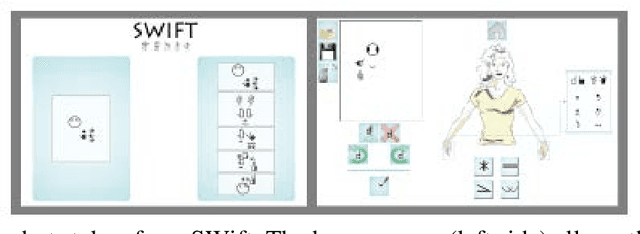
Abstract:We present SWift (SignWriting improved fast transcriber), an advanced editor for computer-aided writing and transcribing using SignWriting (SW). SW is devised to allow deaf people and linguists alike to exploit an easy-to-grasp written form of (any) sign language. Similarly, SWift has been developed for everyone who masters SW, and is not exclusively deaf-oriented. Using SWift, it is possible to compose and save any sign, using elementary components called glyphs. A guided procedure facilitates the composition process. SWift is aimed at helping to break down the "electronic" barriers that keep the deaf community away from Information and Communication Technology (ICT). The editor has been developed modularly and can be integrated everywhere the use of SW, as an alternative to written vocal language, may be advisable.
SWift -- A SignWriting editor to bridge between deaf world and e-learning
Nov 22, 2019



Abstract:SWift (SignWriting improved fast transcriber) is an advanced editor for SignWriting (SW). At present, SW is a promising alternative to provide documents in an easy-to-grasp written form of (any) Sign Language, the gestural way of communication which is widely adopted by the deaf community. SWift was developed SW users, either deaf or not, to support collaboration and exchange of ideas. The application allows composing and saving desired signs using elementary components, called glyphs. The procedure that was devised guides and simplifies the editing process. SWift aims at breaking the "electronic" barriers that keep the deaf community away from ICT in general, and from e-learning in particular. The editor can be contained in a pluggable module; therefore, it can be integrated everywhere the use of SW is an advisable alternative to written "verbal" language, which often hinders information grasping by deaf users.
Resource production of written forms of Sign Languages by a user-centered editor, SWift
Nov 22, 2019



Abstract:The SignWriting improved fast transcriber (SWift), presented in this paper, is an advanced editor for computer-aided writing and transcribing of any Sign Language (SL) using SignWriting (SW). The application is an editor which allows composing and saving desired signs using the SW elementary components, called "glyphs". These make up a sort of alphabet, which does not depend on the national Sign Language and which codes the basic components of any sign. The user is guided through a fully-automated procedure, making the composition process fast and intuitive. SWift pursues the goal of helping to break down the "electronic barriers" that keep deaf people away from the web, and at the same time to support linguistic research about Sign Languages features. For this reason it has been designed with a special attention to deaf user needs, and to general usability issues. The editor has been developed in a modular way, so it can be integrated everywhere the use of SW as an alternative to written "verbal" language may be advisable.
* CITATION INDEX
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge