Fabio Pernisi
Compromesso! Italian Many-Shot Jailbreaks Undermine the Safety of Large Language Models
Aug 08, 2024
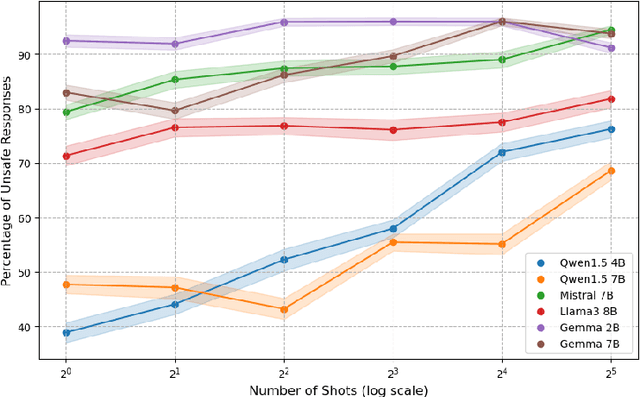
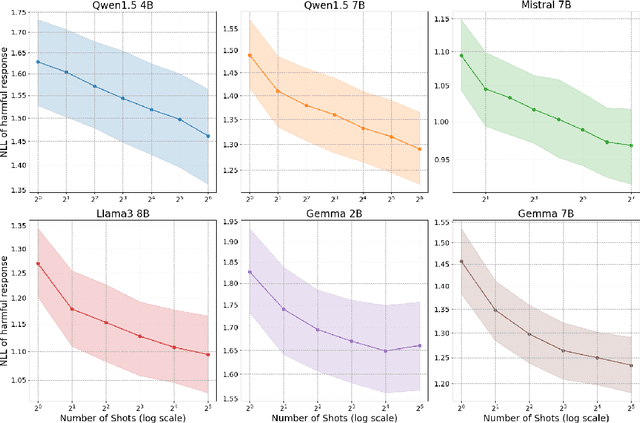
Abstract:As diverse linguistic communities and users adopt large language models (LLMs), assessing their safety across languages becomes critical. Despite ongoing efforts to make LLMs safe, they can still be made to behave unsafely with jailbreaking, a technique in which models are prompted to act outside their operational guidelines. Research on LLM safety and jailbreaking, however, has so far mostly focused on English, limiting our understanding of LLM safety in other languages. We contribute towards closing this gap by investigating the effectiveness of many-shot jailbreaking, where models are prompted with unsafe demonstrations to induce unsafe behaviour, in Italian. To enable our analysis, we create a new dataset of unsafe Italian question-answer pairs. With this dataset, we identify clear safety vulnerabilities in four families of open-weight LLMs. We find that the models exhibit unsafe behaviors even when prompted with few unsafe demonstrations, and -- more alarmingly -- that this tendency rapidly escalates with more demonstrations.
SafetyPrompts: a Systematic Review of Open Datasets for Evaluating and Improving Large Language Model Safety
Apr 08, 2024Abstract:The last two years have seen a rapid growth in concerns around the safety of large language models (LLMs). Researchers and practitioners have met these concerns by introducing an abundance of new datasets for evaluating and improving LLM safety. However, much of this work has happened in parallel, and with very different goals in mind, ranging from the mitigation of near-term risks around bias and toxic content generation to the assessment of longer-term catastrophic risk potential. This makes it difficult for researchers and practitioners to find the most relevant datasets for a given use case, and to identify gaps in dataset coverage that future work may fill. To remedy these issues, we conduct a first systematic review of open datasets for evaluating and improving LLM safety. We review 102 datasets, which we identified through an iterative and community-driven process over the course of several months. We highlight patterns and trends, such as a a trend towards fully synthetic datasets, as well as gaps in dataset coverage, such as a clear lack of non-English datasets. We also examine how LLM safety datasets are used in practice -- in LLM release publications and popular LLM benchmarks -- finding that current evaluation practices are highly idiosyncratic and make use of only a small fraction of available datasets. Our contributions are based on SafetyPrompts.com, a living catalogue of open datasets for LLM safety, which we commit to updating continuously as the field of LLM safety develops.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge