Claudia Bianchini
FORELLIS
A concrete example of inclusive design: deaf-oriented accessibility
Nov 27, 2019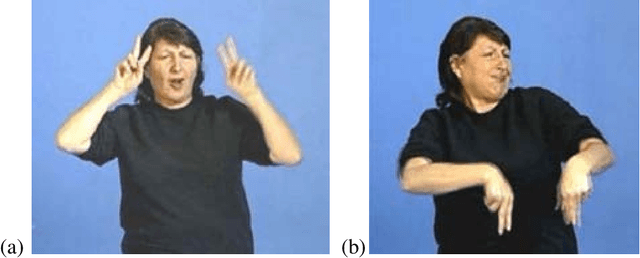

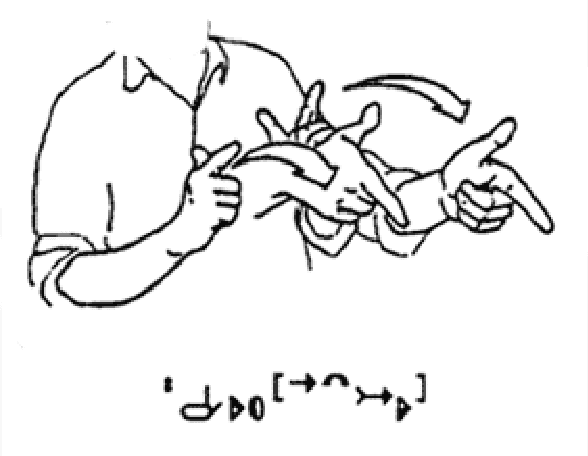
Abstract:One of the continuing challenges of Human Computer Interaction research is the full inclusion of people with special needs into the digital world. In particular, this crucial category includes people that experiences some kind of limitation in exploiting traditional information communication channels. One immediately thinks about blind people, and several researches aim at addressing their needs. On the contrary, limitations suffered by deaf people are often underestimated. This often the result of a kind of ignorance or misunderstanding of the real nature of their communication difficulties. This chapter aims at both increasing the awareness of deaf problems in the digital world, and at proposing the project of a comprehensive solution for their better inclusion. As for the former goal, we will provide a bird's-eye presentation of history and evolution of understanding of deafness issues, and of strategies to address them. As for the latter, we will present the design, implementation and evaluation of the first nucleus of a comprehensive digital framework to facilitate the access of deaf people into the digital world.
* SCOPUS - ISI?
Towards improving the e-learning experience for deaf students: e-LUX
Nov 27, 2019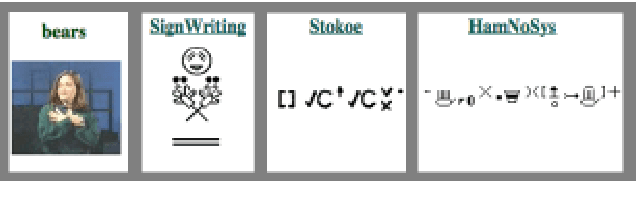
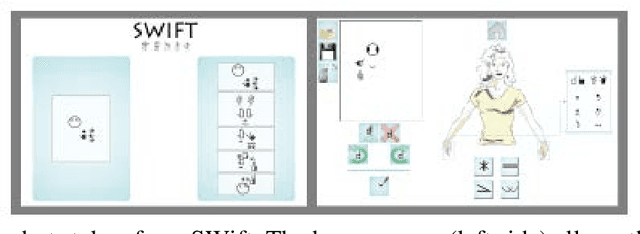
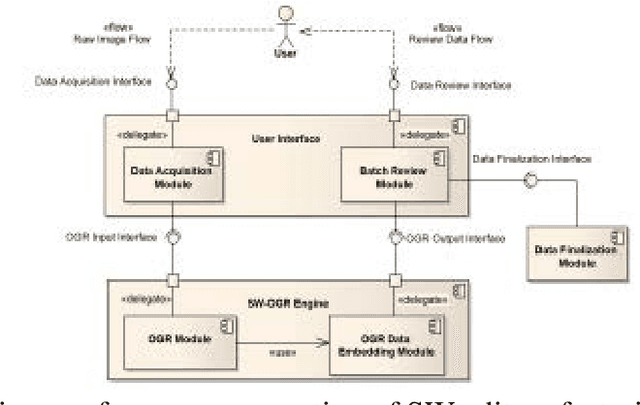
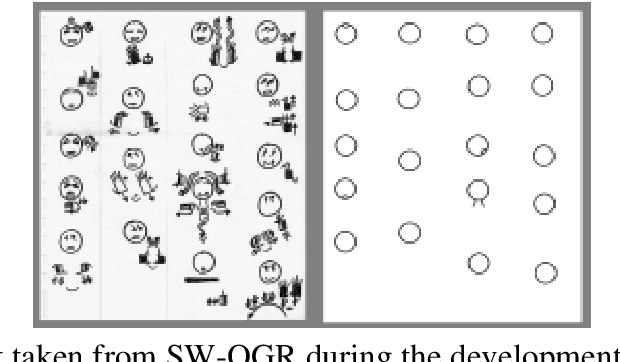
Abstract:Deaf people are more heavily affected by the digital divide than many would expect. Moreover, most accessibility guidelines addressing their needs just deal with captioning and audio-content transcription. However, this approach to the problem does not consider that deaf people have big troubles with vocal languages, even in their written form. At present, only a few organizations, like W3C, produced guidelines dealing with one of their most distinctive expressions: Sign Language (SL). SL is, in fact, the visual-gestural language used by many deaf people to communicate with each other. The present work aims at supporting e-learning user experience (e-LUX) for these specific users by enhancing the accessibility of content and container services. In particular, we propose preliminary solutions to tailor activities which can be more fruitful when performed in one's own "native" language, which for most deaf people, especially younger ones, is represented by national SL.
* anche ISBN 978-3-319-07436-9
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge